Hwa Hui Tew
Drive As You Like: Strategy-Level Motion Planning Based on A Multi-Head Diffusion Model
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in motion planning for autonomous driving have led to models capable of generating high-quality trajectories. However, most existing planners tend to fix their policy after supervised training, leading to consistent but rigid driving behaviors. This limits their ability to reflect human preferences or adapt to dynamic, instruction-driven demands. In this work, we propose a diffusion-based multi-head trajectory planner(M-diffusion planner). During the early training stage, all output heads share weights to learn to generate high-quality trajectories. Leveraging the probabilistic nature of diffusion models, we then apply Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to fine-tune the pre-trained model for diverse policy-specific behaviors. At inference time, we incorporate a large language model (LLM) to guide strategy selection, enabling dynamic, instruction-aware planning without switching models. Closed-loop simulation demonstrates that our post-trained planner retains strong planning capability while achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the nuPlan val14 benchmark. Open-loop results further show that the generated trajectories exhibit clear diversity, effectively satisfying multi-modal driving behavior requirements. The code and related experiments will be released upon acceptance of the paper.
Learning Energy-Based Generative Models via Potential Flow: A Variational Principle Approach to Probability Density Homotopy Matching
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Energy-based models (EBMs) are a powerful class of probabilistic generative models due to their flexibility and interpretability. However, relationships between potential flows and explicit EBMs remain underexplored, while contrastive divergence training via implicit Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling is often unstable and expensive in high-dimensional settings. In this paper, we propose Variational Potential Flow Bayes (VPFB), a new energy-based generative framework that eliminates the need for implicit MCMC sampling and does not rely on auxiliary networks or cooperative training. VPFB learns an energy-parameterized potential flow by constructing a flow-driven density homotopy that is matched to the data distribution through a variational loss minimizing the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the flow-driven and marginal homotopies. This principled formulation enables robust and efficient generative modeling while preserving the interpretability of EBMs. Experimental results on image generation, interpolation, out-of-distribution detection, and compositional generation confirm the effectiveness of VPFB, showing that our method performs competitively with existing approaches in terms of sample quality and versatility across diverse generative modeling tasks.
SenseRAG: Constructing Environmental Knowledge Bases with Proactive Querying for LLM-Based Autonomous Driving
Jan 08, 2025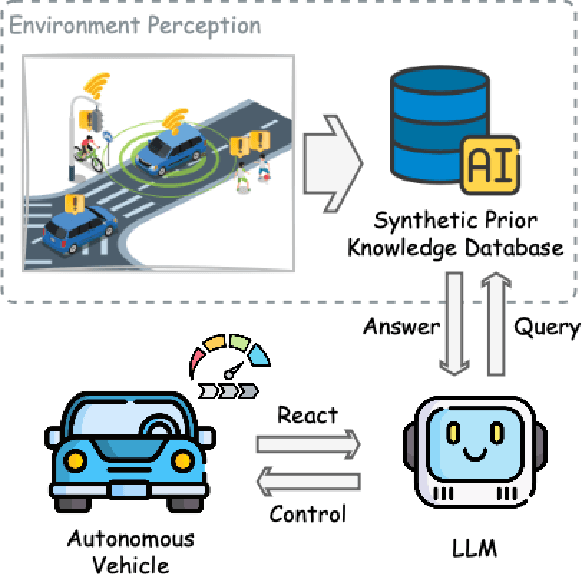
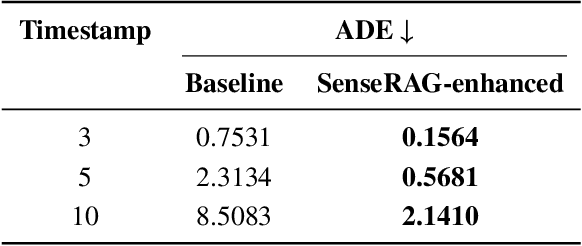
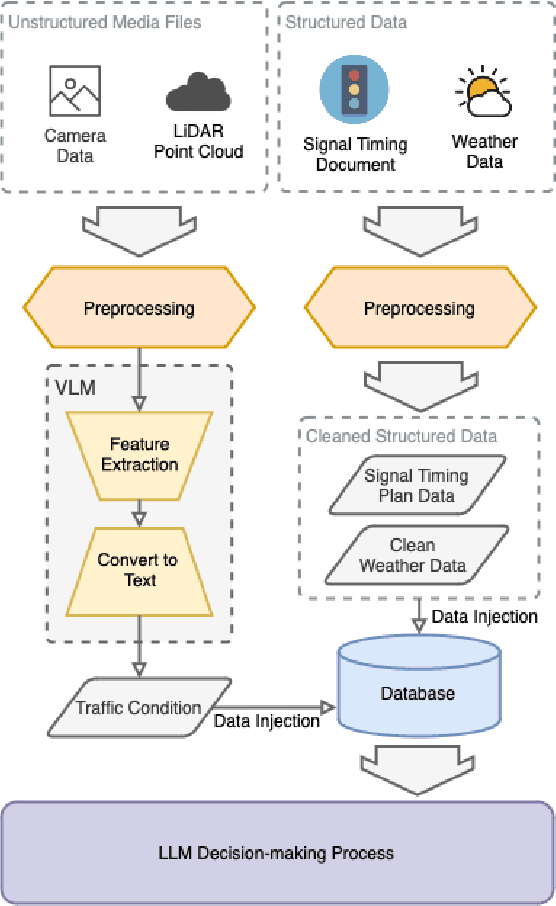
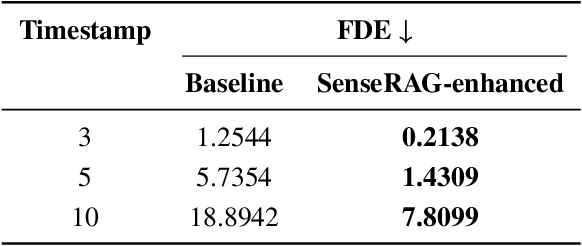
Abstract:This study addresses the critical need for enhanced situational awareness in autonomous driving (AD) by leveraging the contextual reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Unlike traditional perception systems that rely on rigid, label-based annotations, it integrates real-time, multimodal sensor data into a unified, LLMs-readable knowledge base, enabling LLMs to dynamically understand and respond to complex driving environments. To overcome the inherent latency and modality limitations of LLMs, a proactive Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is designed for AD, combined with a chain-of-thought prompting mechanism, ensuring rapid and context-rich understanding. Experimental results using real-world Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) datasets demonstrate significant improvements in perception and prediction performance, highlighting the potential of this framework to enhance safety, adaptability, and decision-making in next-generation AD systems.
KANS: Knowledge Discovery Graph Attention Network for Soft Sensing in Multivariate Industrial Processes
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Soft sensing of hard-to-measure variables is often crucial in industrial processes. Current practices rely heavily on conventional modeling techniques that show success in improving accuracy. However, they overlook the non-linear nature, dynamics characteristics, and non-Euclidean dependencies between complex process variables. To tackle these challenges, we present a framework known as a Knowledge discovery graph Attention Network for effective Soft sensing (KANS). Unlike the existing deep learning soft sensor models, KANS can discover the intrinsic correlations and irregular relationships between the multivariate industrial processes without a predefined topology. First, an unsupervised graph structure learning method is introduced, incorporating the cosine similarity between different sensor embedding to capture the correlations between sensors. Next, we present a graph attention-based representation learning that can compute the multivariate data parallelly to enhance the model in learning complex sensor nodes and edges. To fully explore KANS, knowledge discovery analysis has also been conducted to demonstrate the interpretability of the model. Experimental results demonstrate that KANS significantly outperforms all the baselines and state-of-the-art methods in soft sensing performance. Furthermore, the analysis shows that KANS can find sensors closely related to different process variables without domain knowledge, significantly improving soft sensing accuracy.
ST-HCSS: Deep Spatio-Temporal Hypergraph Convolutional Neural Network for Soft Sensing
Jan 02, 2025Abstract:Higher-order sensor networks are more accurate in characterizing the nonlinear dynamics of sensory time-series data in modern industrial settings by allowing multi-node connections beyond simple pairwise graph edges. In light of this, we propose a deep spatio-temporal hypergraph convolutional neural network for soft sensing (ST-HCSS). In particular, our proposed framework is able to construct and leverage a higher-order graph (hypergraph) to model the complex multi-interactions between sensor nodes in the absence of prior structural knowledge. To capture rich spatio-temporal relationships underlying sensor data, our proposed ST-HCSS incorporates stacked gated temporal and hypergraph convolution layers to effectively aggregate and update hypergraph information across time and nodes. Our results validate the superiority of ST-HCSS compared to existing state-of-the-art soft sensors, and demonstrates that the learned hypergraph feature representations aligns well with the sensor data correlations. The code is available at https://github.com/htew0001/ST-HCSS.git
Cross-Domain Transfer Learning using Attention Latent Features for Multi-Agent Trajectory Prediction
Nov 12, 2024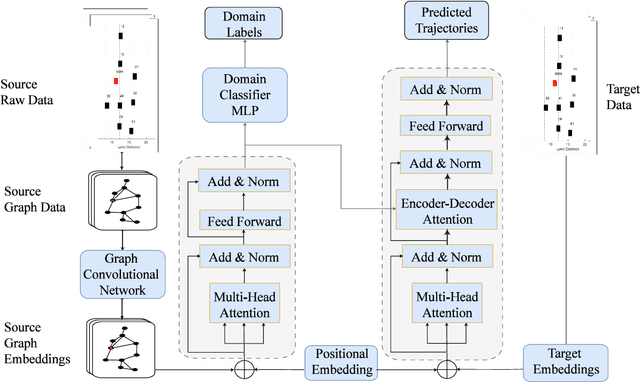
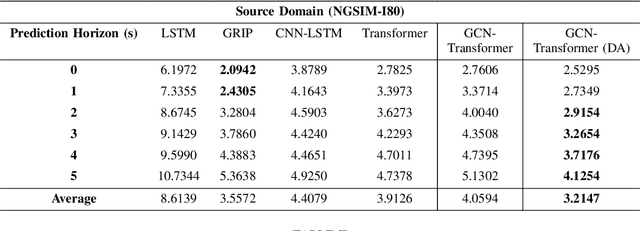
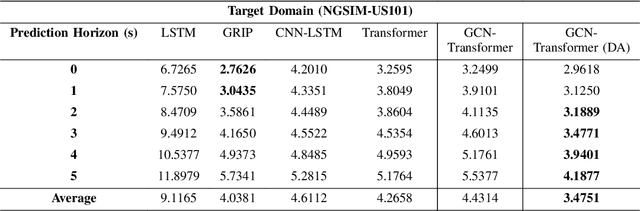
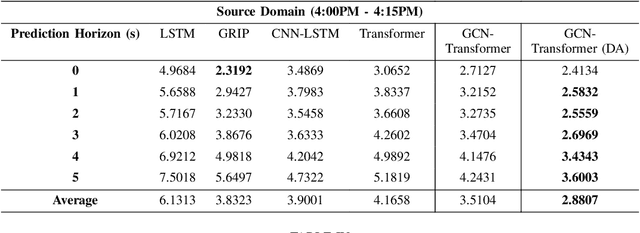
Abstract:With the advancements of sensor hardware, traffic infrastructure and deep learning architectures, trajectory prediction of vehicles has established a solid foundation in intelligent transportation systems. However, existing solutions are often tailored to specific traffic networks at particular time periods. Consequently, deep learning models trained on one network may struggle to generalize effectively to unseen networks. To address this, we proposed a novel spatial-temporal trajectory prediction framework that performs cross-domain adaption on the attention representation of a Transformer-based model. A graph convolutional network is also integrated to construct dynamic graph feature embeddings that accurately model the complex spatial-temporal interactions between the multi-agent vehicles across multiple traffic domains. The proposed framework is validated on two case studies involving the cross-city and cross-period settings. Experimental results show that our proposed framework achieves superior trajectory prediction and domain adaptation performances over the state-of-the-art models.
Energy-efficient Hybrid Model Predictive Trajectory Planning for Autonomous Electric Vehicles
Nov 09, 2024Abstract:To tackle the twin challenges of limited battery life and lengthy charging durations in electric vehicles (EVs), this paper introduces an Energy-efficient Hybrid Model Predictive Planner (EHMPP), which employs an energy-saving optimization strategy. EHMPP focuses on refining the design of the motion planner to be seamlessly integrated with the existing automatic driving algorithms, without additional hardware. It has been validated through simulation experiments on the Prescan, CarSim, and Matlab platforms, demonstrating that it can increase passive recovery energy by 11.74\% and effectively track motor speed and acceleration at optimal power. To sum up, EHMPP not only aids in trajectory planning but also significantly boosts energy efficiency in autonomous EVs.
FedBChain: A Blockchain-enabled Federated Learning Framework for Improving DeepConvLSTM with Comparative Strategy Insights
Jul 31, 2024


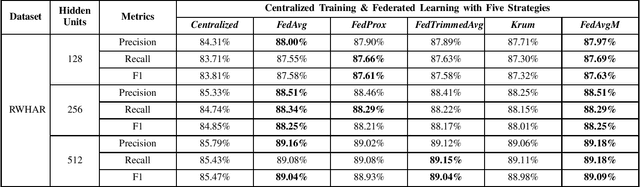
Abstract:Recent research in the field of Human Activity Recognition has shown that an improvement in prediction performance can be achieved by reducing the number of LSTM layers. However, this kind of enhancement is only significant on monolithic architectures, and when it runs on large-scale distributed training, data security and privacy issues will be reconsidered, and its prediction performance is unknown. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework: FedBChain, which integrates the federated learning paradigm based on a modified DeepConvLSTM architecture with a single LSTM layer. This framework performs comparative tests of prediction performance on three different real-world datasets based on three different hidden layer units (128, 256, and 512) combined with five different federated learning strategies, respectively. The results show that our architecture has significant improvements in Precision, Recall and F1-score compared to the centralized training approach on all datasets with all hidden layer units for all strategies: FedAvg strategy improves on average by 4.54%, FedProx improves on average by 4.57%, FedTrimmedAvg improves on average by 4.35%, Krum improves by 4.18% on average, and FedAvgM improves by 4.46% on average. Based on our results, it can be seen that FedBChain not only improves in performance, but also guarantees the security and privacy of user data compared to centralized training methods during the training process. The code for our experiments is publicly available (https://github.com/Glen909/FedBChain).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge