Hua Lu
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Baseline Method of the Foundation Model Challenge for Ultrasound Image Analysis
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Ultrasound (US) imaging exhibits substantial heterogeneity across anatomical structures and acquisition protocols, posing significant challenges to the development of generalizable analysis models. Most existing methods are task-specific, limiting their suitability as clinically deployable foundation models. To address this limitation, the Foundation Model Challenge for Ultrasound Image Analysis (FM\_UIA~2026) introduces a large-scale multi-task benchmark comprising 27 subtasks across segmentation, classification, detection, and regression. In this paper, we present the official baseline for FM\_UIA~2026 based on a unified Multi-Head Multi-Task Learning (MH-MTL) framework that supports all tasks within a single shared network. The model employs an ImageNet-pretrained EfficientNet--B4 backbone for robust feature extraction, combined with a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) to capture multi-scale contextual information. A task-specific routing strategy enables global tasks to leverage high-level semantic features, while dense prediction tasks exploit spatially detailed FPN representations. Training incorporates a composite loss with task-adaptive learning rate scaling and a cosine annealing schedule. Validation results demonstrate the feasibility and robustness of this unified design, establishing a strong and extensible baseline for ultrasound foundation model research. The code and dataset are publicly available at \href{https://github.com/lijiake2408/Foundation-Model-Challenge-for-Ultrasound-Image-Analysis}{GitHub}.
MovSemCL: Movement-Semantics Contrastive Learning for Trajectory Similarity
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Trajectory similarity computation is fundamental functionality that is used for, e.g., clustering, prediction, and anomaly detection. However, existing learning-based methods exhibit three key limitations: (1) insufficient modeling of trajectory semantics and hierarchy, lacking both movement dynamics extraction and multi-scale structural representation; (2) high computational costs due to point-wise encoding; and (3) use of physically implausible augmentations that distort trajectory semantics. To address these issues, we propose MovSemCL, a movement-semantics contrastive learning framework for trajectory similarity computation. MovSemCL first transforms raw GPS trajectories into movement-semantics features and then segments them into patches. Next, MovSemCL employs intra- and inter-patch attentions to encode local as well as global trajectory patterns, enabling efficient hierarchical representation and reducing computational costs. Moreover, MovSemCL includes a curvature-guided augmentation strategy that preserves informative segments (e.g., turns and intersections) and masks redundant ones, generating physically plausible augmented views. Experiments on real-world datasets show that MovSemCL is capable of outperforming state-of-the-art methods, achieving mean ranks close to the ideal value of 1 at similarity search tasks and improvements by up to 20.3% at heuristic approximation, while reducing inference latency by up to 43.4%.
Large Foundation Model for Ads Recommendation
Aug 20, 2025


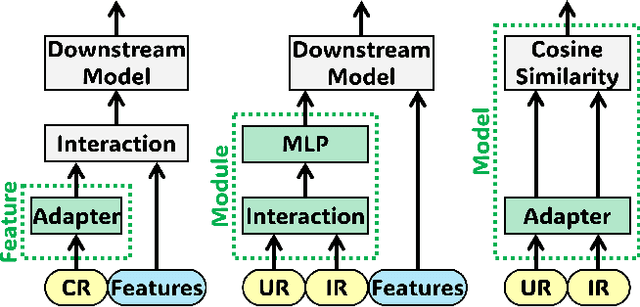
Abstract:Online advertising relies on accurate recommendation models, with recent advances using pre-trained large-scale foundation models (LFMs) to capture users' general interests across multiple scenarios and tasks. However, existing methods have critical limitations: they extract and transfer only user representations (URs), ignoring valuable item representations (IRs) and user-item cross representations (CRs); and they simply use a UR as a feature in downstream applications, which fails to bridge upstream-downstream gaps and overlooks more transfer granularities. In this paper, we propose LFM4Ads, an All-Representation Multi-Granularity transfer framework for ads recommendation. It first comprehensively transfers URs, IRs, and CRs, i.e., all available representations in the pre-trained foundation model. To effectively utilize the CRs, it identifies the optimal extraction layer and aggregates them into transferable coarse-grained forms. Furthermore, we enhance the transferability via multi-granularity mechanisms: non-linear adapters for feature-level transfer, an Isomorphic Interaction Module for module-level transfer, and Standalone Retrieval for model-level transfer. LFM4Ads has been successfully deployed in Tencent's industrial-scale advertising platform, processing tens of billions of daily samples while maintaining terabyte-scale model parameters with billions of sparse embedding keys across approximately two thousand features. Since its production deployment in Q4 2024, LFM4Ads has achieved 10+ successful production launches across various advertising scenarios, including primary ones like Weixin Moments and Channels. These launches achieve an overall GMV lift of 2.45% across the entire platform, translating to estimated annual revenue increases in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
A Comprehensive Survey of Reward Models: Taxonomy, Applications, Challenges, and Future
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Reward Model (RM) has demonstrated impressive potential for enhancing Large Language Models (LLM), as RM can serve as a proxy for human preferences, providing signals to guide LLMs' behavior in various tasks. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive overview of relevant research, exploring RMs from the perspectives of preference collection, reward modeling, and usage. Next, we introduce the applications of RMs and discuss the benchmarks for evaluation. Furthermore, we conduct an in-depth analysis of the challenges existing in the field and dive into the potential research directions. This paper is dedicated to providing beginners with a comprehensive introduction to RMs and facilitating future studies. The resources are publicly available at github\footnote{https://github.com/JLZhong23/awesome-reward-models}.
Not All Data are Good Labels: On the Self-supervised Labeling for Time Series Forecasting
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Time Series Forecasting (TSF) is a crucial task in various domains, yet existing TSF models rely heavily on high-quality data and insufficiently exploit all available data. This paper explores a novel self-supervised approach to re-label time series datasets by inherently constructing candidate datasets. During the optimization of a simple reconstruction network, intermediates are used as pseudo labels in a self-supervised paradigm, improving generalization for any predictor. We introduce the Self-Correction with Adaptive Mask (SCAM), which discards overfitted components and selectively replaces them with pseudo labels generated from reconstructions. Additionally, we incorporate Spectral Norm Regularization (SNR) to further suppress overfitting from a loss landscape perspective. Our experiments on eleven real-world datasets demonstrate that SCAM consistently improves the performance of various backbone models. This work offers a new perspective on constructing datasets and enhancing the generalization of TSF models through self-supervised learning.
Poly2Vec: Polymorphic Encoding of Geospatial Objects for Spatial Reasoning with Deep Neural Networks
Aug 27, 2024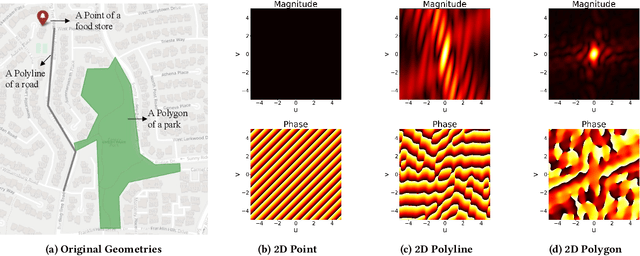
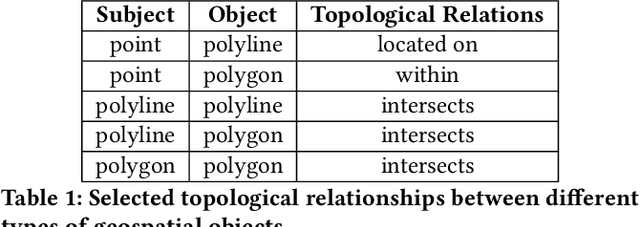
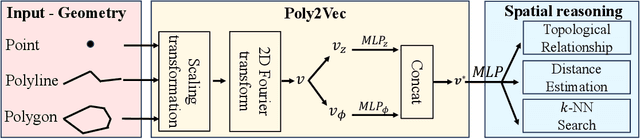
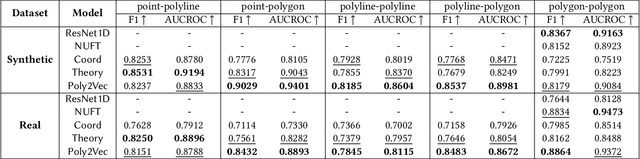
Abstract:Encoding geospatial data is crucial for enabling machine learning (ML) models to perform tasks that require spatial reasoning, such as identifying the topological relationships between two different geospatial objects. However, existing encoding methods are limited as they are typically customized to handle only specific types of spatial data, which impedes their applicability across different downstream tasks where multiple data types coexist. To address this, we introduce Poly2Vec, an encoding framework that unifies the modeling of different geospatial objects, including 2D points, polylines, and polygons, irrespective of the downstream task. We leverage the power of the 2D Fourier transform to encode useful spatial properties, such as shape and location, from geospatial objects into fixed-length vectors. These vectors are then inputted into neural network models for spatial reasoning tasks.This unified approach eliminates the need to develop and train separate models for each distinct spatial type. We evaluate Poly2Vec on both synthetic and real datasets of mixed geometry types and verify its consistent performance across several downstream spatial reasoning tasks.
Missing Value Imputation for Multi-attribute Sensor Data Streams via Message Propagation (Extended Version)
Nov 14, 2023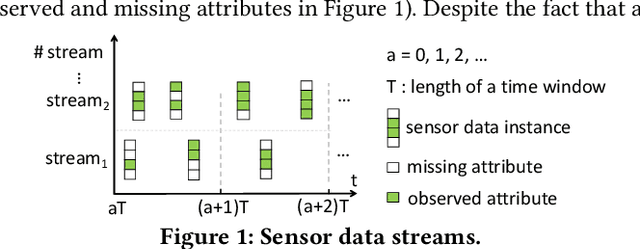
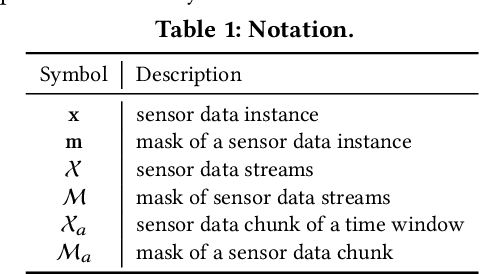
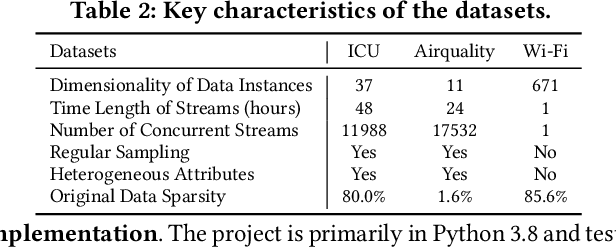
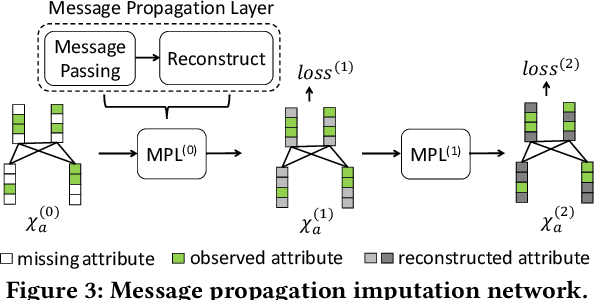
Abstract:Sensor data streams occur widely in various real-time applications in the context of the Internet of Things (IoT). However, sensor data streams feature missing values due to factors such as sensor failures, communication errors, or depleted batteries. Missing values can compromise the quality of real-time analytics tasks and downstream applications. Existing imputation methods either make strong assumptions about streams or have low efficiency. In this study, we aim to accurately and efficiently impute missing values in data streams that satisfy only general characteristics in order to benefit real-time applications more widely. First, we propose a message propagation imputation network (MPIN) that is able to recover the missing values of data instances in a time window. We give a theoretical analysis of why MPIN is effective. Second, we present a continuous imputation framework that consists of data update and model update mechanisms to enable MPIN to perform continuous imputation both effectively and efficiently. Extensive experiments on multiple real datasets show that MPIN can outperform the existing data imputers by wide margins and that the continuous imputation framework is efficient and accurate.
LightCTS: A Lightweight Framework for Correlated Time Series Forecasting
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Correlated time series (CTS) forecasting plays an essential role in many practical applications, such as traffic management and server load control. Many deep learning models have been proposed to improve the accuracy of CTS forecasting. However, while models have become increasingly complex and computationally intensive, they struggle to improve accuracy. Pursuing a different direction, this study aims instead to enable much more efficient, lightweight models that preserve accuracy while being able to be deployed on resource-constrained devices. To achieve this goal, we characterize popular CTS forecasting models and yield two observations that indicate directions for lightweight CTS forecasting. On this basis, we propose the LightCTS framework that adopts plain stacking of temporal and spatial operators instead of alternate stacking that is much more computationally expensive. Moreover, LightCTS features light temporal and spatial operator modules, called L-TCN and GL-Former, that offer improved computational efficiency without compromising their feature extraction capabilities. LightCTS also encompasses a last-shot compression scheme to reduce redundant temporal features and speed up subsequent computations. Experiments with single-step and multi-step forecasting benchmark datasets show that LightCTS is capable of nearly state-of-the-art accuracy at much reduced computational and storage overheads.
PLATO-K: Internal and External Knowledge Enhanced Dialogue Generation
Nov 02, 2022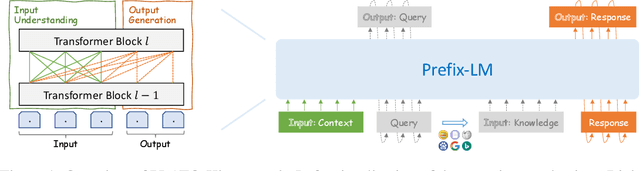
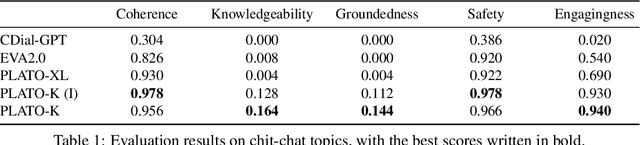

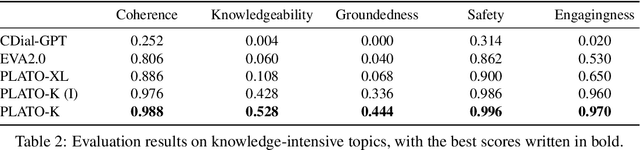
Abstract:Recently, the practical deployment of open-domain dialogue systems has been plagued by the knowledge issue of information deficiency and factual inaccuracy. To this end, we introduce PLATO-K based on two-stage dialogic learning to strengthen internal knowledge memorization and external knowledge exploitation. In the first stage, PLATO-K learns through massive dialogue corpora and memorizes essential knowledge into model parameters. In the second stage, PLATO-K mimics human beings to search for external information and to leverage the knowledge in response generation. Extensive experiments reveal that the knowledge issue is alleviated significantly in PLATO-K with such comprehensive internal and external knowledge enhancement. Compared to the existing state-of-the-art Chinese dialogue model, the overall engagingness of PLATO-K is improved remarkably by 36.2% and 49.2% on chit-chat and knowledge-intensive conversations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge