Wenxiao Zhao
Explore the Reasoning Capability of LLMs in the Chess Testbed
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Reasoning is a central capability of human intelligence. In recent years, with the advent of large-scale datasets, pretrained large language models have emerged with new capabilities, including reasoning. However, these models still struggle with long-term, complex reasoning tasks, such as playing chess. Based on the observation that expert chess players employ a dual approach combining long-term strategic play with short-term tactical play along with language explanation, we propose improving the reasoning capability of large language models in chess by integrating annotated strategy and tactic. Specifically, we collect a dataset named MATE, which consists of 1 million chess positions with candidate moves annotated by chess experts for strategy and tactics. We finetune the LLaMA-3-8B model and compare it against state-of-the-art commercial language models in the task of selecting better chess moves. Our experiments show that our models perform better than GPT, Claude, and Gemini models. We find that language explanations can enhance the reasoning capability of large language models.
CtrSVDD: A Benchmark Dataset and Baseline Analysis for Controlled Singing Voice Deepfake Detection
Jun 04, 2024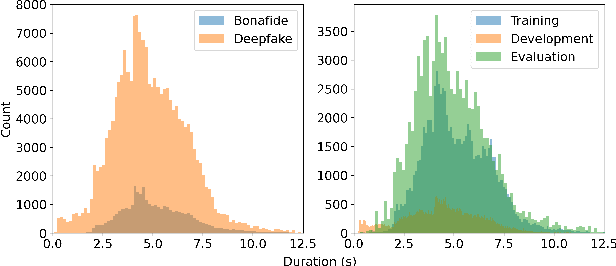
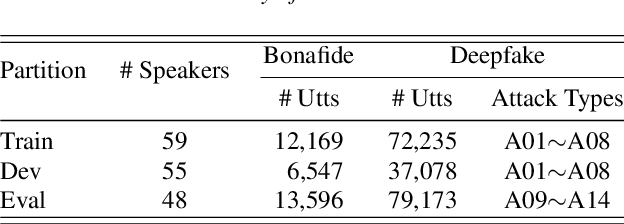
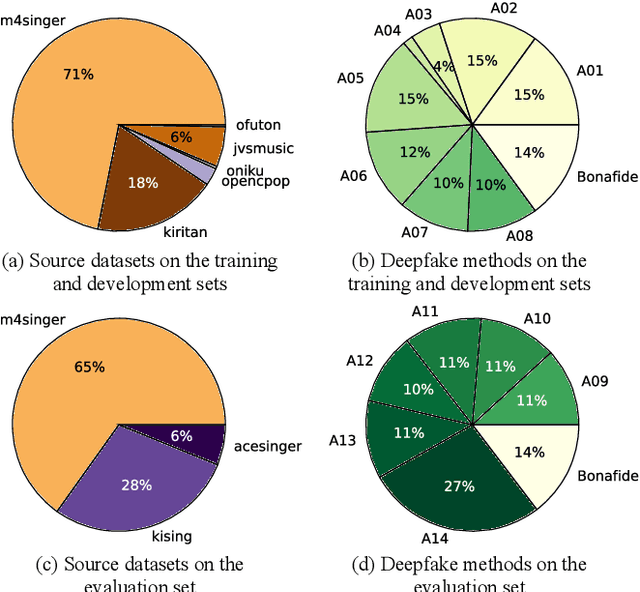
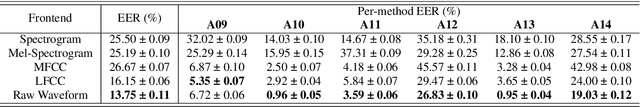
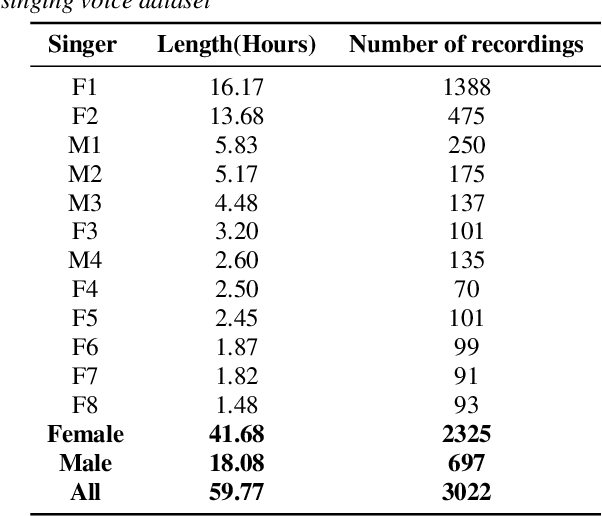
Abstract:Recent singing voice synthesis and conversion advancements necessitate robust singing voice deepfake detection (SVDD) models. Current SVDD datasets face challenges due to limited controllability, diversity in deepfake methods, and licensing restrictions. Addressing these gaps, we introduce CtrSVDD, a large-scale, diverse collection of bonafide and deepfake singing vocals. These vocals are synthesized using state-of-the-art methods from publicly accessible singing voice datasets. CtrSVDD includes 47.64 hours of bonafide and 260.34 hours of deepfake singing vocals, spanning 14 deepfake methods and involving 164 singer identities. We also present a baseline system with flexible front-end features, evaluated against a structured train/dev/eval split. The experiments show the importance of feature selection and highlight a need for generalization towards deepfake methods that deviate further from training distribution. The CtrSVDD dataset and baselines are publicly accessible.
RefineGAN: Universally Generating Waveform Better than Ground Truth with Highly Accurate Pitch and Intensity Responses
Nov 02, 2021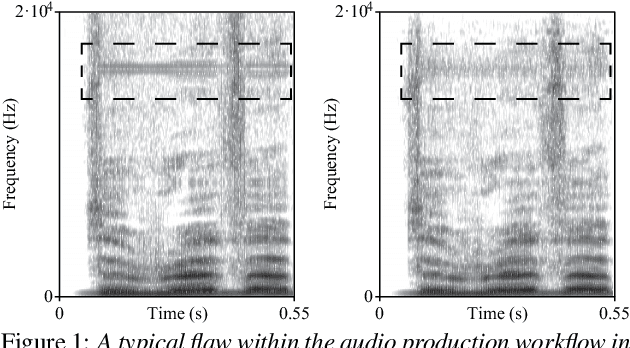
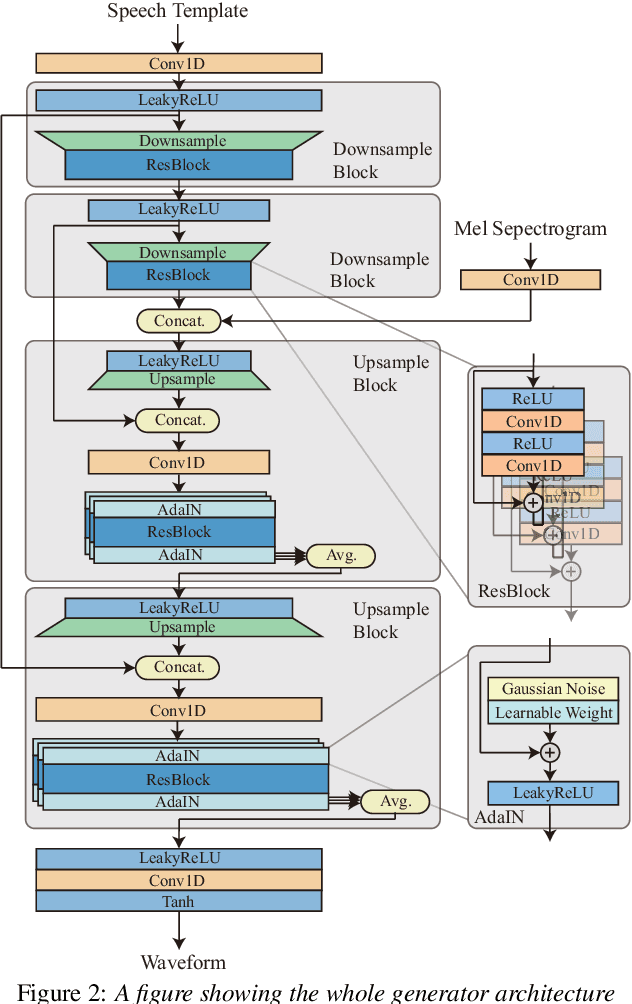
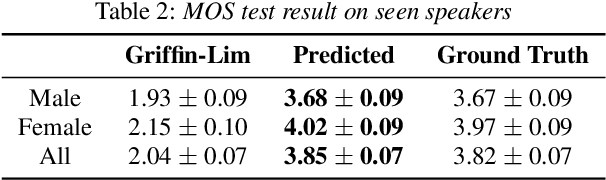
Abstract:Most GAN(Generative Adversarial Network)-based approaches towards high-fidelity waveform generation heavily rely on discriminators to improve their performance. However, the over-use of this GAN method introduces much uncertainty into the generation process and often result in mismatches of pitch and intensity, which is fatal when it comes to sensitive using cases such as singing voice synthesis(SVS). To address this problem, we propose RefineGAN, a high-fidelity neural vocoder with faster-than-real-time generation capability, and focused on the robustness, pitch and intensity accuracy, and full-band audio generation. We employed a pitch-guided refine architecture with a multi-scale spectrogram-based loss function to help stabilize the training process and maintain the robustness of the neural vocoder while using the GAN-based training method. Audio generated using this method shows a better performance in subjective tests when compared with the ground-truth audio. This result shows that the fidelity is even improved during the waveform reconstruction by eliminating defects produced by the speaker and the recording procedure. Moreover, a further study shows that models trained on a specified type of data can perform on totally unseen language and unseen speaker identically well. Generated sample pairs are provided on https://timedomain-tech.github.io/refinegan/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge