Wenlu Wang
Spatio-Temporal Graph Unlearning
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Spatio-temporal graphs are widely used in modeling complex dynamic processes such as traffic forecasting, molecular dynamics, and healthcare monitoring. Recently, stringent privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA have introduced significant new challenges for existing spatio-temporal graph models, requiring complete unlearning of unauthorized data. Since each node in a spatio-temporal graph diffuses information globally across both spatial and temporal dimensions, existing unlearning methods primarily designed for static graphs and localized data removal cannot efficiently erase a single node without incurring costs nearly equivalent to full model retraining. Therefore, an effective approach for complete spatio-temporal graph unlearning is a pressing need. To address this, we propose CallosumNet, a divide-and-conquer spatio-temporal graph unlearning framework inspired by the corpus callosum structure that facilitates communication between the brain's two hemispheres. CallosumNet incorporates two novel techniques: (1) Enhanced Subgraph Construction (ESC), which adaptively constructs multiple localized subgraphs based on several factors, including biologically-inspired virtual ganglions; and (2) Global Ganglion Bridging (GGB), which reconstructs global spatio-temporal dependencies from these localized subgraphs, effectively restoring the full graph representation. Empirical results on four diverse real-world datasets show that CallosumNet achieves complete unlearning with only 1%-2% relative MAE loss compared to the gold model, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. Ablation studies verify the effectiveness of both proposed techniques.
Accessible and Portable LLM Inference by Compiling Computational Graphs into SQL
Feb 05, 2025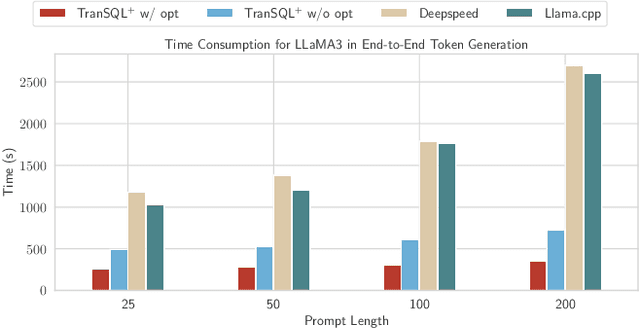
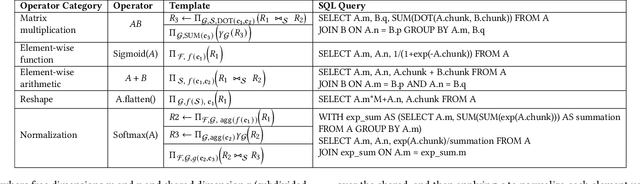
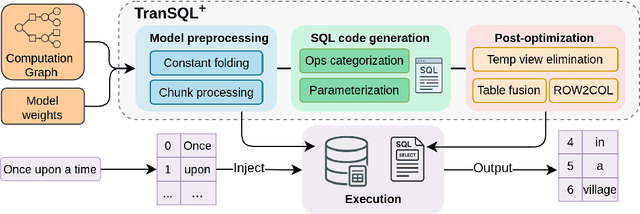
Abstract:Serving large language models (LLMs) often demands specialized hardware, dedicated frameworks, and substantial development efforts, which restrict their accessibility, especially for edge devices and organizations with limited technical resources. We propose a novel compiler that translates LLM inference graphs into SQL queries, enabling relational databases, one of the most widely used and mature software systems globally, to serve as the runtime. By mapping neural operators such as matrix multiplication and attention into relational primitives like joins and aggregations, our approach leverages database capabilities, including disk-based data management and native caching. Supporting key transformer components, such as attention mechanisms and key-value caching, our system generates SQL pipelines for end-to-end LLM inference. Using the Llama3 family as a case study, we demonstrate up to 30x speedup in token generation for memory-constrained scenarios comparable to competitive CPU-based frameworks. Our work offers an accessible, portable, and efficient solution, facilitating the serving of LLMs across diverse deployment environments.
SouLLMate: An Application Enhancing Diverse Mental Health Support with Adaptive LLMs, Prompt Engineering, and RAG Techniques
Oct 17, 2024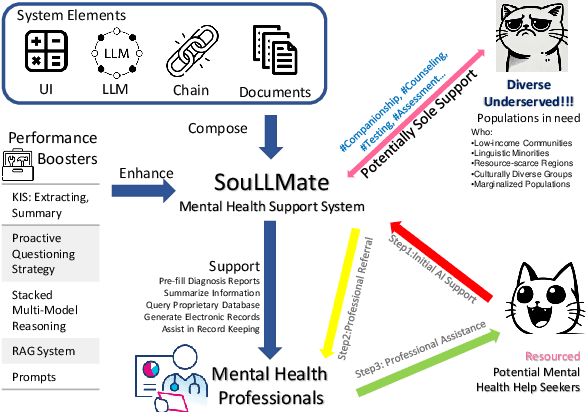
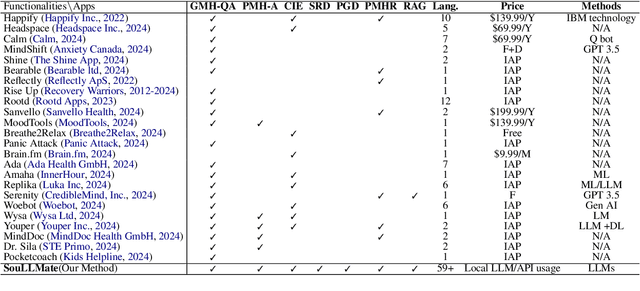
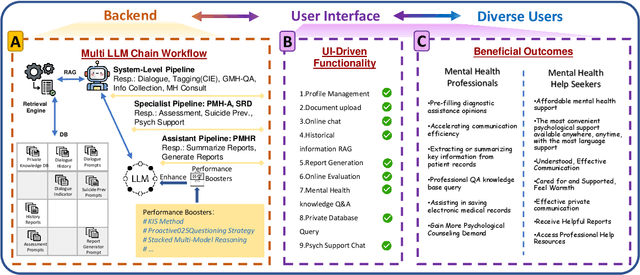

Abstract:Mental health issues significantly impact individuals' daily lives, yet many do not receive the help they need even with available online resources. This study aims to provide diverse, accessible, stigma-free, personalized, and real-time mental health support through cutting-edge AI technologies. It makes the following contributions: (1) Conducting an extensive survey of recent mental health support methods to identify prevalent functionalities and unmet needs. (2) Introducing SouLLMate, an adaptive LLM-driven system that integrates LLM technologies, Chain, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), prompt engineering, and domain knowledge. This system offers advanced features such as Risk Detection and Proactive Guidance Dialogue, and utilizes RAG for personalized profile uploads and Conversational Information Extraction. (3) Developing novel evaluation approaches for preliminary assessments and risk detection via professionally annotated interview data and real-life suicide tendency data. (4) Proposing the Key Indicator Summarization (KIS), Proactive Questioning Strategy (PQS), and Stacked Multi-Model Reasoning (SMMR) methods to enhance model performance and usability through context-sensitive response adjustments, semantic coherence evaluations, and enhanced accuracy of long-context reasoning in language models. This study contributes to advancing mental health support technologies, potentially improving the accessibility and effectiveness of mental health care globally.
Interpretable Spatio-Temporal Embedding for Brain Structural-Effective Network with Ordinary Differential Equation
May 21, 2024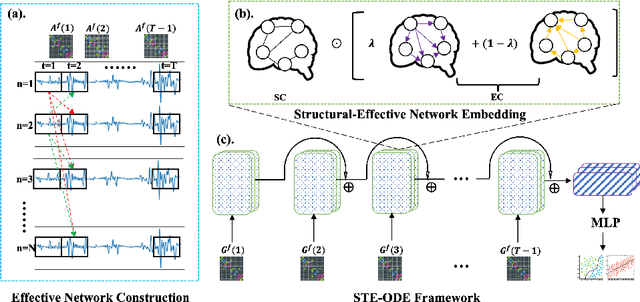
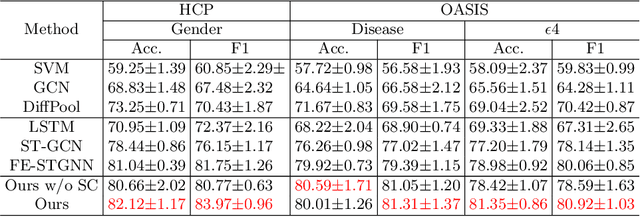
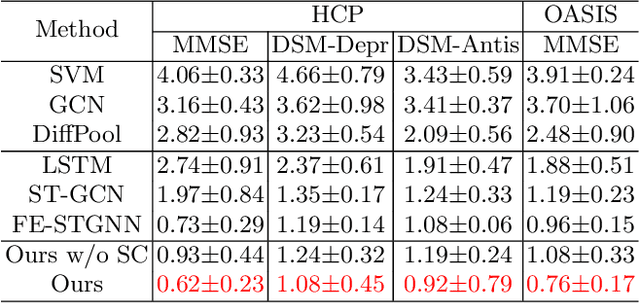
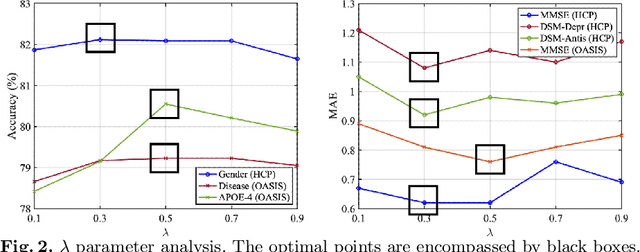
Abstract:The MRI-derived brain network serves as a pivotal instrument in elucidating both the structural and functional aspects of the brain, encompassing the ramifications of diseases and developmental processes. However, prevailing methodologies, often focusing on synchronous BOLD signals from functional MRI (fMRI), may not capture directional influences among brain regions and rarely tackle temporal functional dynamics. In this study, we first construct the brain-effective network via the dynamic causal model. Subsequently, we introduce an interpretable graph learning framework termed Spatio-Temporal Embedding ODE (STE-ODE). This framework incorporates specifically designed directed node embedding layers, aiming at capturing the dynamic interplay between structural and effective networks via an ordinary differential equation (ODE) model, which characterizes spatial-temporal brain dynamics. Our framework is validated on several clinical phenotype prediction tasks using two independent publicly available datasets (HCP and OASIS). The experimental results clearly demonstrate the advantages of our model compared to several state-of-the-art methods.
A Transformer-based Generative Model for De Novo Molecular Design
Oct 17, 2022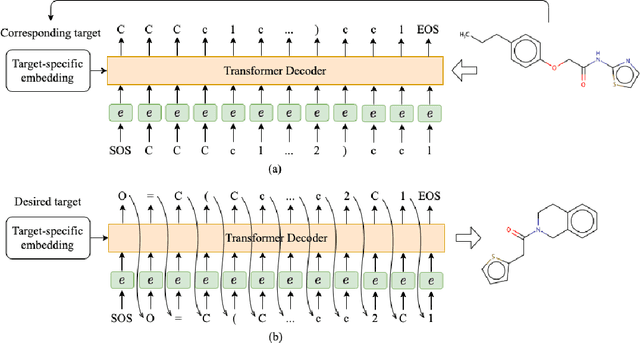
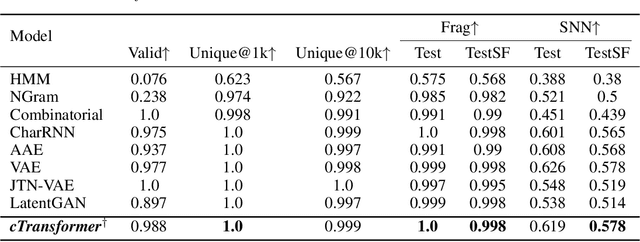
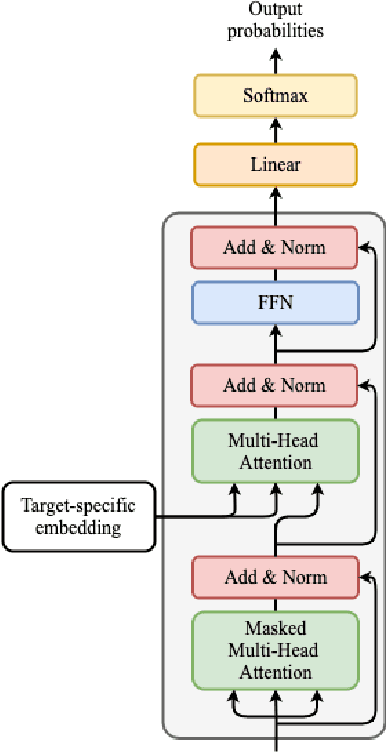
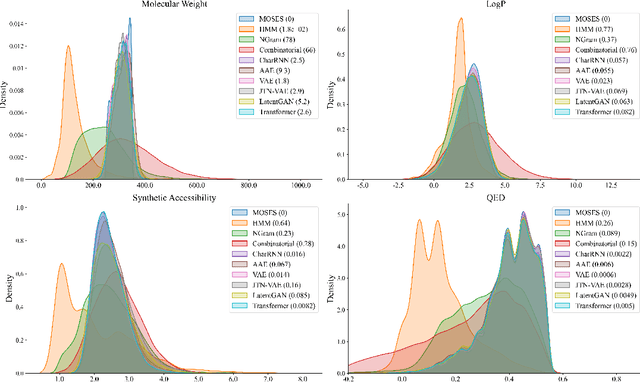
Abstract:Deep learning draws a lot of attention as a new way of generating unseen structures for drug discovery. We propose a Transformer-based deep model for de novo target-specific molecular design. The proposed method is capable of generating both drug-like compounds and target-specific compounds. The latter are generated by enforcing different keys and values of the multi-head attention for each target. We allow the generation of SMILES strings to be conditional on the specified target. The sampled compounds largely occupy the real target-specific data's chemical space and also cover a significant fraction of novel compounds.
RFID-Based Indoor Spatial Query Evaluation with Bayesian Filtering Techniques
Apr 02, 2022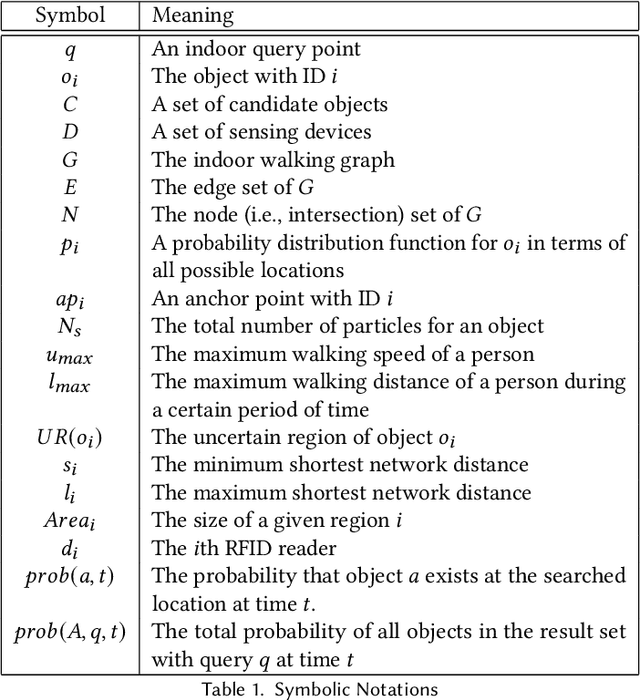
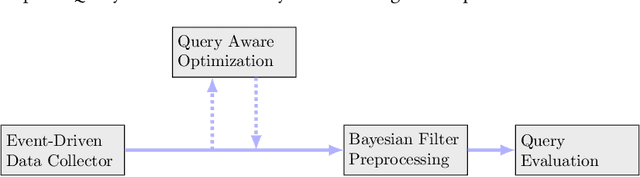
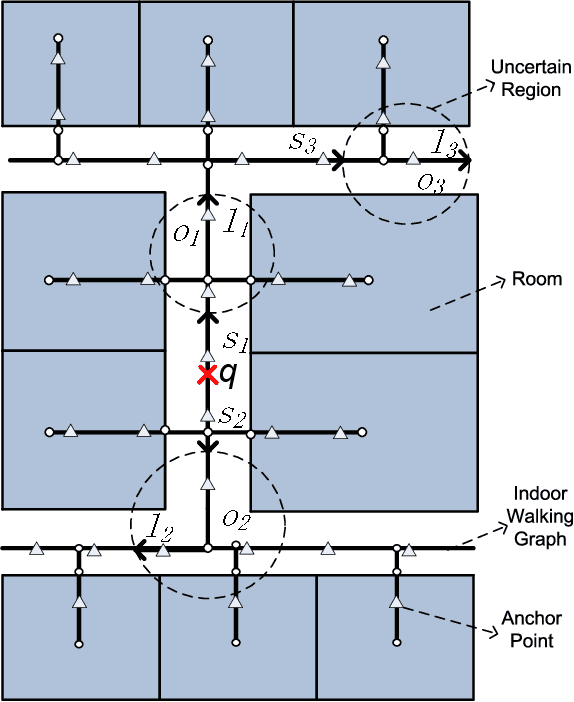
Abstract:People spend a significant amount of time in indoor spaces (e.g., office buildings, subway systems, etc.) in their daily lives. Therefore, it is important to develop efficient indoor spatial query algorithms for supporting various location-based applications. However, indoor spaces differ from outdoor spaces because users have to follow the indoor floor plan for their movements. In addition, positioning in indoor environments is mainly based on sensing devices (e.g., RFID readers) rather than GPS devices. Consequently, we cannot apply existing spatial query evaluation techniques devised for outdoor environments for this new challenge. Because Bayesian filtering techniques can be employed to estimate the state of a system that changes over time using a sequence of noisy measurements made on the system, in this research, we propose the Bayesian filtering-based location inference methods as the basis for evaluating indoor spatial queries with noisy RFID raw data. Furthermore, two novel models, indoor walking graph model and anchor point indexing model, are created for tracking object locations in indoor environments. Based on the inference method and tracking models, we develop innovative indoor range and k nearest neighbor (kNN) query algorithms. We validate our solution through use of both synthetic data and real-world data. Our experimental results show that the proposed algorithms can evaluate indoor spatial queries effectively and efficiently. We open-source the code, data, and floor plan at https://github.com/DataScienceLab18/IndoorToolKit.
SpatialNLI: A Spatial Domain Natural Language Interface to Databases Using Spatial Comprehension
Aug 28, 2019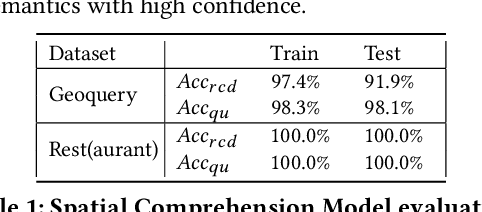
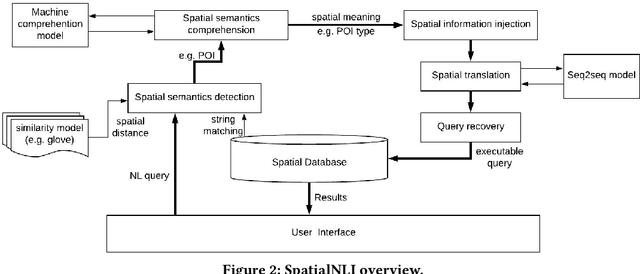
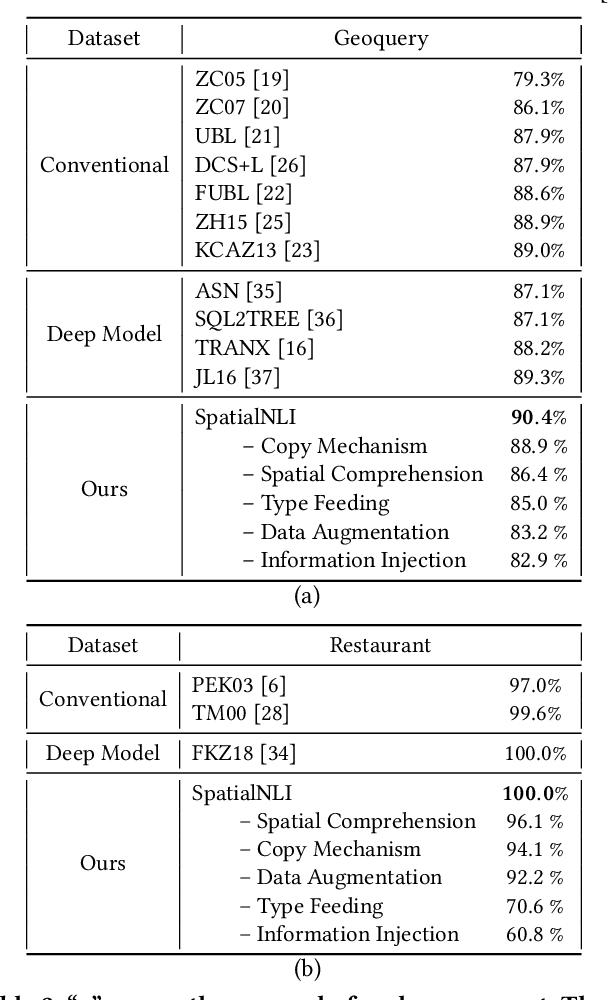

Abstract:A natural language interface (NLI) to databases is an interface that translates a natural language question to a structured query that is executable by database management systems (DBMS). However, an NLI that is trained in the general domain is hard to apply in the spatial domain due to the idiosyncrasy and expressiveness of the spatial questions. Inspired by the machine comprehension model, we propose a spatial comprehension model that is able to recognize the meaning of spatial entities based on the semantics of the context. The spatial semantics learned from the spatial comprehension model is then injected to the natural language question to ease the burden of capturing the spatial-specific semantics. With our spatial comprehension model and information injection, our NLI for the spatial domain, named SpatialNLI, is able to capture the semantic structure of the question and translate it to the corresponding syntax of an executable query accurately. We also experimentally ascertain that SpatialNLI outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
A Transfer-Learnable Natural Language Interface for Databases
Sep 07, 2018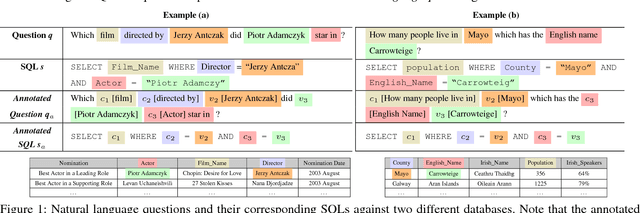
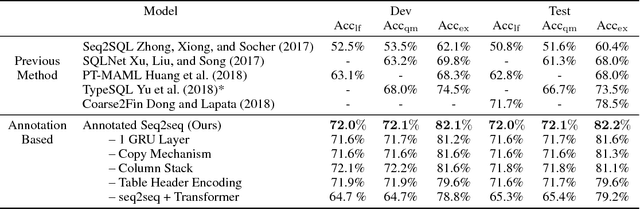
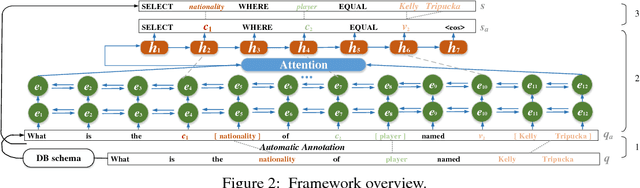
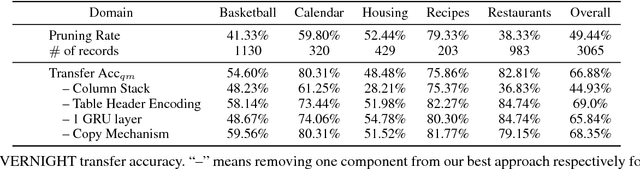
Abstract:Relational database management systems (RDBMSs) are powerful because they are able to optimize and answer queries against any relational database. A natural language interface (NLI) for a database, on the other hand, is tailored to support that specific database. In this work, we introduce a general purpose transfer-learnable NLI with the goal of learning one model that can be used as NLI for any relational database. We adopt the data management principle of separating data and its schema, but with the additional support for the idiosyncrasy and complexity of natural languages. Specifically, we introduce an automatic annotation mechanism that separates the schema and the data, where the schema also covers knowledge about natural language. Furthermore, we propose a customized sequence model that translates annotated natural language queries to SQL statements. We show in experiments that our approach outperforms previous NLI methods on the WikiSQL dataset and the model we learned can be applied to another benchmark dataset OVERNIGHT without retraining.
Adversarial Texts with Gradient Methods
Jan 24, 2018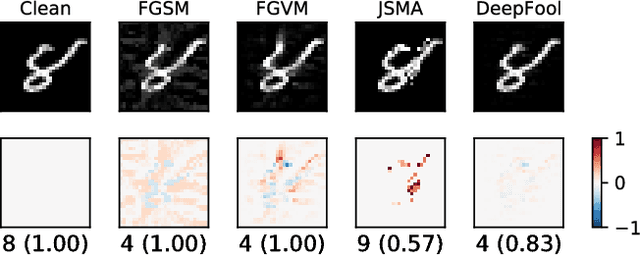
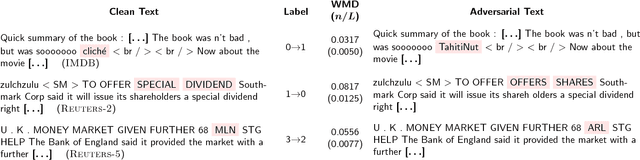
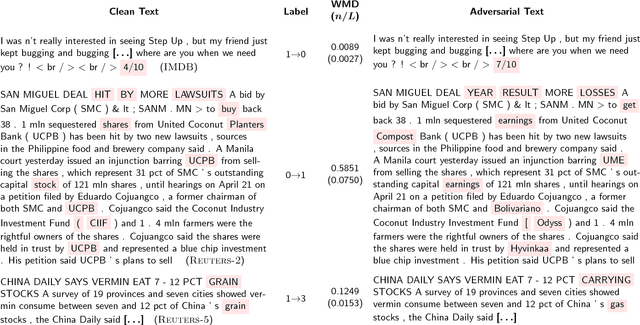
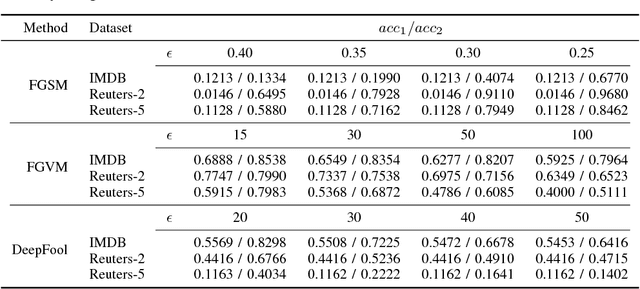
Abstract:Adversarial samples for images have been extensively studied in the literature. Among many of the attacking methods, gradient-based methods are both effective and easy to compute. In this work, we propose a framework to adapt the gradient attacking methods on images to text domain. The main difficulties for generating adversarial texts with gradient methods are i) the input space is discrete, which makes it difficult to accumulate small noise directly in the inputs, and ii) the measurement of the quality of the adversarial texts is difficult. We tackle the first problem by searching for adversarials in the embedding space and then reconstruct the adversarial texts via nearest neighbor search. For the latter problem, we employ the Word Mover's Distance (WMD) to quantify the quality of adversarial texts. Through extensive experiments on three datasets, IMDB movie reviews, Reuters-2 and Reuters-5 newswires, we show that our framework can leverage gradient attacking methods to generate very high-quality adversarial texts that are only a few words different from the original texts. There are many cases where we can change one word to alter the label of the whole piece of text. We successfully incorporate FGM and DeepFool into our framework. In addition, we empirically show that WMD is closely related to the quality of adversarial texts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge