Ryoko Tokuhisa
Accuracy-Preserving Calibration via Statistical Modeling on Probability Simplex
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:Classification models based on deep neural networks (DNNs) must be calibrated to measure the reliability of predictions. Some recent calibration methods have employed a probabilistic model on the probability simplex. However, these calibration methods cannot preserve the accuracy of pre-trained models, even those with a high classification accuracy. We propose an accuracy-preserving calibration method using the Concrete distribution as the probabilistic model on the probability simplex. We theoretically prove that a DNN model trained on cross-entropy loss has optimality as the parameter of the Concrete distribution. We also propose an efficient method that synthetically generates samples for training probabilistic models on the probability simplex. We demonstrate that the proposed method can outperform previous methods in accuracy-preserving calibration tasks using benchmarks.
Chat Translation Error Detection for Assisting Cross-lingual Communications
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we describe the development of a communication support system that detects erroneous translations to facilitate crosslingual communications due to the limitations of current machine chat translation methods. We trained an error detector as the baseline of the system and constructed a new Japanese-English bilingual chat corpus, BPersona-chat, which comprises multiturn colloquial chats augmented with crowdsourced quality ratings. The error detector can serve as an encouraging foundation for more advanced erroneous translation detection systems.
StyleDiff: Attribute Comparison Between Unlabeled Datasets in Latent Disentangled Space
Mar 09, 2023Abstract:One major challenge in machine learning applications is coping with mismatches between the datasets used in the development and those obtained in real-world applications. These mismatches may lead to inaccurate predictions and errors, resulting in poor product quality and unreliable systems. In this study, we propose StyleDiff to inform developers of the differences between the two datasets for the steady development of machine learning systems. Using disentangled image spaces obtained from recently proposed generative models, StyleDiff compares the two datasets by focusing on attributes in the images and provides an easy-to-understand analysis of the differences between the datasets. The proposed StyleDiff performs in $O (d N\log N)$, where $N$ is the size of the datasets and $d$ is the number of attributes, enabling the application to large datasets. We demonstrate that StyleDiff accurately detects differences between datasets and presents them in an understandable format using, for example, driving scenes datasets.
Bipartite-play Dialogue Collection for Practical Automatic Evaluation of Dialogue Systems
Nov 19, 2022Abstract:Automation of dialogue system evaluation is a driving force for the efficient development of dialogue systems. This paper introduces the bipartite-play method, a dialogue collection method for automating dialogue system evaluation. It addresses the limitations of existing dialogue collection methods: (i) inability to compare with systems that are not publicly available, and (ii) vulnerability to cheating by intentionally selecting systems to be compared. Experimental results show that the automatic evaluation using the bipartite-play method mitigates these two drawbacks and correlates as strongly with human subjectivity as existing methods.
Target-Guided Open-Domain Conversation Planning
Sep 20, 2022



Abstract:Prior studies addressing target-oriented conversational tasks lack a crucial notion that has been intensively studied in the context of goal-oriented artificial intelligence agents, namely, planning. In this study, we propose the task of Target-Guided Open-Domain Conversation Planning (TGCP) task to evaluate whether neural conversational agents have goal-oriented conversation planning abilities. Using the TGCP task, we investigate the conversation planning abilities of existing retrieval models and recent strong generative models. The experimental results reveal the challenges facing current technology.
N-best Response-based Analysis of Contradiction-awareness in Neural Response Generation Models
Aug 04, 2022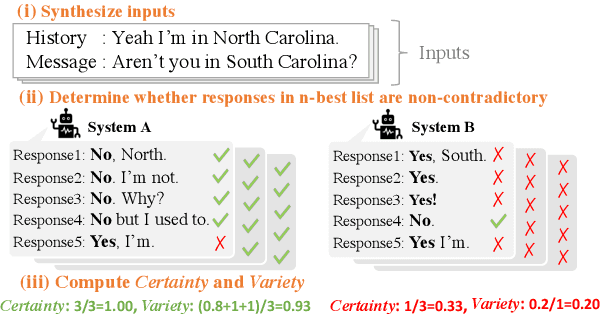

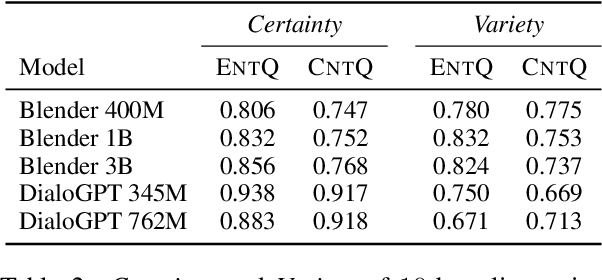
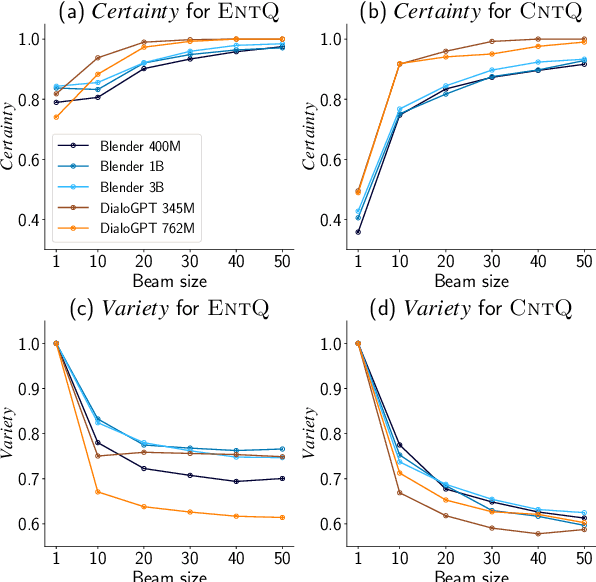
Abstract:Avoiding the generation of responses that contradict the preceding context is a significant challenge in dialogue response generation. One feasible method is post-processing, such as filtering out contradicting responses from a resulting n-best response list. In this scenario, the quality of the n-best list considerably affects the occurrence of contradictions because the final response is chosen from this n-best list. This study quantitatively analyzes the contextual contradiction-awareness of neural response generation models using the consistency of the n-best lists. Particularly, we used polar questions as stimulus inputs for concise and quantitative analyses. Our tests illustrate the contradiction-awareness of recent neural response generation models and methodologies, followed by a discussion of their properties and limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge