Masato Mita
Exploring the Effects of Alignment on Numerical Bias in Large Language Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:"LLM-as-a-judge," which utilizes large language models (LLMs) as evaluators, has proven effective in many evaluation tasks. However, evaluator LLMs exhibit numerical bias, a phenomenon where certain evaluation scores are generated disproportionately often, leading reduced evaluation performance. This study investigates the cause of this bias. Given that most evaluator LLMs are aligned through instruction tuning and preference tuning, and that prior research suggests alignment reduces output diversity, we hypothesize that numerical bias arises from alignment. To test this, we compare outputs from pre- and post-alignment LLMs, and observe that alignment indeed increases numerical bias. We also explore mitigation strategies for post-alignment LLMs, including temperature scaling, distribution calibration, and score range adjustment. Among these, score range adjustment is most effective in reducing bias and improving performance, though still heuristic. Our findings highlight the need for further work on optimal score range selection and more robust mitigation strategies.
Developmentally-plausible Working Memory Shapes a Critical Period for Language Acquisition
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Large language models exhibit general linguistic abilities but significantly differ from humans in their efficiency of language acquisition. This study proposes a method for integrating the developmental characteristics of working memory during the critical period, a stage when human language acquisition is particularly efficient, into language models. The proposed method introduces a mechanism that initially constrains working memory during the early stages of training and gradually relaxes this constraint in an exponential manner as learning progresses. Targeted syntactic evaluation shows that the proposed method outperforms conventional models without memory constraints or with static memory constraints. These findings not only provide new directions for designing data-efficient language models but also offer indirect evidence supporting the underlying mechanisms of the critical period hypothesis in human language acquisition.
LCTG Bench: LLM Controlled Text Generation Benchmark
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:The rise of large language models (LLMs) has led to more diverse and higher-quality machine-generated text. However, their high expressive power makes it difficult to control outputs based on specific business instructions. In response, benchmarks focusing on the controllability of LLMs have been developed, but several issues remain: (1) They primarily cover major languages like English and Chinese, neglecting low-resource languages like Japanese; (2) Current benchmarks employ task-specific evaluation metrics, lacking a unified framework for selecting models based on controllability across different use cases. To address these challenges, this research introduces LCTG Bench, the first Japanese benchmark for evaluating the controllability of LLMs. LCTG Bench provides a unified framework for assessing control performance, enabling users to select the most suitable model for their use cases based on controllability. By evaluating nine diverse Japanese-specific and multilingual LLMs like GPT-4, we highlight the current state and challenges of controllability in Japanese LLMs and reveal the significant gap between multilingual models and Japanese-specific models.
FaithCAMERA: Construction of a Faithful Dataset for Ad Text Generation
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:In ad text generation (ATG), desirable ad text is both faithful and informative. That is, it should be faithful to the input document, while at the same time containing important information that appeals to potential customers. The existing evaluation data, CAMERA (arXiv:2309.12030), is suitable for evaluating informativeness, as it consists of reference ad texts created by ad creators. However, these references often include information unfaithful to the input, which is a notable obstacle in promoting ATG research. In this study, we collaborate with in-house ad creators to refine the CAMERA references and develop an alternative ATG evaluation dataset called FaithCAMERA, in which the faithfulness of references is guaranteed. Using FaithCAMERA, we can evaluate how well existing methods for improving faithfulness can generate informative ad text while maintaining faithfulness. Our experiments show that removing training data that contains unfaithful entities improves the faithfulness and informativeness at the entity level, but decreases both at the sentence level. This result suggests that for future ATG research, it is essential not only to scale the training data but also to ensure their faithfulness. Our dataset will be publicly available.
AdTEC: A Unified Benchmark for Evaluating Text Quality in Search Engine Advertising
Aug 12, 2024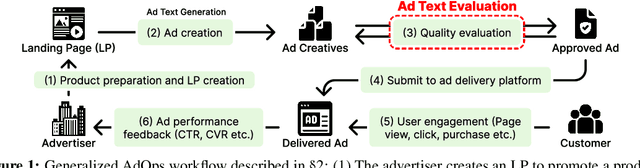

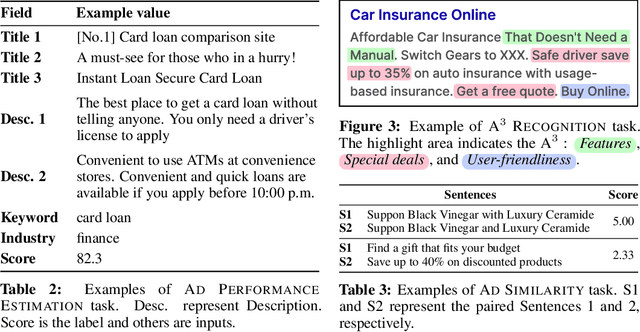
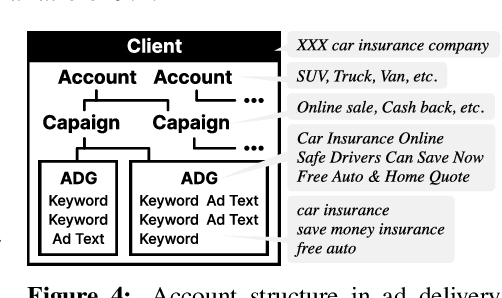
Abstract:With the increase in the more fluent ad texts automatically created by natural language generation technology, it is in the high demand to verify the quality of these creatives in a real-world setting. We propose AdTEC, the first public benchmark to evaluate ad texts in multiple aspects from the perspective of practical advertising operations. Our contributions are: (i) Defining five tasks for evaluating the quality of ad texts and building a dataset based on the actual operational experience of advertising agencies, which is typically kept in-house. (ii) Validating the performance of existing pre-trained language models (PLMs) and human evaluators on the dataset. (iii) Analyzing the characteristics and providing challenges of the benchmark. The results show that while PLMs have already reached the practical usage level in several tasks, human still outperforms in certain domains, implying that there is significant room for improvement in such area.
Not Eliminate but Aggregate: Post-Hoc Control over Mixture-of-Experts to Address Shortcut Shifts in Natural Language Understanding
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Recent models for natural language understanding are inclined to exploit simple patterns in datasets, commonly known as shortcuts. These shortcuts hinge on spurious correlations between labels and latent features existing in the training data. At inference time, shortcut-dependent models are likely to generate erroneous predictions under distribution shifts, particularly when some latent features are no longer correlated with the labels. To avoid this, previous studies have trained models to eliminate the reliance on shortcuts. In this study, we explore a different direction: pessimistically aggregating the predictions of a mixture-of-experts, assuming each expert captures relatively different latent features. The experimental results demonstrate that our post-hoc control over the experts significantly enhances the model's robustness to the distribution shift in shortcuts. Besides, we show that our approach has some practical advantages. We also analyze our model and provide results to support the assumption.
Large Language Models Are State-of-the-Art Evaluator for Grammatical Error Correction
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been reported to outperform existing automatic evaluation metrics in some tasks, such as text summarization and machine translation. However, there has been a lack of research on LLMs as evaluators in grammatical error correction (GEC). In this study, we investigate the performance of LLMs in GEC evaluation by employing prompts designed to incorporate various evaluation criteria inspired by previous research. Our extensive experimental results demonstrate that GPT-4 achieved Kendall's rank correlation of 0.662 with human judgments, surpassing all existing methods. Furthermore, in recent GEC evaluations, we have underscored the significance of the LLMs scale and particularly emphasized the importance of fluency among evaluation criteria.
Revisiting Meta-evaluation for Grammatical Error Correction
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Metrics are the foundation for automatic evaluation in grammatical error correction (GEC), with their evaluation of the metrics (meta-evaluation) relying on their correlation with human judgments. However, conventional meta-evaluations in English GEC encounter several challenges including biases caused by inconsistencies in evaluation granularity, and an outdated setup using classical systems. These problems can lead to misinterpretation of metrics and potentially hinder the applicability of GEC techniques. To address these issues, this paper proposes SEEDA, a new dataset for GEC meta-evaluation. SEEDA consists of corrections with human ratings along two different granularities: edit-based and sentence-based, covering 12 state-of-the-art systems including large language models (LLMs), and two human corrections with different focuses. The results of improved correlations by aligning the granularity in the sentence-level meta-evaluation, suggest that edit-based metrics may have been underestimated in existing studies. Furthermore, correlations of most metrics decrease when changing from classical to neural systems, indicating that traditional metrics are relatively poor at evaluating fluently corrected sentences with many edits.
CAMERA: A Multimodal Dataset and Benchmark for Ad Text Generation
Sep 21, 2023



Abstract:In response to the limitations of manual online ad production, significant research has been conducted in the field of automatic ad text generation (ATG). However, comparing different methods has been challenging because of the lack of benchmarks encompassing the entire field and the absence of well-defined problem sets with clear model inputs and outputs. To address these challenges, this paper aims to advance the field of ATG by introducing a redesigned task and constructing a benchmark. Specifically, we defined ATG as a cross-application task encompassing various aspects of the Internet advertising. As part of our contribution, we propose a first benchmark dataset, CA Multimodal Evaluation for Ad Text GeneRAtion (CAMERA), carefully designed for ATG to be able to leverage multi-modal information and conduct an industry-wise evaluation. Furthermore, we demonstrate the usefulness of our proposed benchmark through evaluation experiments using multiple baseline models, which vary in terms of the type of pre-trained language model used and the incorporation of multi-modal information. We also discuss the current state of the task and the future challenges.
Japanese Lexical Complexity for Non-Native Readers: A New Dataset
Jun 30, 2023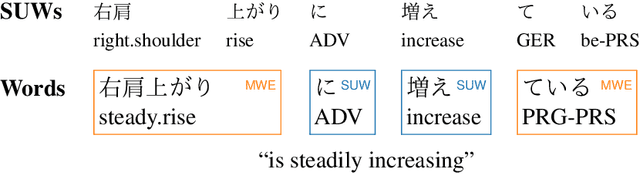
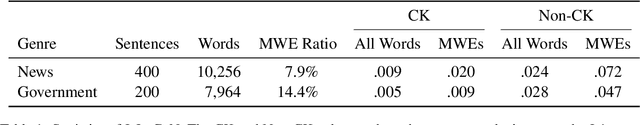
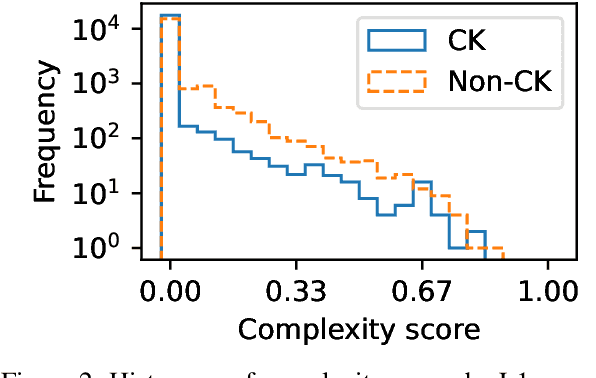
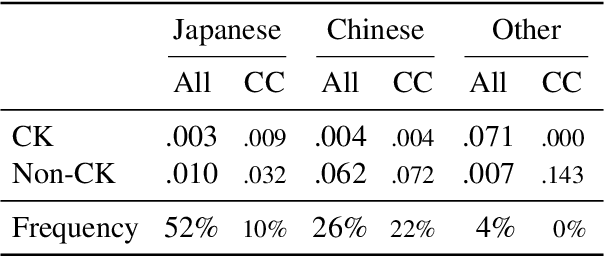
Abstract:Lexical complexity prediction (LCP) is the task of predicting the complexity of words in a text on a continuous scale. It plays a vital role in simplifying or annotating complex words to assist readers. To study lexical complexity in Japanese, we construct the first Japanese LCP dataset. Our dataset provides separate complexity scores for Chinese/Korean annotators and others to address the readers' L1-specific needs. In the baseline experiment, we demonstrate the effectiveness of a BERT-based system for Japanese LCP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge