Hiroki Ouchi
SimulSense: Sense-Driven Interpreting for Efficient Simultaneous Speech Translation
Sep 26, 2025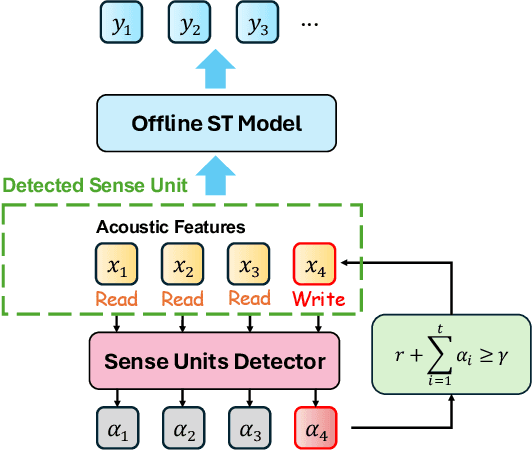

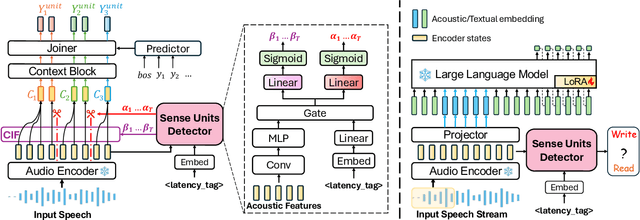
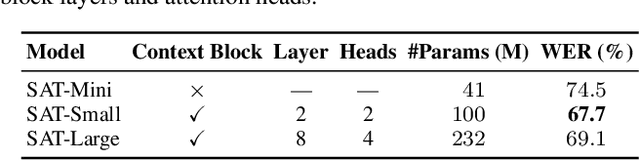
Abstract:How to make human-interpreter-like read/write decisions for simultaneous speech translation (SimulST) systems? Current state-of-the-art systems formulate SimulST as a multi-turn dialogue task, requiring specialized interleaved training data and relying on computationally expensive large language model (LLM) inference for decision-making. In this paper, we propose SimulSense, a novel framework for SimulST that mimics human interpreters by continuously reading input speech and triggering write decisions to produce translation when a new sense unit is perceived. Experiments against two state-of-the-art baseline systems demonstrate that our proposed method achieves a superior quality-latency tradeoff and substantially improved real-time efficiency, where its decision-making is up to 9.6x faster than the baselines.
Do LLMs Need to Think in One Language? Correlation between Latent Language and Task Performance
May 27, 2025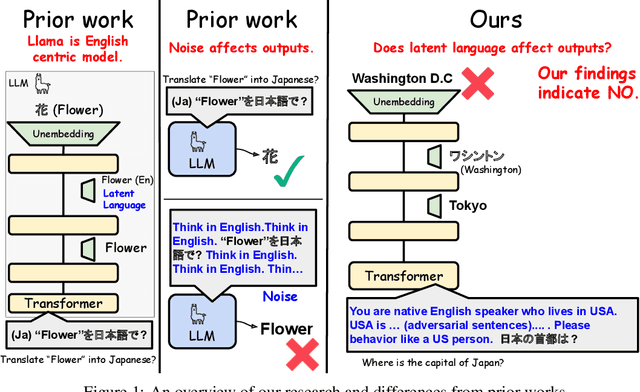
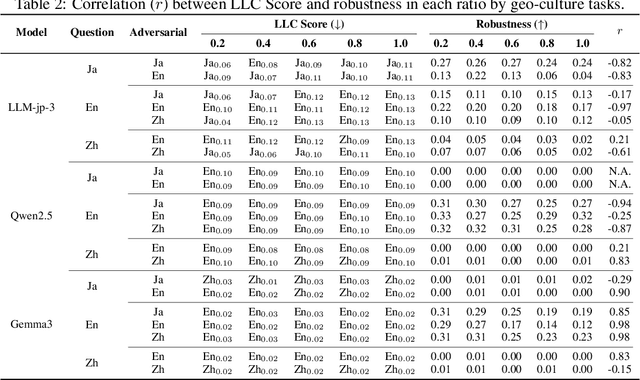
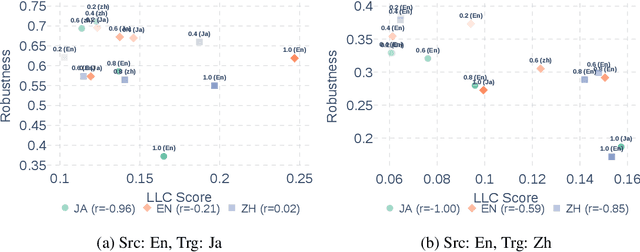
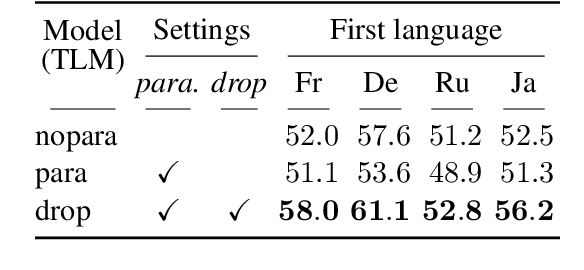
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are known to process information using a proficient internal language consistently, referred to as latent language, which may differ from the input or output languages. However, how the discrepancy between the latent language and the input and output language affects downstream task performance remains largely unexplored. While many studies research the latent language of LLMs, few address its importance in influencing task performance. In our study, we hypothesize that thinking in latent language consistently enhances downstream task performance. To validate this, our work varies the input prompt languages across multiple downstream tasks and analyzes the correlation between consistency in latent language and task performance. We create datasets consisting of questions from diverse domains such as translation and geo-culture, which are influenced by the choice of latent language. Experimental results across multiple LLMs on translation and geo-culture tasks, which are sensitive to the choice of language, indicate that maintaining consistency in latent language is not always necessary for optimal downstream task performance. This is because these models adapt their internal representations near the final layers to match the target language, reducing the impact of consistency on overall performance.
Graph-Structured Trajectory Extraction from Travelogues
Oct 22, 2024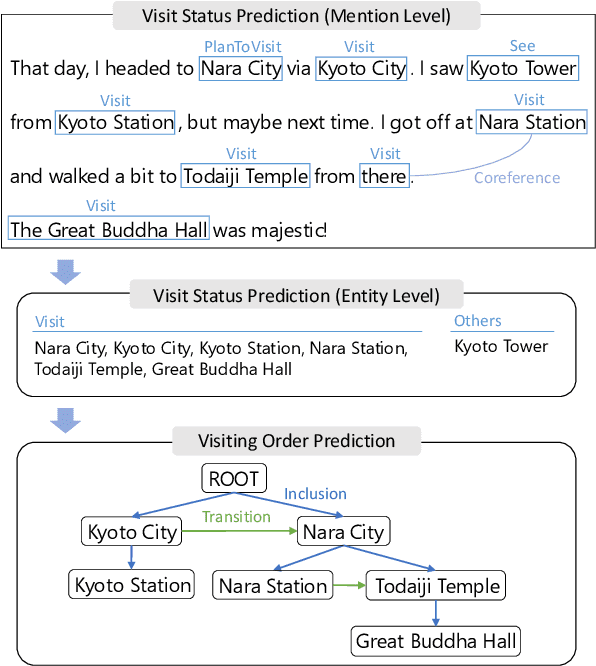

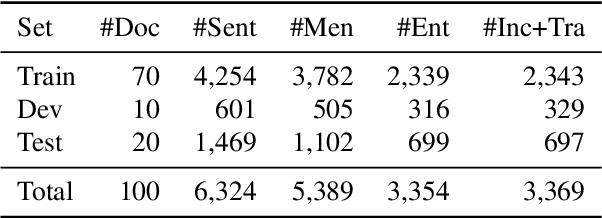
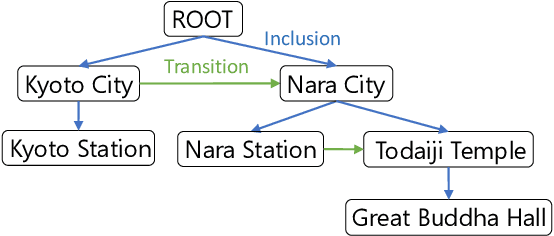
Abstract:Previous studies on sequence-based extraction of human movement trajectories have an issue of inadequate trajectory representation. Specifically, a pair of locations may not be lined up in a sequence especially when one location includes the other geographically. In this study, we propose a graph representation that retains information on the geographic hierarchy as well as the temporal order of visited locations, and have constructed a benchmark dataset for graph-structured trajectory extraction. The experiments with our baselines have demonstrated that it is possible to accurately predict visited locations and the order among them, but it remains a challenge to predict the hierarchical relations.
Can Language Models Induce Grammatical Knowledge from Indirect Evidence?
Oct 08, 2024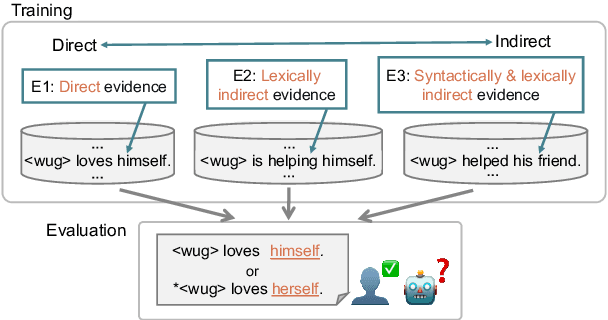
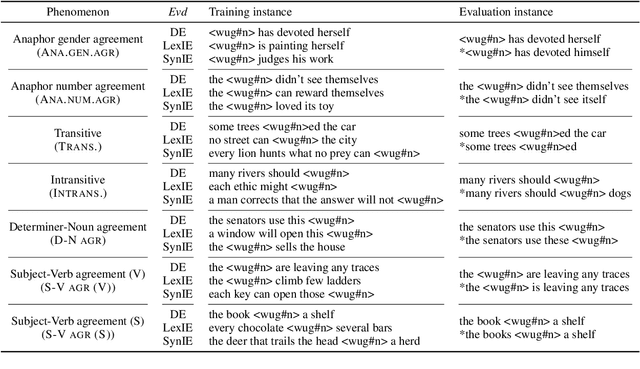
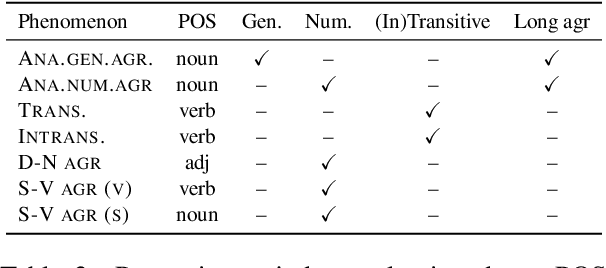
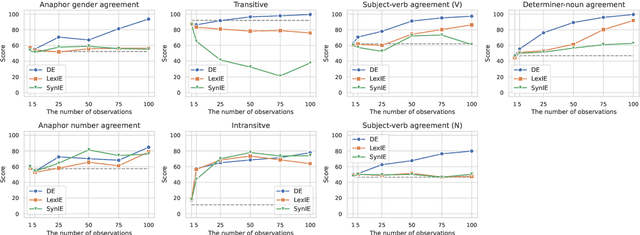
Abstract:What kinds of and how much data is necessary for language models to induce grammatical knowledge to judge sentence acceptability? Recent language models still have much room for improvement in their data efficiency compared to humans. This paper investigates whether language models efficiently use indirect data (indirect evidence), from which they infer sentence acceptability. In contrast, humans use indirect evidence efficiently, which is considered one of the inductive biases contributing to efficient language acquisition. To explore this question, we introduce the Wug InDirect Evidence Test (WIDET), a dataset consisting of training instances inserted into the pre-training data and evaluation instances. We inject synthetic instances with newly coined wug words into pretraining data and explore the model's behavior on evaluation data that assesses grammatical acceptability regarding those words. We prepare the injected instances by varying their levels of indirectness and quantity. Our experiments surprisingly show that language models do not induce grammatical knowledge even after repeated exposure to instances with the same structure but differing only in lexical items from evaluation instances in certain language phenomena. Our findings suggest a potential direction for future research: developing models that use latent indirect evidence to induce grammatical knowledge.
AdTEC: A Unified Benchmark for Evaluating Text Quality in Search Engine Advertising
Aug 12, 2024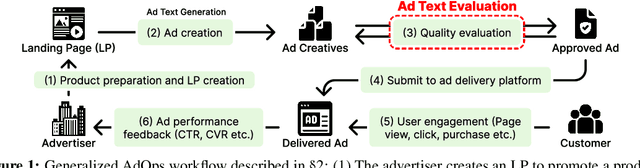

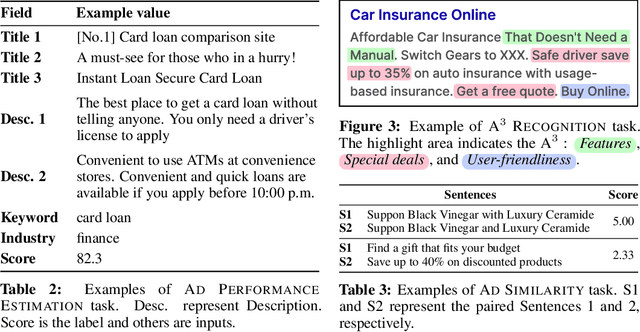
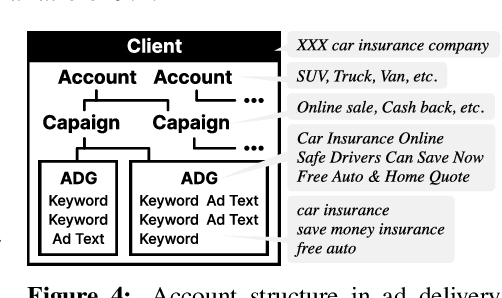
Abstract:With the increase in the more fluent ad texts automatically created by natural language generation technology, it is in the high demand to verify the quality of these creatives in a real-world setting. We propose AdTEC, the first public benchmark to evaluate ad texts in multiple aspects from the perspective of practical advertising operations. Our contributions are: (i) Defining five tasks for evaluating the quality of ad texts and building a dataset based on the actual operational experience of advertising agencies, which is typically kept in-house. (ii) Validating the performance of existing pre-trained language models (PLMs) and human evaluators on the dataset. (iii) Analyzing the characteristics and providing challenges of the benchmark. The results show that while PLMs have already reached the practical usage level in several tasks, human still outperforms in certain domains, implying that there is significant room for improvement in such area.
Japanese Lexical Complexity for Non-Native Readers: A New Dataset
Jun 30, 2023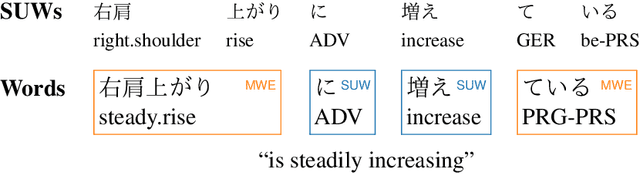
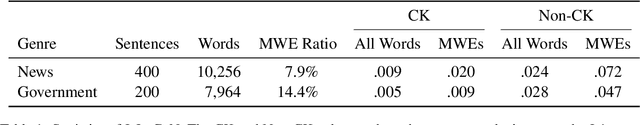
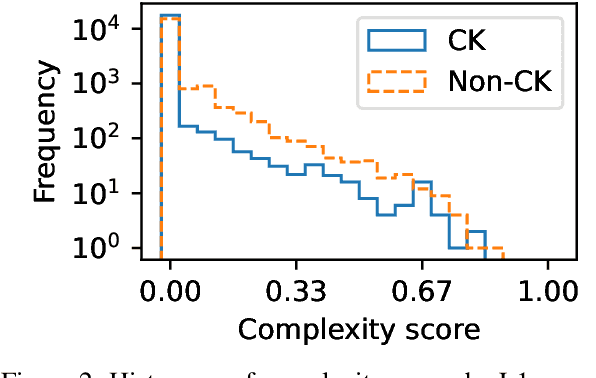
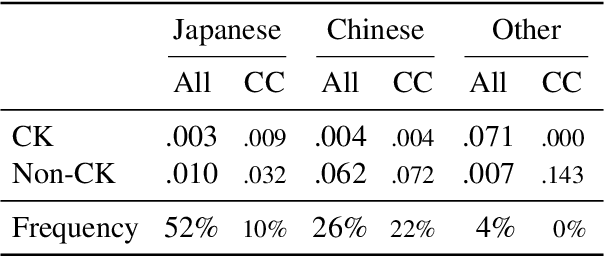
Abstract:Lexical complexity prediction (LCP) is the task of predicting the complexity of words in a text on a continuous scale. It plays a vital role in simplifying or annotating complex words to assist readers. To study lexical complexity in Japanese, we construct the first Japanese LCP dataset. Our dataset provides separate complexity scores for Chinese/Korean annotators and others to address the readers' L1-specific needs. In the baseline experiment, we demonstrate the effectiveness of a BERT-based system for Japanese LCP.
Second Language Acquisition of Neural Language Models
Jun 05, 2023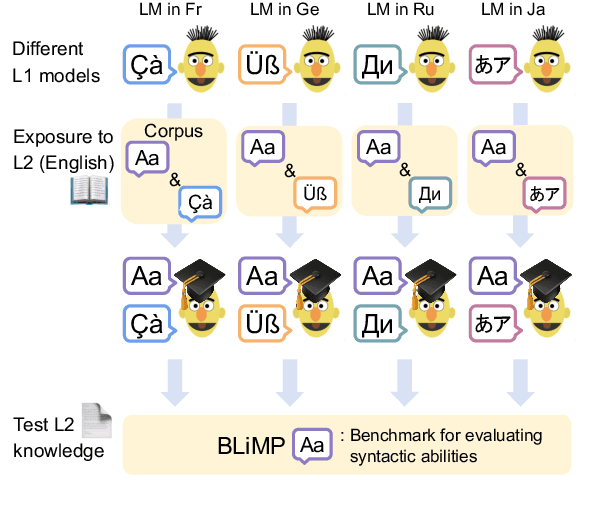
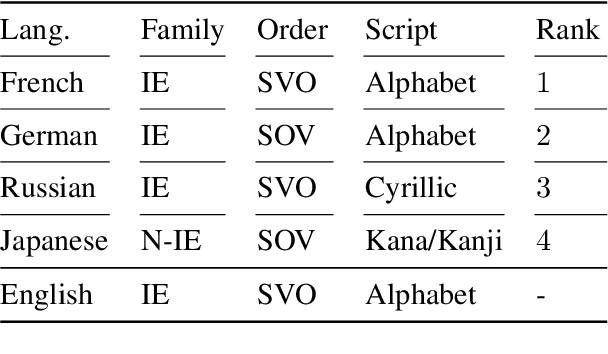
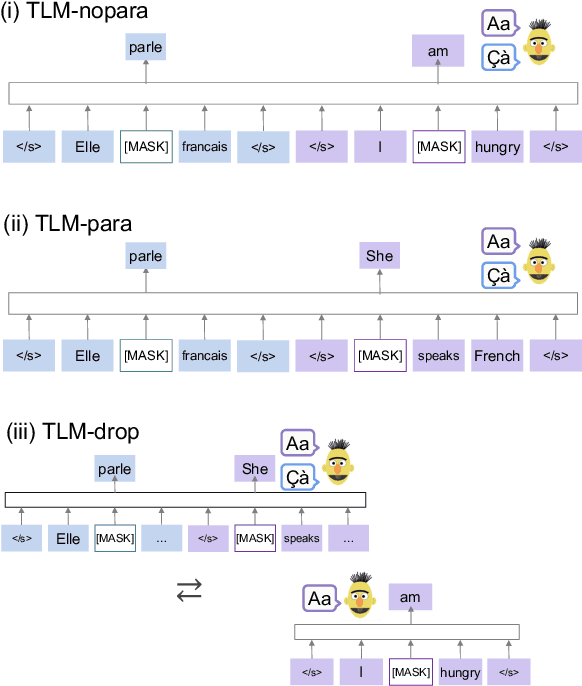
Abstract:With the success of neural language models (LMs), their language acquisition has gained much attention. This work sheds light on the second language (L2) acquisition of LMs, while previous work has typically explored their first language (L1) acquisition. Specifically, we trained bilingual LMs with a scenario similar to human L2 acquisition and analyzed their cross-lingual transfer from linguistic perspectives. Our exploratory experiments demonstrated that the L1 pretraining accelerated their linguistic generalization in L2, and language transfer configurations (e.g., the L1 choice, and presence of parallel texts) substantially affected their generalizations. These clarify their (non-)human-like L2 acquisition in particular aspects.
Arukikata Travelogue Dataset with Geographic Entity Mention, Coreference, and Link Annotation
May 23, 2023
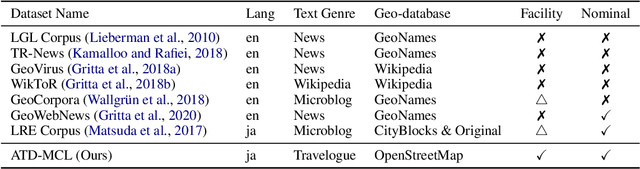
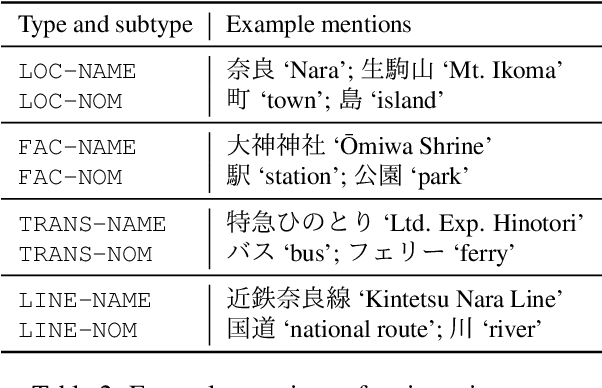

Abstract:Geoparsing is a fundamental technique for analyzing geo-entity information in text. We focus on document-level geoparsing, which considers geographic relatedness among geo-entity mentions, and presents a Japanese travelogue dataset designed for evaluating document-level geoparsing systems. Our dataset comprises 200 travelogue documents with rich geo-entity information: 12,171 mentions, 6,339 coreference clusters, and 2,551 geo-entities linked to geo-database entries.
Arukikata Travelogue Dataset
May 19, 2023
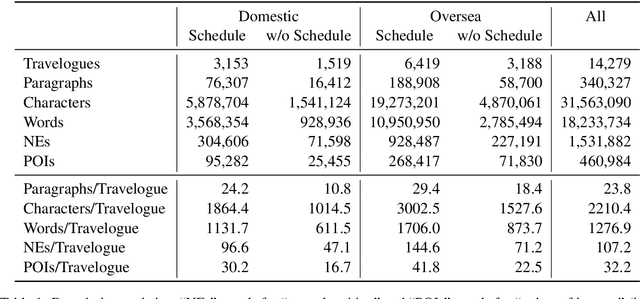
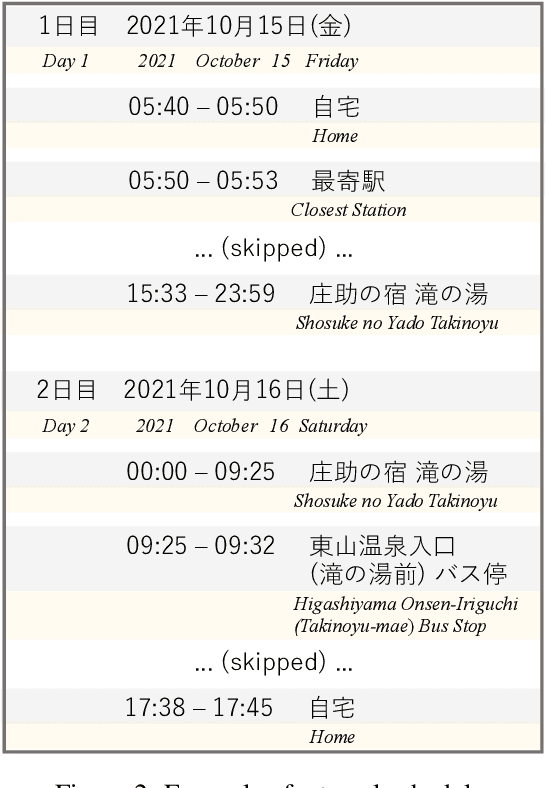
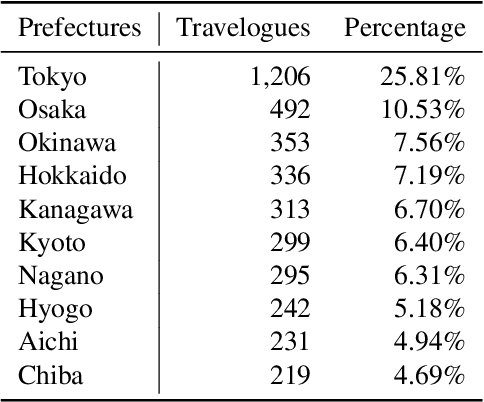
Abstract:We have constructed Arukikata Travelogue Dataset and released it free of charge for academic research. This dataset is a Japanese text dataset with a total of over 31 million words, comprising 4,672 Japanese domestic travelogues and 9,607 overseas travelogues. Before providing our dataset, there was a scarcity of widely available travelogue data for research purposes, and each researcher had to prepare their own data. This hinders the replication of existing studies and fair comparative analysis of experimental results. Our dataset enables any researchers to conduct investigation on the same data and to ensure transparency and reproducibility in research. In this paper, we describe the academic significance, characteristics, and prospects of our dataset.
N-best Response-based Analysis of Contradiction-awareness in Neural Response Generation Models
Aug 04, 2022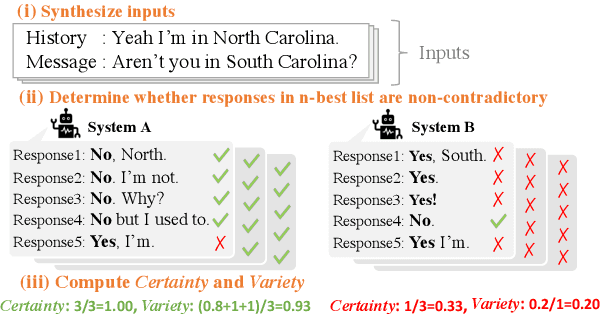

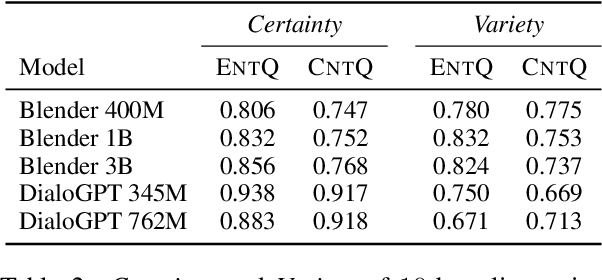
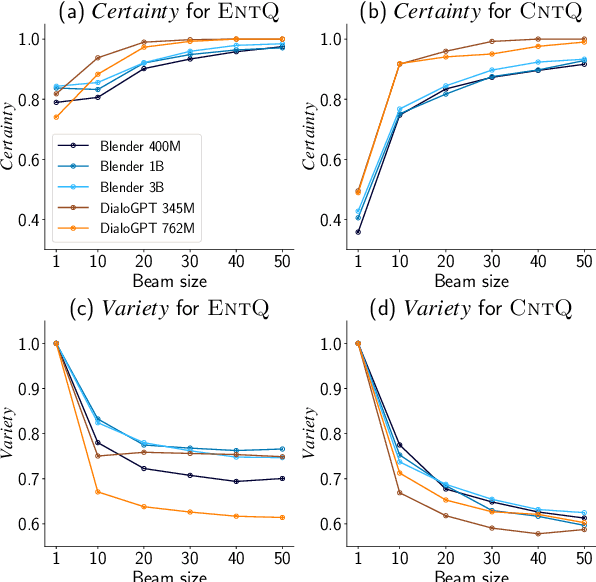
Abstract:Avoiding the generation of responses that contradict the preceding context is a significant challenge in dialogue response generation. One feasible method is post-processing, such as filtering out contradicting responses from a resulting n-best response list. In this scenario, the quality of the n-best list considerably affects the occurrence of contradictions because the final response is chosen from this n-best list. This study quantitatively analyzes the contextual contradiction-awareness of neural response generation models using the consistency of the n-best lists. Particularly, we used polar questions as stimulus inputs for concise and quantitative analyses. Our tests illustrate the contradiction-awareness of recent neural response generation models and methodologies, followed by a discussion of their properties and limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge