Reina Akama
User Willingness-aware Sales Talk Dataset
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:User willingness is a crucial element in the sales talk process that affects the achievement of the salesperson's or sales system's objectives. Despite the importance of user willingness, to the best of our knowledge, no previous study has addressed the development of automated sales talk dialogue systems that explicitly consider user willingness. A major barrier is the lack of sales talk datasets with reliable user willingness data. Thus, in this study, we developed a user willingness-aware sales talk collection by leveraging the ecological validity concept, which is discussed in the field of human-computer interaction. Our approach focused on three types of user willingness essential in real sales interactions. We created a dialogue environment that closely resembles real-world scenarios to elicit natural user willingness, with participants evaluating their willingness at the utterance level from multiple perspectives. We analyzed the collected data to gain insights into practical user willingness-aware sales talk strategies. In addition, as a practical application of the constructed dataset, we developed and evaluated a sales dialogue system aimed at enhancing the user's intent to purchase.
Detecting Response Generation Not Requiring Factual Judgment
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:With the remarkable development of large language models (LLMs), ensuring the factuality of output has become a challenge. However, having all the contents of the response with given knowledge or facts is not necessarily a good thing in dialogues. This study aimed to achieve both attractiveness and factuality in a dialogue response for which a task was set to predict sentences that do not require factual correctness judgment such as agreeing, or personal opinions/feelings. We created a dataset, dialogue dataset annotated with fact-check-needed label (DDFC), for this task via crowdsourcing, and classification tasks were performed on several models using this dataset. The model with the highest classification accuracy could yield about 88% accurate classification results.
A Large Collection of Model-generated Contradictory Responses for Consistency-aware Dialogue Systems
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:Mitigating the generation of contradictory responses poses a substantial challenge in dialogue response generation. The quality and quantity of available contradictory response data play a vital role in suppressing these contradictions, offering two significant benefits. First, having access to large contradiction data enables a comprehensive examination of their characteristics. Second, data-driven methods to mitigate contradictions may be enhanced with large-scale contradiction data for training. Nevertheless, no attempt has been made to build an extensive collection of model-generated contradictory responses. In this paper, we build a large dataset of response generation models' contradictions for the first time. Then, we acquire valuable insights into the characteristics of model-generated contradictions through an extensive analysis of the collected responses. Lastly, we also demonstrate how this dataset substantially enhances the performance of data-driven contradiction suppression methods.
Bipartite-play Dialogue Collection for Practical Automatic Evaluation of Dialogue Systems
Nov 19, 2022Abstract:Automation of dialogue system evaluation is a driving force for the efficient development of dialogue systems. This paper introduces the bipartite-play method, a dialogue collection method for automating dialogue system evaluation. It addresses the limitations of existing dialogue collection methods: (i) inability to compare with systems that are not publicly available, and (ii) vulnerability to cheating by intentionally selecting systems to be compared. Experimental results show that the automatic evaluation using the bipartite-play method mitigates these two drawbacks and correlates as strongly with human subjectivity as existing methods.
Target-Guided Open-Domain Conversation Planning
Sep 20, 2022



Abstract:Prior studies addressing target-oriented conversational tasks lack a crucial notion that has been intensively studied in the context of goal-oriented artificial intelligence agents, namely, planning. In this study, we propose the task of Target-Guided Open-Domain Conversation Planning (TGCP) task to evaluate whether neural conversational agents have goal-oriented conversation planning abilities. Using the TGCP task, we investigate the conversation planning abilities of existing retrieval models and recent strong generative models. The experimental results reveal the challenges facing current technology.
N-best Response-based Analysis of Contradiction-awareness in Neural Response Generation Models
Aug 04, 2022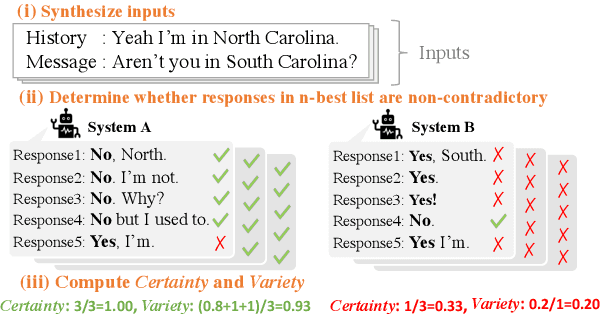

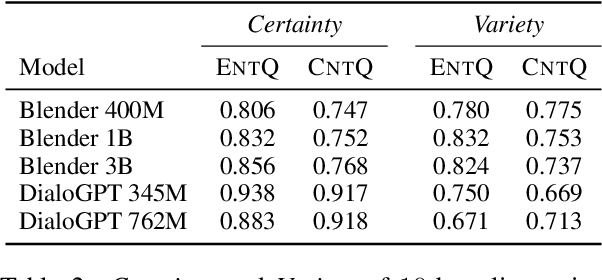
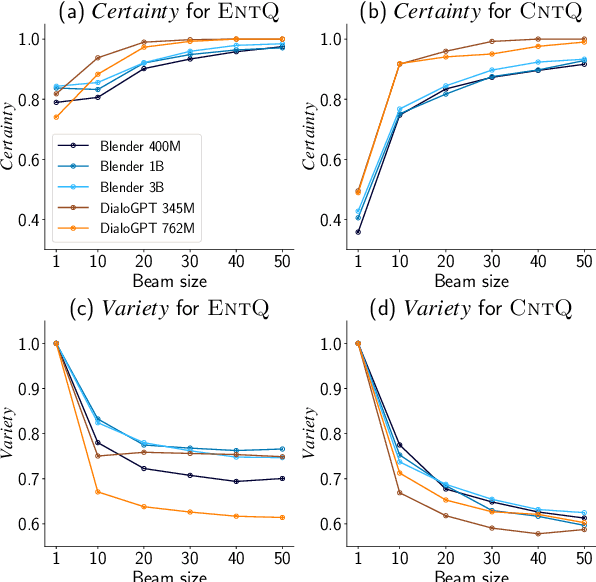
Abstract:Avoiding the generation of responses that contradict the preceding context is a significant challenge in dialogue response generation. One feasible method is post-processing, such as filtering out contradicting responses from a resulting n-best response list. In this scenario, the quality of the n-best list considerably affects the occurrence of contradictions because the final response is chosen from this n-best list. This study quantitatively analyzes the contextual contradiction-awareness of neural response generation models using the consistency of the n-best lists. Particularly, we used polar questions as stimulus inputs for concise and quantitative analyses. Our tests illustrate the contradiction-awareness of recent neural response generation models and methodologies, followed by a discussion of their properties and limitations.
Word Rotator's Distance: Decomposing Vectors Gives Better Representations
Apr 30, 2020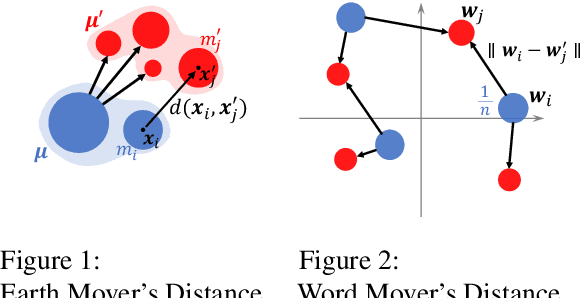
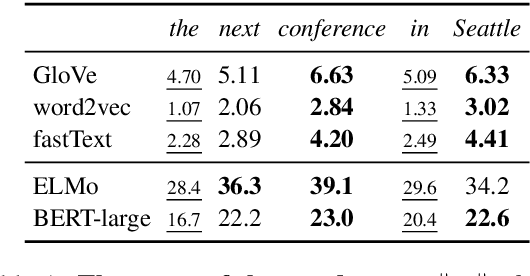
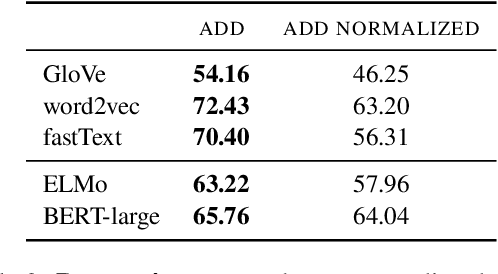
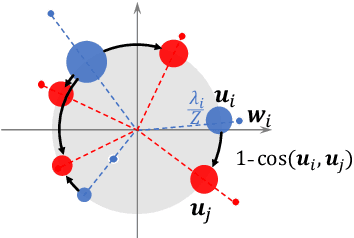
Abstract:One key principle for assessing semantic similarity between texts is to measure the degree of semantic overlap of them by considering word-by-word alignment. However, alignment-based approaches} are inferior to the generic sentence vectors in terms of performance. We hypothesize that the reason for the inferiority of alignment-based methods is due to the fact that they do not distinguish word importance and word meaning. To solve this, we propose to separate word importance and word meaning by decomposing word vectors into their norm and direction, then compute the alignment-based similarity with the help of earth mover's distance. We call the method word rotator's distance (WRD) because direction vectors are aligned by rotation on the unit hypersphere. In addition, to incorporate the advance of cutting edge additive sentence encoders, we propose to re-decompose such sentence vectors into word vectors and use them as inputs to WRD. Empirically, the proposed method outperforms current methods considering the word-by-word alignment including word mover's distance with a big difference; moreover, our method outperforms state-of-the-art additive sentence encoders on the most competitive dataset, STS-benchmark.
Evaluating Dialogue Generation Systems via Response Selection
Apr 29, 2020



Abstract:Existing automatic evaluation metrics for open-domain dialogue response generation systems correlate poorly with human evaluation. We focus on evaluating response generation systems via response selection. To evaluate systems properly via response selection, we propose the method to construct response selection test sets with well-chosen false candidates. Specifically, we propose to construct test sets filtering out some types of false candidates: (i) those unrelated to the ground-truth response and (ii) those acceptable as appropriate responses. Through experiments, we demonstrate that evaluating systems via response selection with the test sets developed by our method correlates more strongly with human evaluation, compared with widely used automatic evaluation metrics such as BLEU.
Utterance Pair Scoring for Noisy Dialogue Data Filtering
Apr 29, 2020



Abstract:Filtering noisy training data is one of the key approaches to improving the quality of neural network-based language generation. The dialogue research community especially suffers from a lack of less-noisy and sufficiently large data. In this work, we propose a scoring function that is specifically designed to identify low-quality utterance--response pairs to filter noisy training data. Our scoring function models the naturalness of the interconnection within dialogue pairs and their content-relatedness, which is based on previous findings in dialogue response generation and linguistics. We then demonstrate the effectiveness of our scoring function by confirming (i) the correlation between automatic scoring by the proposed function and human evaluation, and (ii) the performance of a dialogue response generator trained with filtered data. Furthermore, we experimentally confirm that our scoring function potentially works as a language-independent method.
Unsupervised Learning of Style-sensitive Word Vectors
May 15, 2018



Abstract:This paper presents the first study aimed at capturing stylistic similarity between words in an unsupervised manner. We propose extending the continuous bag of words (CBOW) model (Mikolov et al., 2013) to learn style-sensitive word vectors using a wider context window under the assumption that the style of all the words in an utterance is consistent. In addition, we introduce a novel task to predict lexical stylistic similarity and to create a benchmark dataset for this task. Our experiment with this dataset supports our assumption and demonstrates that the proposed extensions contribute to the acquisition of style-sensitive word embeddings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge