Masato Hagiwara
Crossing the Species Divide: Transfer Learning from Speech to Animal Sounds
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Self-supervised speech models have demonstrated impressive performance in speech processing, but their effectiveness on non-speech data remains underexplored. We study the transfer learning capabilities of such models on bioacoustic detection and classification tasks. We show that models such as HuBERT, WavLM, and XEUS can generate rich latent representations of animal sounds across taxa. We analyze the models properties with linear probing on time-averaged representations. We then extend the approach to account for the effect of time-wise information with other downstream architectures. Finally, we study the implication of frequency range and noise on performance. Notably, our results are competitive with fine-tuned bioacoustic pre-trained models and show the impact of noise-robust pre-training setups. These findings highlight the potential of speech-based self-supervised learning as an efficient framework for advancing bioacoustic research.
Robust detection of overlapping bioacoustic sound events
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:We propose a method for accurately detecting bioacoustic sound events that is robust to overlapping events, a common issue in domains such as ethology, ecology and conservation. While standard methods employ a frame-based, multi-label approach, we introduce an onset-based detection method which we name Voxaboxen. It takes inspiration from object detection methods in computer vision, but simultaneously takes advantage of recent advances in self-supervised audio encoders. For each time window, Voxaboxen predicts whether it contains the start of a vocalization and how long the vocalization is. It also does the same in reverse, predicting whether each window contains the end of a vocalization, and how long ago it started. The two resulting sets of bounding boxes are then fused using a graph-matching algorithm. We also release a new dataset designed to measure performance on detecting overlapping vocalizations. This consists of recordings of zebra finches annotated with temporally-strong labels and showing frequent overlaps. We test Voxaboxen on seven existing data sets and on our new data set. We compare Voxaboxen to natural baselines and existing sound event detection methods and demonstrate SotA results. Further experiments show that improvements are robust to frequent vocalization overlap.
NatureLM-audio: an Audio-Language Foundation Model for Bioacoustics
Nov 11, 2024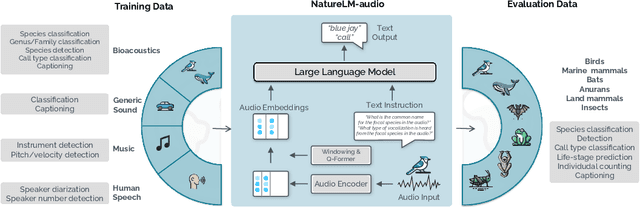
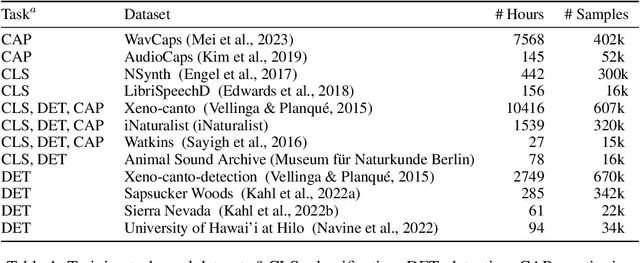

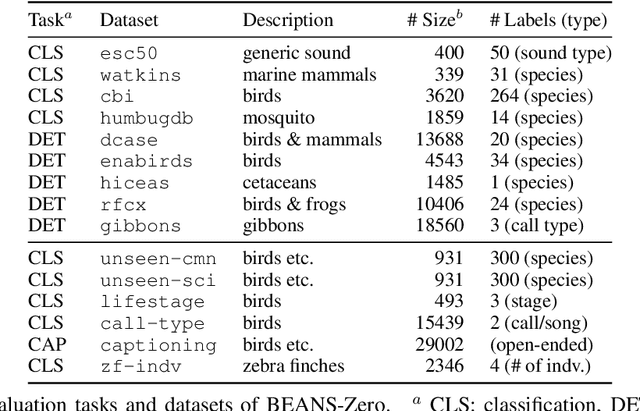
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) prompted with text and audio represent the state of the art in various auditory tasks, including speech, music, and general audio, showing emergent abilities on unseen tasks. However, these capabilities have yet to be fully demonstrated in bioacoustics tasks, such as detecting animal vocalizations in large recordings, classifying rare and endangered species, and labeling context and behavior - tasks that are crucial for conservation, biodiversity monitoring, and the study of animal behavior. In this work, we present NatureLM-audio, the first audio-language foundation model specifically designed for bioacoustics. Our carefully curated training dataset comprises text-audio pairs spanning a diverse range of bioacoustics, speech, and music data, designed to address the challenges posed by limited annotated datasets in the field. We demonstrate successful transfer of learned representations from music and speech to bioacoustics, and our model shows promising generalization to unseen taxa and tasks. Importantly, we test NatureLM-audio on a novel benchmark (BEANS-Zero) and it sets the new state of the art (SotA) on several bioacoustics tasks, including zero-shot classification of unseen species. To advance bioacoustics research, we also open-source the code for generating training and benchmark data, as well as for training the model.
Biodenoising: animal vocalization denoising without access to clean data
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:Animal vocalization denoising is a task similar to human speech enhancement, a well-studied field of research. In contrast to the latter, it is applied to a higher diversity of sound production mechanisms and recording environments, and this higher diversity is a challenge for existing models. Adding to the challenge and in contrast to speech, we lack large and diverse datasets comprising clean vocalizations. As a solution we use as training data pseudo-clean targets, i.e. pre-denoised vocalizations, and segments of background noise without a vocalization. We propose a train set derived from bioacoustics datasets and repositories representing diverse species, acoustic environments, geographic regions. Additionally, we introduce a non-overlapping benchmark set comprising clean vocalizations from different taxa and noise samples. We show that that denoising models (demucs, CleanUNet) trained on pseudo-clean targets obtained with speech enhancement models achieve competitive results on the benchmarking set. We publish data, code, libraries, and demos https://mariusmiron.com/research/biodenoising.
Project MOSLA: Recording Every Moment of Second Language Acquisition
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:Second language acquisition (SLA) is a complex and dynamic process. Many SLA studies that have attempted to record and analyze this process have typically focused on a single modality (e.g., textual output of learners), covered only a short period of time, and/or lacked control (e.g., failed to capture every aspect of the learning process). In Project MOSLA (Moments of Second Language Acquisition), we have created a longitudinal, multimodal, multilingual, and controlled dataset by inviting participants to learn one of three target languages (Arabic, Spanish, and Chinese) from scratch over a span of two years, exclusively through online instruction, and recording every lesson using Zoom. The dataset is semi-automatically annotated with speaker/language IDs and transcripts by both human annotators and fine-tuned state-of-the-art speech models. Our experiments reveal linguistic insights into learners' proficiency development over time, as well as the potential for automatically detecting the areas of focus on the screen purely from the unannotated multimodal data. Our dataset is freely available for research purposes and can serve as a valuable resource for a wide range of applications, including but not limited to SLA, proficiency assessment, language and speech processing, pedagogy, and multimodal learning analytics.
ISPA: Inter-Species Phonetic Alphabet for Transcribing Animal Sounds
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Traditionally, bioacoustics has relied on spectrograms and continuous, per-frame audio representations for the analysis of animal sounds, also serving as input to machine learning models. Meanwhile, the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) system has provided an interpretable, language-independent method for transcribing human speech sounds. In this paper, we introduce ISPA (Inter-Species Phonetic Alphabet), a precise, concise, and interpretable system designed for transcribing animal sounds into text. We compare acoustics-based and feature-based methods for transcribing and classifying animal sounds, demonstrating their comparable performance with baseline methods utilizing continuous, dense audio representations. By representing animal sounds with text, we effectively treat them as a "foreign language," and we show that established human language ML paradigms and models, such as language models, can be successfully applied to improve performance.
AVES: Animal Vocalization Encoder based on Self-Supervision
Oct 26, 2022



Abstract:The lack of annotated training data in bioacoustics hinders the use of large-scale neural network models trained in a supervised way. In order to leverage a large amount of unannotated audio data, we propose AVES (Animal Vocalization Encoder based on Self-Supervision), a self-supervised, transformer-based audio representation model for encoding animal vocalizations. We pretrain AVES on a diverse set of unannotated audio datasets and fine-tune them for downstream bioacoustics tasks. Comprehensive experiments with a suite of classification and detection tasks have shown that AVES outperforms all the strong baselines and even the supervised "topline" models trained on annotated audio classification datasets. The results also suggest that curating a small training subset related to downstream tasks is an efficient way to train high-quality audio representation models. We open-source our models at \url{https://github.com/earthspecies/aves}.
Modeling Animal Vocalizations through Synthesizers
Oct 19, 2022


Abstract:Modeling real-world sound is a fundamental problem in the creative use of machine learning and many other fields, including human speech processing and bioacoustics. Transformer-based generative models and some prior work (e.g., DDSP) are known to produce realistic sound, although they have limited control and are hard to interpret. As an alternative, we aim to use modular synthesizers, i.e., compositional, parametric electronic musical instruments, for modeling non-music sounds. However, inferring synthesizer parameters given a target sound, i.e., the parameter inference task, is not trivial for general sounds, and past research has typically focused on musical sound. In this work, we optimize a differentiable synthesizer from TorchSynth in order to model, emulate, and creatively generate animal vocalizations. We compare an array of optimization methods, from gradient-based search to genetic algorithms, for inferring its parameters, and then demonstrate how one can control and interpret the parameters for modeling non-music sounds.
Towards Automated Document Revision: Grammatical Error Correction, Fluency Edits, and Beyond
May 23, 2022

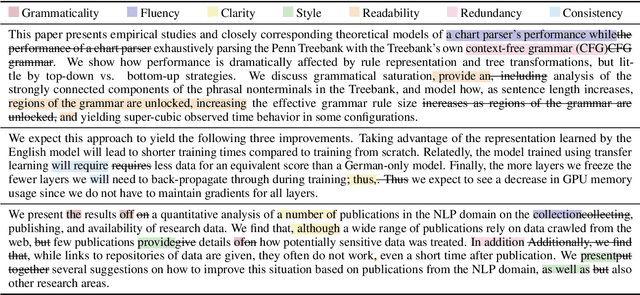
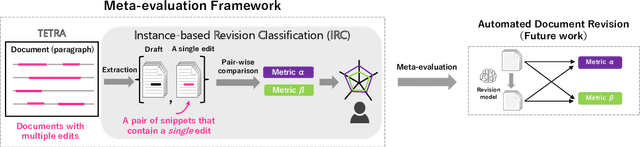
Abstract:Natural language processing technology has rapidly improved automated grammatical error correction tasks, and the community begins to explore document-level revision as one of the next challenges. To go beyond sentence-level automated grammatical error correction to NLP-based document-level revision assistant, there are two major obstacles: (1) there are few public corpora with document-level revisions being annotated by professional editors, and (2) it is not feasible to elicit all possible references and evaluate the quality of revision with such references because there are infinite possibilities of revision. This paper tackles these challenges. First, we introduce a new document-revision corpus, TETRA, where professional editors revised academic papers sampled from the ACL anthology which contain few trivial grammatical errors that enable us to focus more on document- and paragraph-level edits such as coherence and consistency. Second, we explore reference-less and interpretable methods for meta-evaluation that can detect quality improvements by document revision. We show the uniqueness of TETRA compared with existing document revision corpora and demonstrate that a fine-tuned pre-trained language model can discriminate the quality of documents after revision even when the difference is subtle. This promising result will encourage the community to further explore automated document revision models and metrics in future.
Semi-Supervised Joint Estimation of Word and Document Readability
Apr 27, 2021



Abstract:Readability or difficulty estimation of words and documents has been investigated independently in the literature, often assuming the existence of extensive annotated resources for the other. Motivated by our analysis showing that there is a recursive relationship between word and document difficulty, we propose to jointly estimate word and document difficulty through a graph convolutional network (GCN) in a semi-supervised fashion. Our experimental results reveal that the GCN-based method can achieve higher accuracy than strong baselines, and stays robust even with a smaller amount of labeled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge