Mamoru Komachi
Exploring the Effects of Alignment on Numerical Bias in Large Language Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:"LLM-as-a-judge," which utilizes large language models (LLMs) as evaluators, has proven effective in many evaluation tasks. However, evaluator LLMs exhibit numerical bias, a phenomenon where certain evaluation scores are generated disproportionately often, leading reduced evaluation performance. This study investigates the cause of this bias. Given that most evaluator LLMs are aligned through instruction tuning and preference tuning, and that prior research suggests alignment reduces output diversity, we hypothesize that numerical bias arises from alignment. To test this, we compare outputs from pre- and post-alignment LLMs, and observe that alignment indeed increases numerical bias. We also explore mitigation strategies for post-alignment LLMs, including temperature scaling, distribution calibration, and score range adjustment. Among these, score range adjustment is most effective in reducing bias and improving performance, though still heuristic. Our findings highlight the need for further work on optimal score range selection and more robust mitigation strategies.
Tracking Temporal Dynamics of Vector Sets with Gaussian Process
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Understanding the temporal evolution of sets of vectors is a fundamental challenge across various domains, including ecology, crime analysis, and linguistics. For instance, ecosystem structures evolve due to interactions among plants, herbivores, and carnivores; the spatial distribution of crimes shifts in response to societal changes; and word embedding vectors reflect cultural and semantic trends over time. However, analyzing such time-varying sets of vectors is challenging due to their complicated structures, which also evolve over time. In this work, we propose a novel method for modeling the distribution underlying each set of vectors using infinite-dimensional Gaussian processes. By approximating the latent function in the Gaussian process with Random Fourier Features, we obtain compact and comparable vector representations over time. This enables us to track and visualize temporal transitions of vector sets in a low-dimensional space. We apply our method to both sociological data (crime distributions) and linguistic data (word embeddings), demonstrating its effectiveness in capturing temporal dynamics. Our results show that the proposed approach provides interpretable and robust representations, offering a powerful framework for analyzing structural changes in temporally indexed vector sets across diverse domains.
Assessing the Capabilities of LLMs in Humor:A Multi-dimensional Analysis of Oogiri Generation and Evaluation
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Computational humor is a frontier for creating advanced and engaging natural language processing (NLP) applications, such as sophisticated dialogue systems. While previous studies have benchmarked the humor capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), they have often relied on single-dimensional evaluations, such as judging whether something is simply ``funny.'' This paper argues that a multifaceted understanding of humor is necessary and addresses this gap by systematically evaluating LLMs through the lens of Oogiri, a form of Japanese improvisational comedy games. To achieve this, we expanded upon existing Oogiri datasets with data from new sources and then augmented the collection with Oogiri responses generated by LLMs. We then manually annotated this expanded collection with 5-point absolute ratings across six dimensions: Novelty, Clarity, Relevance, Intelligence, Empathy, and Overall Funniness. Using this dataset, we assessed the capabilities of state-of-the-art LLMs on two core tasks: their ability to generate creative Oogiri responses and their ability to evaluate the funniness of responses using a six-dimensional evaluation. Our results show that while LLMs can generate responses at a level between low- and mid-tier human performance, they exhibit a notable lack of Empathy. This deficit in Empathy helps explain their failure to replicate human humor assessment. Correlation analyses of human and model evaluation data further reveal a fundamental divergence in evaluation criteria: LLMs prioritize Novelty, whereas humans prioritize Empathy. We release our annotated corpus to the community to pave the way for the development of more emotionally intelligent and sophisticated conversational agents.
Analyzing Continuous Semantic Shifts with Diachronic Word Similarity Matrices
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:The meanings and relationships of words shift over time. This phenomenon is referred to as semantic shift.Research focused on understanding how semantic shifts occur over multiple time periods is essential for gaining a detailed understanding of semantic shifts.However, detecting change points only between adjacent time periods is insufficient for analyzing detailed semantic shifts, and using BERT-based methods to examine word sense proportions incurs a high computational cost.To address those issues, we propose a simple yet intuitive framework for how semantic shifts occur over multiple time periods by leveraging a similarity matrix between the embeddings of the same word through time.We compute a diachronic word similarity matrix using fast and lightweight word embeddings across arbitrary time periods, making it deeper to analyze continuous semantic shifts.Additionally, by clustering the similarity matrices for different words, we can categorize words that exhibit similar behavior of semantic shift in an unsupervised manner.
Pruning Multilingual Large Language Models for Multilingual Inference
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:Multilingual large language models (MLLMs), trained on multilingual balanced data, demonstrate better zero-shot learning performance in non-English languages compared to large language models trained on English-dominant data. However, the disparity in performance between English and non-English languages remains a challenge yet to be fully addressed. A distinctive characteristic of MLLMs is their high-quality translation capabilities, indicating an acquired proficiency in aligning between languages. This study explores how to enhance the zero-shot performance of MLLMs in non-English languages by leveraging their alignment capability between English and non-English languages. To achieve this, we first analyze the behavior of MLLMs when performing translation and reveal that there are large magnitude features that play a critical role in the translation process. Inspired by these findings, we retain the weights associated with operations involving the large magnitude features and prune other weights to force MLLMs to rely on these features for tasks beyond translation. We empirically demonstrate that this pruning strategy can enhance the MLLMs' performance in non-English language.
Large Language Models Are State-of-the-Art Evaluator for Grammatical Error Correction
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been reported to outperform existing automatic evaluation metrics in some tasks, such as text summarization and machine translation. However, there has been a lack of research on LLMs as evaluators in grammatical error correction (GEC). In this study, we investigate the performance of LLMs in GEC evaluation by employing prompts designed to incorporate various evaluation criteria inspired by previous research. Our extensive experimental results demonstrate that GPT-4 achieved Kendall's rank correlation of 0.662 with human judgments, surpassing all existing methods. Furthermore, in recent GEC evaluations, we have underscored the significance of the LLMs scale and particularly emphasized the importance of fluency among evaluation criteria.
Revisiting Meta-evaluation for Grammatical Error Correction
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Metrics are the foundation for automatic evaluation in grammatical error correction (GEC), with their evaluation of the metrics (meta-evaluation) relying on their correlation with human judgments. However, conventional meta-evaluations in English GEC encounter several challenges including biases caused by inconsistencies in evaluation granularity, and an outdated setup using classical systems. These problems can lead to misinterpretation of metrics and potentially hinder the applicability of GEC techniques. To address these issues, this paper proposes SEEDA, a new dataset for GEC meta-evaluation. SEEDA consists of corrections with human ratings along two different granularities: edit-based and sentence-based, covering 12 state-of-the-art systems including large language models (LLMs), and two human corrections with different focuses. The results of improved correlations by aligning the granularity in the sentence-level meta-evaluation, suggest that edit-based metrics may have been underestimated in existing studies. Furthermore, correlations of most metrics decrease when changing from classical to neural systems, indicating that traditional metrics are relatively poor at evaluating fluently corrected sentences with many edits.
WikiSQE: A Large-Scale Dataset for Sentence Quality Estimation in Wikipedia
May 10, 2023



Abstract:Wikipedia can be edited by anyone and thus contains various quality sentences. Therefore, Wikipedia includes some poor-quality edits, which are often marked up by other editors. While editors' reviews enhance the credibility of Wikipedia, it is hard to check all edited text. Assisting in this process is very important, but a large and comprehensive dataset for studying it does not currently exist. Here, we propose WikiSQE, the first large-scale dataset for sentence quality estimation in Wikipedia. Each sentence is extracted from the entire revision history of Wikipedia, and the target quality labels were carefully investigated and selected. WikiSQE has about 3.4 M sentences with 153 quality labels. In the experiment with automatic classification using competitive machine learning models, sentences that had problems with citation, syntax/semantics, or propositions were found to be more difficult to detect. In addition, we conducted automated essay scoring experiments to evaluate the generalizability of the dataset. We show that the models trained on WikiSQE perform better than the vanilla model, indicating its potential usefulness in other domains. WikiSQE is expected to be a valuable resource for other tasks in NLP.
Is In-hospital Meta-information Useful for Abstractive Discharge Summary Generation?
Mar 10, 2023



Abstract:During the patient's hospitalization, the physician must record daily observations of the patient and summarize them into a brief document called "discharge summary" when the patient is discharged. Automated generation of discharge summary can greatly relieve the physicians' burden, and has been addressed recently in the research community. Most previous studies of discharge summary generation using the sequence-to-sequence architecture focus on only inpatient notes for input. However, electric health records (EHR) also have rich structured metadata (e.g., hospital, physician, disease, length of stay, etc.) that might be useful. This paper investigates the effectiveness of medical meta-information for summarization tasks. We obtain four types of meta-information from the EHR systems and encode each meta-information into a sequence-to-sequence model. Using Japanese EHRs, meta-information encoded models increased ROUGE-1 by up to 4.45 points and BERTScore by 3.77 points over the vanilla Longformer. Also, we found that the encoded meta-information improves the precisions of its related terms in the outputs. Our results showed the benefit of the use of medical meta-information.
Exploring Optimal Granularity for Extractive Summarization of Unstructured Health Records: Analysis of the Largest Multi-Institutional Archive of Health Records in Japan
Sep 20, 2022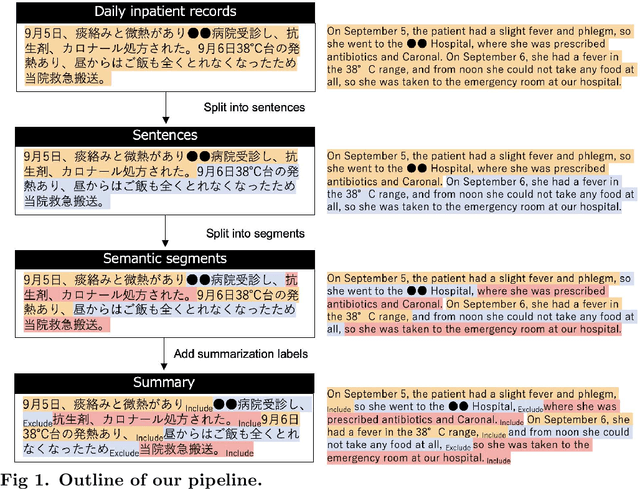
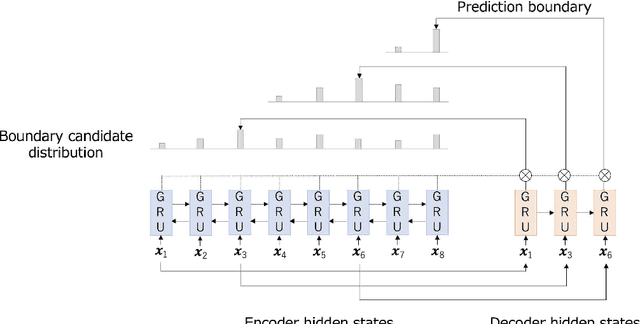
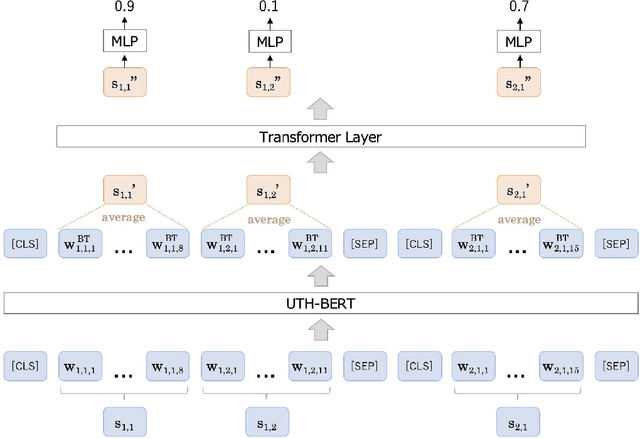
Abstract:Automated summarization of clinical texts can reduce the burden of medical professionals. "Discharge summaries" are one promising application of the summarization, because they can be generated from daily inpatient records. Our preliminary experiment suggests that 20-31% of the descriptions in discharge summaries overlap with the content of the inpatient records. However, it remains unclear how the summaries should be generated from the unstructured source. To decompose the physician's summarization process, this study aimed to identify the optimal granularity in summarization. We first defined three types of summarization units with different granularities to compare the performance of the discharge summary generation: whole sentences, clinical segments, and clauses. We defined clinical segments in this study, aiming to express the smallest medically meaningful concepts. To obtain the clinical segments, it was necessary to automatically split the texts in the first stage of the pipeline. Accordingly, we compared rule-based methods and a machine learning method, and the latter outperformed the formers with an F1 score of 0.846 in the splitting task. Next, we experimentally measured the accuracy of extractive summarization using the three types of units, based on the ROUGE-1 metric, on a multi-institutional national archive of health records in Japan. The measured accuracies of extractive summarization using whole sentences, clinical segments, and clauses were 31.91, 36.15, and 25.18, respectively. We found that the clinical segments yielded higher accuracy than sentences and clauses. This result indicates that summarization of inpatient records demands finer granularity than sentence-oriented processing. Although we used only Japanese health records, it can be interpreted as follows: physicians extract "concepts of medical significance" from patient records and recombine them ...
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge