Xiaolei Wang
RecNet: Self-Evolving Preference Propagation for Agentic Recommender Systems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Agentic recommender systems leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to model complex user behaviors and support personalized decision-making. However, existing methods primarily model preference changes based on explicit user-item interactions, which are sparse, noisy, and unable to reflect the real-time, mutual influences among users and items. To address these limitations, we propose RecNet, a self-evolving preference propagation framework that proactively propagates real-time preference updates across related users and items. RecNet consists of two complementary phases. In the forward phase, the centralized preference routing mechanism leverages router agents to integrate preference updates and dynamically propagate them to the most relevant agents. To ensure accurate and personalized integration of propagated preferences, we further introduce a personalized preference reception mechanism, which combines a message buffer for temporary caching and an optimizable, rule-based filter memory to guide selective preference assimilation based on past experience and interests. In the backward phase, the feedback-driven propagation optimization mechanism simulates a multi-agent reinforcement learning framework, using LLMs for credit assignment, gradient analysis, and module-level optimization, enabling continuous self-evolution of propagation strategies. Extensive experiments on various scenarios demonstrate the effectiveness of RecNet in modeling preference propagation for recommender systems.
Normal-Abnormal Guided Generalist Anomaly Detection
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Generalist Anomaly Detection (GAD) aims to train a unified model on an original domain that can detect anomalies in new target domains. Previous GAD methods primarily use only normal samples as references, overlooking the valuable information contained in anomalous samples that are often available in real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we propose a more practical approach: normal-abnormal-guided generalist anomaly detection, which leverages both normal and anomalous samples as references to guide anomaly detection across diverse domains. We introduce the Normal-Abnormal Generalist Learning (NAGL) framework, consisting of two key components: Residual Mining (RM) and Anomaly Feature Learning (AFL). RM extracts abnormal patterns from normal-abnormal reference residuals to establish transferable anomaly representations, while AFL adaptively learns anomaly features in query images through residual mapping to identify instance-aware anomalies. Our approach effectively utilizes both normal and anomalous references for more accurate and efficient cross-domain anomaly detection. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing GAD approaches. This work represents the first to adopt a mixture of normal and abnormal samples as references in generalist anomaly detection. The code and datasets are available at https://github.com/JasonKyng/NAGL.
DeepRec: Towards a Deep Dive Into the Item Space with Large Language Model Based Recommendation
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recently, large language models (LLMs) have been introduced into recommender systems (RSs), either to enhance traditional recommendation models (TRMs) or serve as recommendation backbones. However, existing LLM-based RSs often do not fully exploit the complementary advantages of LLMs (e.g., world knowledge and reasoning) and TRMs (e.g., recommendation-specific knowledge and efficiency) to fully explore the item space. To address this, we propose DeepRec, a novel LLM-based RS that enables autonomous multi-turn interactions between LLMs and TRMs for deep exploration of the item space. In each interaction turn, LLMs reason over user preferences and interact with TRMs to retrieve candidate items. After multi-turn interactions, LLMs rank the retrieved items to generate the final recommendations. We adopt reinforcement learning(RL) based optimization and propose novel designs from three aspects: recommendation model based data rollout, recommendation-oriented hierarchical rewards, and a two-stage RL training strategy. For data rollout, we introduce a preference-aware TRM, with which LLMs interact to construct trajectory data. For rewards, we design a hierarchical reward function that involves both process-level and outcome-level rewards to optimize the interaction process and recommendation performance, respectively. For RL training, we develop a two-stage training strategy, where the first stage aims to guide LLMs to interact with TRMs and the second stage focuses on performance improvement. Experiments on public datasets demonstrate that DeepRec significantly outperforms both traditional and LLM-based baselines, offering a new paradigm for deep exploration in recommendation systems.
Action is All You Need: Dual-Flow Generative Ranking Network for Recommendation
May 22, 2025Abstract:We introduce the Dual-Flow Generative Ranking Network (DFGR), a two-stream architecture designed for recommendation systems. DFGR integrates innovative interaction patterns between real and fake flows within the QKV modules of the self-attention mechanism, enhancing both training and inference efficiency. This approach effectively addresses a key limitation observed in Meta's proposed HSTU generative recommendation approach, where heterogeneous information volumes are mapped into identical vector spaces, leading to training instability. Unlike traditional recommendation models, DFGR only relies on user history behavior sequences and minimal attribute information, eliminating the need for extensive manual feature engineering. Comprehensive evaluations on open-source and industrial datasets reveal DFGR's superior performance compared to established baselines such as DIN, DCN, DIEN, and DeepFM. We also investigate optimal parameter allocation strategies under computational constraints, establishing DFGR as an efficient and effective next-generation generate ranking paradigm.
LARES: Latent Reasoning for Sequential Recommendation
May 22, 2025Abstract:Sequential recommender systems have become increasingly important in real-world applications that model user behavior sequences to predict their preferences. However, existing sequential recommendation methods predominantly rely on non-reasoning paradigms, which may limit the model's computational capacity and result in suboptimal recommendation performance. To address these limitations, we present LARES, a novel and scalable LAtent REasoning framework for Sequential recommendation that enhances model's representation capabilities through increasing the computation density of parameters by depth-recurrent latent reasoning. Our proposed approach employs a recurrent architecture that allows flexible expansion of reasoning depth without increasing parameter complexity, thereby effectively capturing dynamic and intricate user interest patterns. A key difference of LARES lies in refining all input tokens at each implicit reasoning step to improve the computation utilization. To fully unlock the model's reasoning potential, we design a two-phase training strategy: (1) Self-supervised pre-training (SPT) with dual alignment objectives; (2) Reinforcement post-training (RPT). During the first phase, we introduce trajectory-level alignment and step-level alignment objectives, which enable the model to learn recommendation-oriented latent reasoning patterns without requiring supplementary annotated data. The subsequent phase utilizes reinforcement learning (RL) to harness the model's exploratory ability, further refining its reasoning capabilities. Comprehensive experiments on real-world benchmarks demonstrate our framework's superior performance. Notably, LARES exhibits seamless compatibility with existing advanced models, further improving their recommendation performance.
Search-Based Interaction For Conversation Recommendation via Generative Reward Model Based Simulated User
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Conversational recommendation systems (CRSs) use multi-turn interaction to capture user preferences and provide personalized recommendations. A fundamental challenge in CRSs lies in effectively understanding user preferences from conversations. User preferences can be multifaceted and complex, posing significant challenges for accurate recommendations even with access to abundant external knowledge. While interaction with users can clarify their true preferences, frequent user involvement can lead to a degraded user experience. To address this problem, we propose a generative reward model based simulated user, named GRSU, for automatic interaction with CRSs. The simulated user provides feedback to the items recommended by CRSs, enabling them to better capture intricate user preferences through multi-turn interaction. Inspired by generative reward models, we design two types of feedback actions for the simulated user: i.e., generative item scoring, which offers coarse-grained feedback, and attribute-based item critique, which provides fine-grained feedback. To ensure seamless integration, these feedback actions are unified into an instruction-based format, allowing the development of a unified simulated user via instruction tuning on synthesized data. With this simulated user, automatic multi-turn interaction with CRSs can be effectively conducted. Furthermore, to strike a balance between effectiveness and efficiency, we draw inspiration from the paradigm of reward-guided search in complex reasoning tasks and employ beam search for the interaction process. On top of this, we propose an efficient candidate ranking method to improve the recommendation results derived from interaction. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness, efficiency, and transferability of our approach.
Unlocking General Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Capabilities of Large Language Models via Representation Engineering
Mar 14, 2025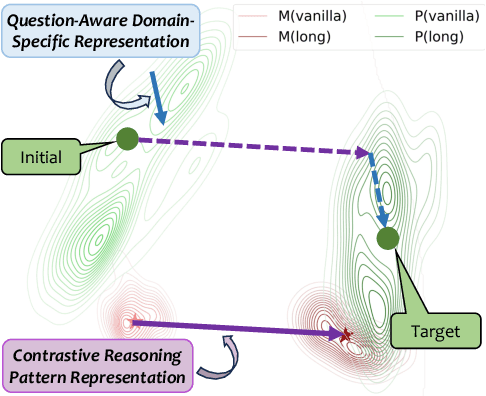



Abstract:Recent advancements in long chain-of-thoughts(long CoTs) have significantly improved the reasoning capabilities of large language models(LLMs). Existing work finds that the capability of long CoT reasoning can be efficiently elicited by tuning on only a few examples and can easily transfer to other tasks. This motivates us to investigate whether long CoT reasoning is a general capability for LLMs. In this work, we conduct an empirical analysis for this question from the perspective of representation. We find that LLMs do encode long CoT reasoning as a general capability, with a clear distinction from vanilla CoTs. Furthermore, domain-specific representations are also required for the effective transfer of long CoT reasoning. Inspired by these findings, we propose GLoRE, a novel representation engineering method to unleash the general long CoT reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of GLoRE in both in-domain and cross-domain scenarios.
CNC: Cross-modal Normality Constraint for Unsupervised Multi-class Anomaly Detection
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Existing unsupervised distillation-based methods rely on the differences between encoded and decoded features to locate abnormal regions in test images. However, the decoder trained only on normal samples still reconstructs abnormal patch features well, degrading performance. This issue is particularly pronounced in unsupervised multi-class anomaly detection tasks. We attribute this behavior to over-generalization(OG) of decoder: the significantly increasing diversity of patch patterns in multi-class training enhances the model generalization on normal patches, but also inadvertently broadens its generalization to abnormal patches. To mitigate OG, we propose a novel approach that leverages class-agnostic learnable prompts to capture common textual normality across various visual patterns, and then apply them to guide the decoded features towards a normal textual representation, suppressing over-generalization of the decoder on abnormal patterns. To further improve performance, we also introduce a gated mixture-of-experts module to specialize in handling diverse patch patterns and reduce mutual interference between them in multi-class training. Our method achieves competitive performance on the MVTec AD and VisA datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness.
DAWN-ICL: Strategic Planning of Problem-solving Trajectories for Zero-Shot In-Context Learning
Oct 26, 2024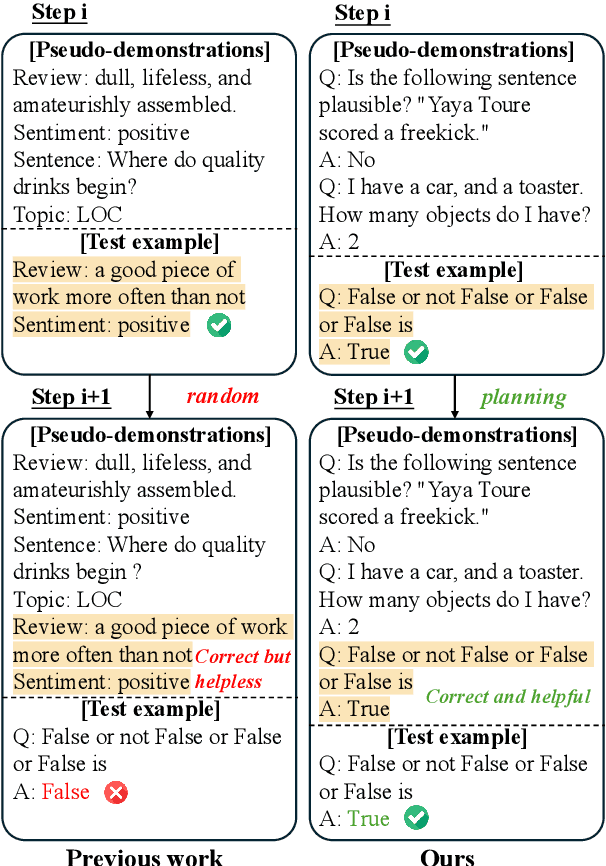
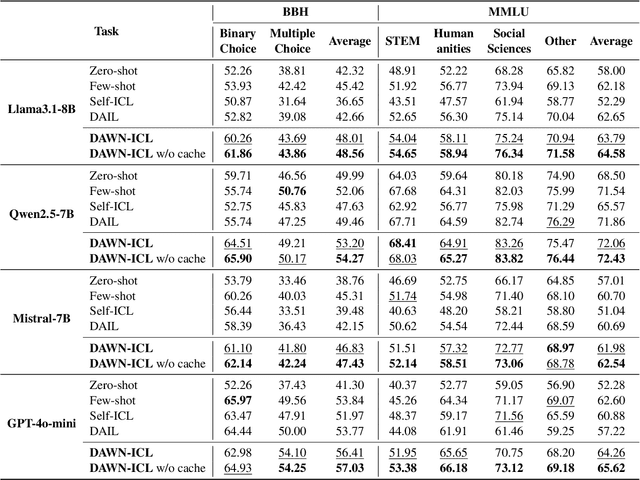
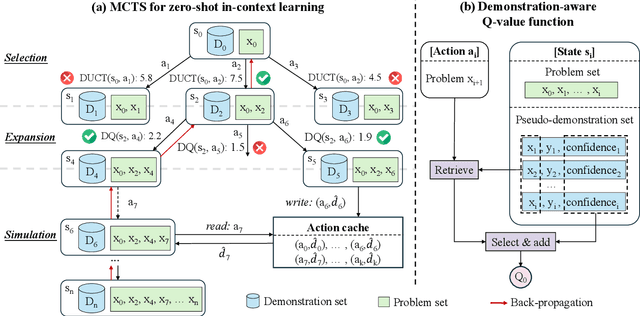
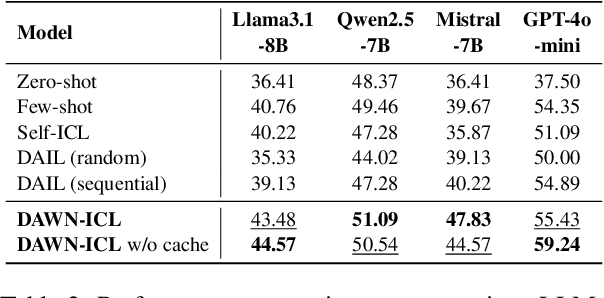
Abstract:Zero-shot in-context learning (ZS-ICL) aims to conduct in-context learning (ICL) without using human-annotated demonstrations. Most ZS-ICL methods use large language models (LLMs) to generate (input, label) pairs as pseudo-demonstrations and leverage historical pseudo-demonstrations to help solve the current problem. They assume that problems are from the same task and traverse them in a random order. However, in real-world scenarios, problems usually come from diverse tasks, and only a few belong to the same task. The random traversing order may generate unreliable pseudo-demonstrations and lead to error accumulation. To address this problem, we reformulate ZS-ICL as a planning problem and propose a Demonstration-aware Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) approach (DAWN-ICL), which leverages MCTS to strategically plan the problem-solving trajectories for ZS-ICL. In addition, to achieve effective and efficient Q value estimation, we propose a novel demonstration-aware Q-value function and use it to enhance the selection phase and accelerate the expansion and simulation phases in MCTS. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of DAWN-ICL on in-domain and cross-domain scenarios, and it even outperforms ICL using human-annotated labels. The code is available at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/MCTS4ZSICL.
YuLan: An Open-source Large Language Model
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have become the foundation of many applications, leveraging their extensive capabilities in processing and understanding natural language. While many open-source LLMs have been released with technical reports, the lack of training details hinders further research and development. This paper presents the development of YuLan, a series of open-source LLMs with $12$ billion parameters. The base model of YuLan is pre-trained on approximately $1.7$T tokens derived from a diverse corpus, including massive English, Chinese, and multilingual texts. We design a three-stage pre-training method to enhance YuLan's overall capabilities. Subsequent phases of training incorporate instruction-tuning and human alignment, employing a substantial volume of high-quality synthesized data. To facilitate the learning of complex and long-tail knowledge, we devise a curriculum-learning framework throughout across these stages, which helps LLMs learn knowledge in an easy-to-hard manner. YuLan's training is finished on Jan, 2024 and has achieved performance on par with state-of-the-art LLMs across various English and Chinese benchmarks. This paper outlines a comprehensive technical roadmap for developing LLMs from scratch. Our model and codes are available at https://github.com/RUC-GSAI/YuLan-Chat.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge