Zekang Li
MiniMax-01: Scaling Foundation Models with Lightning Attention
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-01 series, including MiniMax-Text-01 and MiniMax-VL-01, which are comparable to top-tier models while offering superior capabilities in processing longer contexts. The core lies in lightning attention and its efficient scaling. To maximize computational capacity, we integrate it with Mixture of Experts (MoE), creating a model with 32 experts and 456 billion total parameters, of which 45.9 billion are activated for each token. We develop an optimized parallel strategy and highly efficient computation-communication overlap techniques for MoE and lightning attention. This approach enables us to conduct efficient training and inference on models with hundreds of billions of parameters across contexts spanning millions of tokens. The context window of MiniMax-Text-01 can reach up to 1 million tokens during training and extrapolate to 4 million tokens during inference at an affordable cost. Our vision-language model, MiniMax-VL-01 is built through continued training with 512 billion vision-language tokens. Experiments on both standard and in-house benchmarks show that our models match the performance of state-of-the-art models like GPT-4o and Claude-3.5-Sonnet while offering 20-32 times longer context window. We publicly release MiniMax-01 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI.
Report from the NSF Future Directions Workshop on Automatic Evaluation of Dialog: Research Directions and Challenges
Mar 18, 2022

Abstract:This is a report on the NSF Future Directions Workshop on Automatic Evaluation of Dialog. The workshop explored the current state of the art along with its limitations and suggested promising directions for future work in this important and very rapidly changing area of research.
Relational Surrogate Loss Learning
Feb 26, 2022



Abstract:Evaluation metrics in machine learning are often hardly taken as loss functions, as they could be non-differentiable and non-decomposable, e.g., average precision and F1 score. This paper aims to address this problem by revisiting the surrogate loss learning, where a deep neural network is employed to approximate the evaluation metrics. Instead of pursuing an exact recovery of the evaluation metric through a deep neural network, we are reminded of the purpose of the existence of these evaluation metrics, which is to distinguish whether one model is better or worse than another. In this paper, we show that directly maintaining the relation of models between surrogate losses and metrics suffices, and propose a rank correlation-based optimization method to maximize this relation and learn surrogate losses. Compared to previous works, our method is much easier to optimize and enjoys significant efficiency and performance gains. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves improvements on various tasks including image classification and neural machine translation, and even outperforms state-of-the-art methods on human pose estimation and machine reading comprehension tasks. Code is available at: https://github.com/hunto/ReLoss.
Mental Health Assessment for the Chatbots
Jan 14, 2022



Abstract:Previous researches on dialogue system assessment usually focus on the quality evaluation (e.g. fluency, relevance, etc) of responses generated by the chatbots, which are local and technical metrics. For a chatbot which responds to millions of online users including minors, we argue that it should have a healthy mental tendency in order to avoid the negative psychological impact on them. In this paper, we establish several mental health assessment dimensions for chatbots (depression, anxiety, alcohol addiction, empathy) and introduce the questionnaire-based mental health assessment methods. We conduct assessments on some well-known open-domain chatbots and find that there are severe mental health issues for all these chatbots. We consider that it is due to the neglect of the mental health risks during the dataset building and the model training procedures. We expect to attract researchers' attention to the serious mental health problems of chatbots and improve the chatbots' ability in positive emotional interaction.
Semi-Autoregressive Image Captioning
Oct 13, 2021



Abstract:Current state-of-the-art approaches for image captioning typically adopt an autoregressive manner, i.e., generating descriptions word by word, which suffers from slow decoding issue and becomes a bottleneck in real-time applications. Non-autoregressive image captioning with continuous iterative refinement, which eliminates the sequential dependence in a sentence generation, can achieve comparable performance to the autoregressive counterparts with a considerable acceleration. Nevertheless, based on a well-designed experiment, we empirically proved that iteration times can be effectively reduced when providing sufficient prior knowledge for the language decoder. Towards that end, we propose a novel two-stage framework, referred to as Semi-Autoregressive Image Captioning (SAIC), to make a better trade-off between performance and speed. The proposed SAIC model maintains autoregressive property in global but relieves it in local. Specifically, SAIC model first jumpily generates an intermittent sequence in an autoregressive manner, that is, it predicts the first word in every word group in order. Then, with the help of the partially deterministic prior information and image features, SAIC model non-autoregressively fills all the skipped words with one iteration. Experimental results on the MS COCO benchmark demonstrate that our SAIC model outperforms the preceding non-autoregressive image captioning models while obtaining a competitive inference speedup. Code is available at https://github.com/feizc/SAIC.
Towards Expressive Communication with Internet Memes: A New Multimodal Conversation Dataset and Benchmark
Sep 04, 2021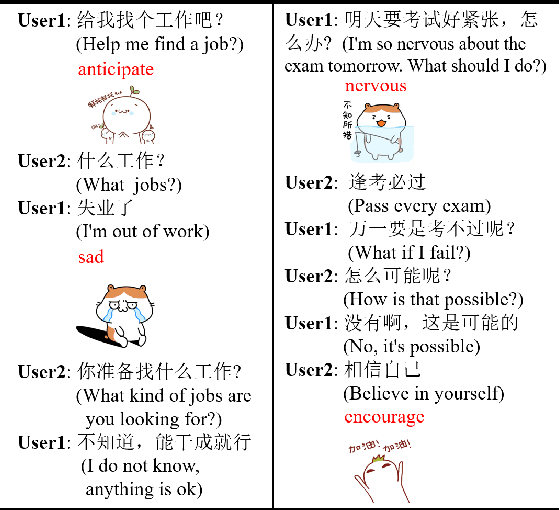
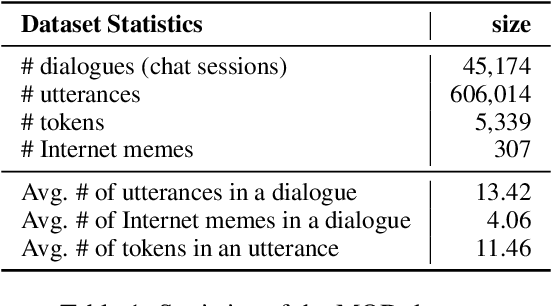
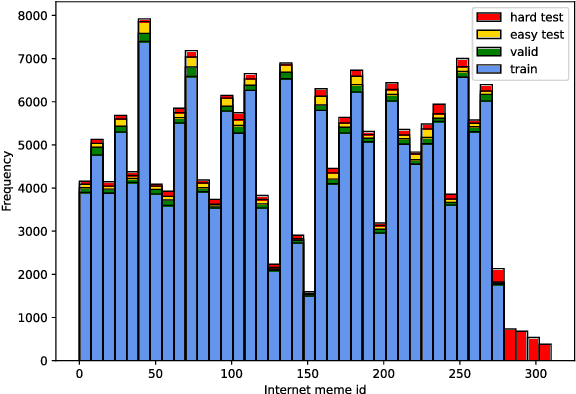

Abstract:As a kind of new expression elements, Internet memes are popular and extensively used in online chatting scenarios since they manage to make dialogues vivid, moving, and interesting. However, most current dialogue researches focus on text-only dialogue tasks. In this paper, we propose a new task named as \textbf{M}eme incorporated \textbf{O}pen-domain \textbf{D}ialogue (MOD). Compared to previous dialogue tasks, MOD is much more challenging since it requires the model to understand the multimodal elements as well as the emotions behind them. To facilitate the MOD research, we construct a large-scale open-domain multimodal dialogue dataset incorporating abundant Internet memes into utterances. The dataset consists of $\sim$45K Chinese conversations with $\sim$606K utterances. Each conversation contains about $13$ utterances with about $4$ Internet memes on average and each utterance equipped with an Internet meme is annotated with the corresponding emotion. In addition, we present a simple and effective method, which utilizes a unified generation network to solve the MOD task. Experimental results demonstrate that our method trained on the proposed corpus is able to achieve expressive communication including texts and memes. The corpus and models have been publicly available at https://github.com/lizekang/DSTC10-MOD.
Addressing Inquiries about History: An Efficient and Practical Framework for Evaluating Open-domain Chatbot Consistency
Jun 04, 2021



Abstract:A good open-domain chatbot should avoid presenting contradictory responses about facts or opinions in a conversational session, known as its consistency capacity. However, evaluating the consistency capacity of a chatbot is still challenging. Employing human judges to interact with chatbots on purpose to check their capacities is costly and low-efficient, and difficult to get rid of subjective bias. In this paper, we propose the Addressing Inquiries about History (AIH), an efficient and practical framework for the consistency evaluation. At the conversation stage, AIH attempts to address appropriate inquiries about the dialogue history to induce the chatbot to redeclare the historical facts or opinions. We carry out the conversation between chatbots, which is more efficient than the human-bot interaction and can also alleviate the subjective bias. In this way, we manage to rapidly obtain a dialog session that contains responses with high contradiction possibilities. At the contradiction recognition stage, we can either employ human judges or a natural language inference (NLI) model to recognize whether the answers to the inquiries are contradictory with history. Finally, we are able to rank chatbots according to the contradiction statistics. Experiments on open-domain chatbots show that our approach can efficiently and reliably assess the consistency capacity of chatbots and achieve a high ranking correlation with the human evaluation. We release the framework and hope to help improve the consistency capacity of chatbots. \footnote{\url{https://github.com/ictnlp/AIH}}
Conversations Are Not Flat: Modeling the Dynamic Information Flow across Dialogue Utterances
Jun 04, 2021



Abstract:Nowadays, open-domain dialogue models can generate acceptable responses according to the historical context based on the large-scale pre-trained language models. However, they generally concatenate the dialogue history directly as the model input to predict the response, which we named as the flat pattern and ignores the dynamic information flow across dialogue utterances. In this work, we propose the DialoFlow model, in which we introduce a dynamic flow mechanism to model the context flow, and design three training objectives to capture the information dynamics across dialogue utterances by addressing the semantic influence brought about by each utterance in large-scale pre-training. Experiments on the multi-reference Reddit Dataset and DailyDialog Dataset demonstrate that our DialoFlow significantly outperforms the DialoGPT on the dialogue generation task. Besides, we propose the Flow score, an effective automatic metric for evaluating interactive human-bot conversation quality based on the pre-trained DialoFlow, which presents high chatbot-level correlation ($r=0.9$) with human ratings among 11 chatbots. Code and pre-trained models will be public. \footnote{\url{https://github.com/ictnlp/DialoFlow}}
WeChat AI's Submission for DSTC9 Interactive Dialogue Evaluation Track
Jan 20, 2021



Abstract:We participate in the DSTC9 Interactive Dialogue Evaluation Track (Gunasekara et al. 2020) sub-task 1 (Knowledge Grounded Dialogue) and sub-task 2 (Interactive Dialogue). In sub-task 1, we employ a pre-trained language model to generate topic-related responses and propose a response ensemble method for response selection. In sub-task2, we propose a novel Dialogue Planning Model (DPM) to capture conversation flow in the interaction with humans. We also design an integrated open-domain dialogue system containing pre-process, dialogue model, scoring model, and post-process, which can generate fluent, coherent, consistent, and humanlike responses. We tie 1st on human ratings and also get the highest Meteor, and Bert-score in sub-task 1, and rank 3rd on interactive human evaluation in sub-task 2.
A Contextual Hierarchical Attention Network with Adaptive Objective for Dialogue State Tracking
Jun 02, 2020



Abstract:Recent studies in dialogue state tracking (DST) leverage historical information to determine states which are generally represented as slot-value pairs. However, most of them have limitations to efficiently exploit relevant context due to the lack of a powerful mechanism for modeling interactions between the slot and the dialogue history. Besides, existing methods usually ignore the slot imbalance problem and treat all slots indiscriminately, which limits the learning of hard slots and eventually hurts overall performance. In this paper, we propose to enhance the DST through employing a contextual hierarchical attention network to not only discern relevant information at both word level and turn level but also learn contextual representations. We further propose an adaptive objective to alleviate the slot imbalance problem by dynamically adjust weights of different slots during training. Experimental results show that our approach reaches 52.68% and 58.55% joint accuracy on MultiWOZ 2.0 and MultiWOZ 2.1 datasets respectively and achieves new state-of-the-art performance with considerable improvements (+1.24% and +5.98%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge