Haokun Liu
Hierarchical Language Models for Semantic Navigation and Manipulation in an Aerial-Ground Robotic System
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Heterogeneous multi-robot systems show great potential in complex tasks requiring coordinated hybrid cooperation. However, traditional approaches relying on static models often struggle with task diversity and dynamic environments. This highlights the need for generalizable intelligence that can bridge high-level reasoning with low-level execution across heterogeneous agents. To address this, we propose a hierarchical framework integrating a prompted Large Language Model (LLM) and a GridMask-enhanced fine-tuned Vision Language Model (VLM). The LLM performs task decomposition and global semantic map construction, while the VLM extracts task-specified semantic labels and 2D spatial information from aerial images to support local planning. Within this framework, the aerial robot follows a globally optimized semantic path and continuously provides bird-view images, guiding the ground robot's local semantic navigation and manipulation, including target-absent scenarios where implicit alignment is maintained. Experiments on a real-world letter-cubes arrangement task demonstrate the framework's adaptability and robustness in dynamic environments. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of an aerial-ground heterogeneous system integrating VLM-based perception with LLM-driven task reasoning and motion planning.
Enhancing Training Data Attribution with Representational Optimization
May 24, 2025Abstract:Training data attribution (TDA) methods aim to measure how training data impacts a model's predictions. While gradient-based attribution methods, such as influence functions, offer theoretical grounding, their computational costs make them impractical for large-scale applications. Representation-based approaches are far more scalable, but typically rely on heuristic embeddings that are not optimized for attribution, limiting their fidelity. To address these challenges, we propose AirRep, a scalable, representation-based approach that closes this gap by learning task-specific and model-aligned representations optimized explicitly for TDA. AirRep introduces two key innovations: a trainable encoder tuned for attribution quality, and an attention-based pooling mechanism that enables accurate estimation of group-wise influence. We train AirRep using a ranking objective over automatically constructed training subsets labeled by their empirical effect on target predictions. Experiments on instruction-tuned LLMs demonstrate that AirRep achieves performance on par with state-of-the-art gradient-based approaches while being nearly two orders of magnitude more efficient at inference time. Further analysis highlights its robustness and generalization across tasks and models. Our code is available at https://github.com/sunnweiwei/AirRep.
HypoBench: Towards Systematic and Principled Benchmarking for Hypothesis Generation
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:There is growing interest in hypothesis generation with large language models (LLMs). However, fundamental questions remain: what makes a good hypothesis, and how can we systematically evaluate methods for hypothesis generation? To address this, we introduce HypoBench, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs and hypothesis generation methods across multiple aspects, including practical utility, generalizability, and hypothesis discovery rate. HypoBench includes 7 real-world tasks and 5 synthetic tasks with 194 distinct datasets. We evaluate four state-of-the-art LLMs combined with six existing hypothesis-generation methods. Overall, our results suggest that existing methods are capable of discovering valid and novel patterns in the data. However, the results from synthetic datasets indicate that there is still significant room for improvement, as current hypothesis generation methods do not fully uncover all relevant or meaningful patterns. Specifically, in synthetic settings, as task difficulty increases, performance significantly drops, with best models and methods only recovering 38.8% of the ground-truth hypotheses. These findings highlight challenges in hypothesis generation and demonstrate that HypoBench serves as a valuable resource for improving AI systems designed to assist scientific discovery.
Explore the Reasoning Capability of LLMs in the Chess Testbed
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Reasoning is a central capability of human intelligence. In recent years, with the advent of large-scale datasets, pretrained large language models have emerged with new capabilities, including reasoning. However, these models still struggle with long-term, complex reasoning tasks, such as playing chess. Based on the observation that expert chess players employ a dual approach combining long-term strategic play with short-term tactical play along with language explanation, we propose improving the reasoning capability of large language models in chess by integrating annotated strategy and tactic. Specifically, we collect a dataset named MATE, which consists of 1 million chess positions with candidate moves annotated by chess experts for strategy and tactics. We finetune the LLaMA-3-8B model and compare it against state-of-the-art commercial language models in the task of selecting better chess moves. Our experiments show that our models perform better than GPT, Claude, and Gemini models. We find that language explanations can enhance the reasoning capability of large language models.
Literature Meets Data: A Synergistic Approach to Hypothesis Generation
Oct 22, 2024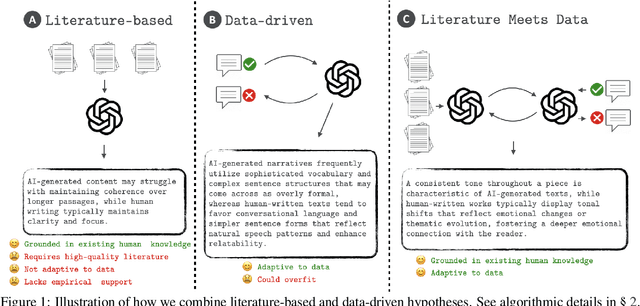
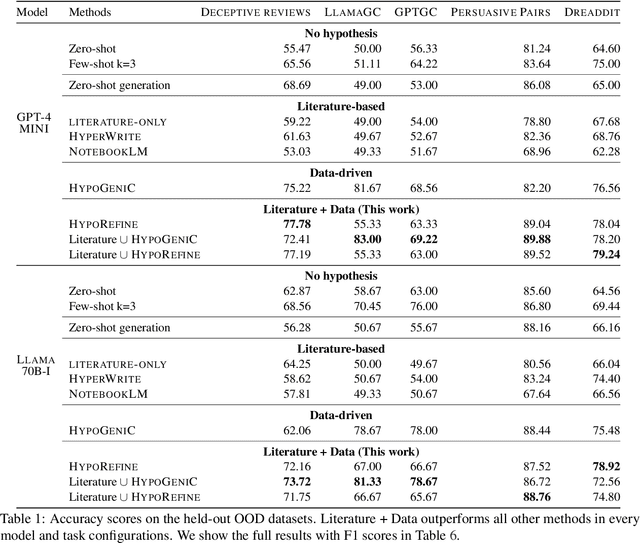
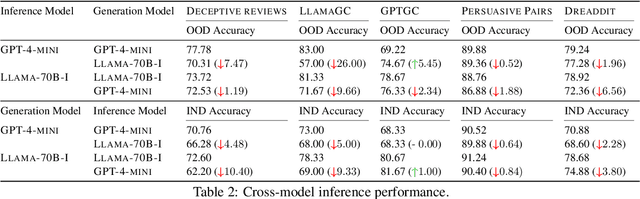
Abstract:AI holds promise for transforming scientific processes, including hypothesis generation. Prior work on hypothesis generation can be broadly categorized into theory-driven and data-driven approaches. While both have proven effective in generating novel and plausible hypotheses, it remains an open question whether they can complement each other. To address this, we develop the first method that combines literature-based insights with data to perform LLM-powered hypothesis generation. We apply our method on five different datasets and demonstrate that integrating literature and data outperforms other baselines (8.97\% over few-shot, 15.75\% over literature-based alone, and 3.37\% over data-driven alone). Additionally, we conduct the first human evaluation to assess the utility of LLM-generated hypotheses in assisting human decision-making on two challenging tasks: deception detection and AI generated content detection. Our results show that human accuracy improves significantly by 7.44\% and 14.19\% on these tasks, respectively. These findings suggest that integrating literature-based and data-driven approaches provides a comprehensive and nuanced framework for hypothesis generation and could open new avenues for scientific inquiry.
A Survey on Model MoErging: Recycling and Routing Among Specialized Experts for Collaborative Learning
Aug 13, 2024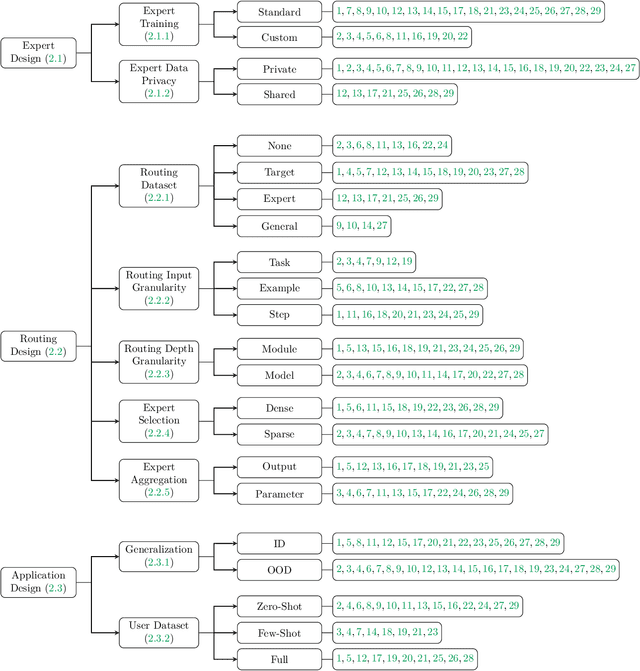
Abstract:The availability of performant pre-trained models has led to a proliferation of fine-tuned expert models that are specialized to a particular domain or task. Model MoErging methods aim to recycle expert models to create an aggregate system with improved performance or generalization. A key component of MoErging methods is the creation of a router that decides which expert model(s) to use for a particular input or application. The promise, effectiveness, and large design space of MoErging has spurred the development of many new methods over the past few years. This rapid pace of development has made it challenging to compare different MoErging methods, which are rarely compared to one another and are often validated in different experimental setups. To remedy such gaps, we present a comprehensive survey of MoErging methods that includes a novel taxonomy for cataloging key design choices and clarifying suitable applications for each method. Apart from surveying MoErging research, we inventory software tools and applications that make use of MoErging. We additionally discuss related fields of study such as model merging, multitask learning, and mixture-of-experts models. Taken as a whole, our survey provides a unified overview of existing MoErging methods and creates a solid foundation for future work in this burgeoning field.
Enhancing the LLM-Based Robot Manipulation Through Human-Robot Collaboration
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are gaining popularity in the field of robotics. However, LLM-based robots are limited to simple, repetitive motions due to the poor integration between language models, robots, and the environment. This paper proposes a novel approach to enhance the performance of LLM-based autonomous manipulation through Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC). The approach involves using a prompted GPT-4 language model to decompose high-level language commands into sequences of motions that can be executed by the robot. The system also employs a YOLO-based perception algorithm, providing visual cues to the LLM, which aids in planning feasible motions within the specific environment. Additionally, an HRC method is proposed by combining teleoperation and Dynamic Movement Primitives (DMP), allowing the LLM-based robot to learn from human guidance. Real-world experiments have been conducted using the Toyota Human Support Robot for manipulation tasks. The outcomes indicate that tasks requiring complex trajectory planning and reasoning over environments can be efficiently accomplished through the incorporation of human demonstrations.
Dense Training, Sparse Inference: Rethinking Training of Mixture-of-Experts Language Models
Apr 08, 2024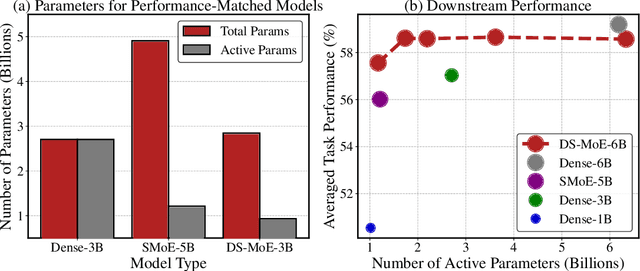
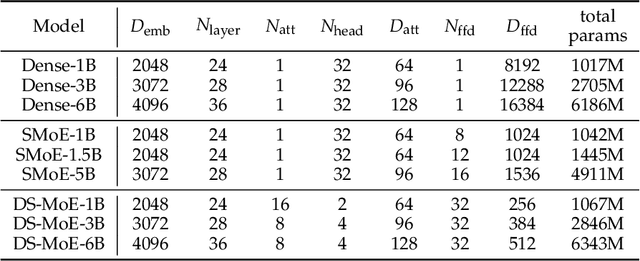
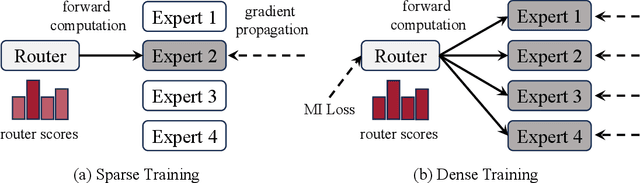
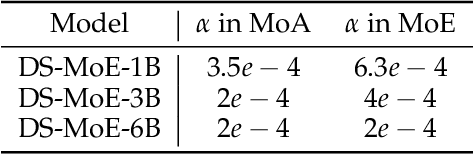
Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language models can reduce computational costs by 2-4$\times$ compared to dense models without sacrificing performance, making them more efficient in computation-bounded scenarios. However, MoE models generally require 2-4$\times$ times more parameters to achieve comparable performance to a dense model, which incurs larger GPU memory requirements and makes MoE models less efficient in I/O-bounded scenarios like autoregressive generation. In this work, we propose a hybrid dense training and sparse inference framework for MoE models (DS-MoE) which achieves strong computation and parameter efficiency by employing dense computation across all experts during training and sparse computation during inference. Our experiments on training LLMs demonstrate that our DS-MoE models are more parameter-efficient than standard sparse MoEs and are on par with dense models in terms of total parameter size and performance while being computationally cheaper (activating 30-40% of the model's parameters). Performance tests using vLLM show that our DS-MoE-6B model runs up to $1.86\times$ faster than similar dense models like Mistral-7B, and between $1.50\times$ and $1.71\times$ faster than comparable MoEs, such as DeepSeekMoE-16B and Qwen1.5-MoE-A2.7B.
Hypothesis Generation with Large Language Models
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:Effective generation of novel hypotheses is instrumental to scientific progress. So far, researchers have been the main powerhouse behind hypothesis generation by painstaking data analysis and thinking (also known as the Eureka moment). In this paper, we examine the potential of large language models (LLMs) to generate hypotheses. We focus on hypothesis generation based on data (i.e., labeled examples). To enable LLMs to handle arbitrarily long contexts, we generate initial hypotheses from a small number of examples and then update them iteratively to improve the quality of hypotheses. Inspired by multi-armed bandits, we design a reward function to inform the exploitation-exploration tradeoff in the update process. Our algorithm is able to generate hypotheses that enable much better predictive performance than few-shot prompting in classification tasks, improving accuracy by 31.7% on a synthetic dataset and by 13.9%, 3.3% and, 24.9% on three real-world datasets. We also outperform supervised learning by 12.8% and 11.2% on two challenging real-world datasets. Furthermore, we find that the generated hypotheses not only corroborate human-verified theories but also uncover new insights for the tasks.
Learning to Route Among Specialized Experts for Zero-Shot Generalization
Feb 08, 2024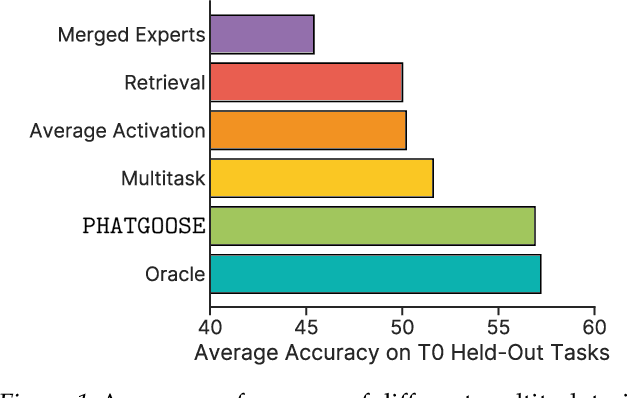

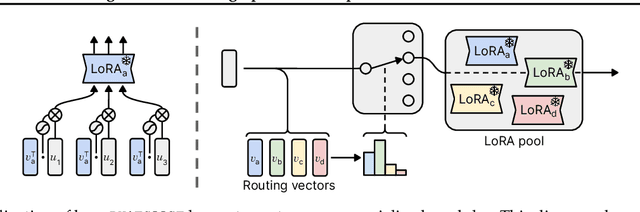

Abstract:Recently, there has been a widespread proliferation of "expert" language models that are specialized to a specific task or domain through parameter-efficient fine-tuning. How can we recycle large collections of expert language models to improve zero-shot generalization to unseen tasks? In this work, we propose Post-Hoc Adaptive Tokenwise Gating Over an Ocean of Specialized Experts (PHATGOOSE), which learns to route among specialized modules that were produced through parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Unlike past methods that learn to route among specialized models, PHATGOOSE explores the possibility that zero-shot generalization will be improved if different experts can be adaptively chosen for each token and at each layer in the model. Crucially, our method is post-hoc - it does not require simultaneous access to the datasets used to create the specialized models and only requires a modest amount of additional compute after each expert model is trained. In experiments covering a range of specialized model collections and zero-shot generalization benchmarks, we find that PHATGOOSE outperforms past methods for post-hoc routing and, in some cases, outperforms explicit multitask training (which requires simultaneous data access). To better understand the routing strategy learned by PHATGOOSE, we perform qualitative experiments to validate that PHATGOOSE's performance stems from its ability to make adaptive per-token and per-module expert choices. We release all of our code to support future work on improving zero-shot generalization by recycling specialized experts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge