Lucas Caccia
MILA
Learning to Extract Context for Context-Aware LLM Inference
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:User prompts to large language models (LLMs) are often ambiguous or under-specified, and subtle contextual cues shaped by user intentions, prior knowledge, and risk factors strongly influence what constitutes an appropriate response. Misinterpreting intent or risks may lead to unsafe outputs, while overly cautious interpretations can cause unnecessary refusal of benign requests. In this paper, we question the conventional framework in which LLMs generate immediate responses to requests without considering broader contextual factors. User requests are situated within broader contexts such as intentions, knowledge, and prior experience, which strongly influence what constitutes an appropriate answer. We propose a framework that extracts and leverages such contextual information from the user prompt itself. Specifically, a reinforcement learning based context generator, designed in an autoencoder-like fashion, is trained to infer contextual signals grounded in the prompt and use them to guide response generation. This approach is particularly important for safety tasks, where ambiguous requests may bypass safeguards while benign but confusing requests can trigger unnecessary refusals. Experiments show that our method reduces harmful responses by an average of 5.6% on the SafetyInstruct dataset across multiple foundation models and improves the harmonic mean of attack success rate and compliance on benign prompts by 6.2% on XSTest and WildJailbreak. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of context extraction for safer and more reliable LLM inferences.
Gistify! Codebase-Level Understanding via Runtime Execution
Oct 30, 2025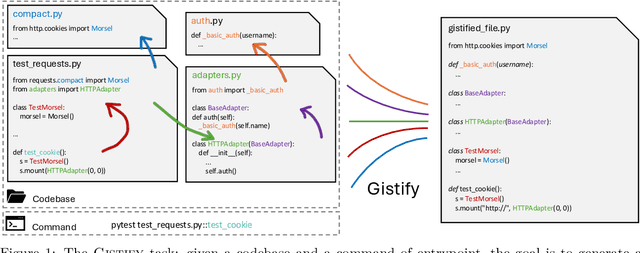
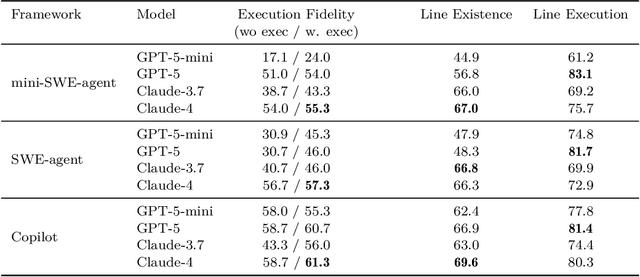
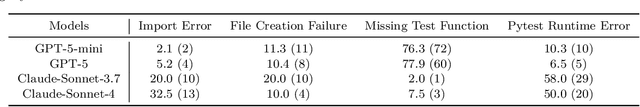
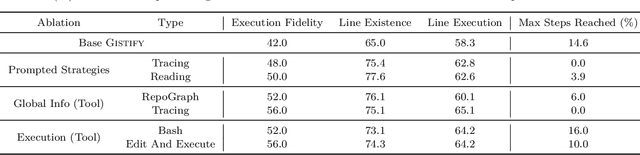
Abstract:As coding agents are increasingly deployed in large codebases, the need to automatically design challenging, codebase-level evaluation is central. We propose Gistify, a task where a coding LLM must create a single, minimal, self-contained file that can reproduce a specific functionality of a codebase. The coding LLM is given full access to a codebase along with a specific entrypoint (e.g., a python command), and the generated file must replicate the output of the same command ran under the full codebase, while containing only the essential components necessary to execute the provided command. Success on Gistify requires both structural understanding of the codebase, accurate modeling of its execution flow as well as the ability to produce potentially large code patches. Our findings show that current state-of-the-art models struggle to reliably solve Gistify tasks, especially ones with long executions traces.
A Modular Approach for Clinical SLMs Driven by Synthetic Data with Pre-Instruction Tuning, Model Merging, and Clinical-Tasks Alignment
May 15, 2025Abstract:High computation costs and latency of large language models such as GPT-4 have limited their deployment in clinical settings. Small language models (SLMs) offer a cost-effective alternative, but their limited capacity requires biomedical domain adaptation, which remains challenging. An additional bottleneck is the unavailability and high sensitivity of clinical data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework for adapting SLMs into high-performing clinical models. We introduce the MediPhi collection of 3.8B-parameter SLMs developed with our novel framework: pre-instruction tuning of experts on relevant medical and clinical corpora (PMC, Medical Guideline, MedWiki, etc.), model merging, and clinical-tasks alignment. To cover most clinical tasks, we extended the CLUE benchmark to CLUE+, doubling its size. Our expert models deliver relative improvements on this benchmark over the base model without any task-specific fine-tuning: 64.3% on medical entities, 49.5% on radiology reports, and 44% on ICD-10 coding (outperforming GPT-4-0125 by 14%). We unify the expert models into MediPhi via model merging, preserving gains across benchmarks. Furthermore, we built the MediFlow collection, a synthetic dataset of 2.5 million high-quality instructions on 14 medical NLP tasks, 98 fine-grained document types, and JSON format support. Alignment of MediPhi using supervised fine-tuning and direct preference optimization achieves further gains of 18.9% on average.
debug-gym: A Text-Based Environment for Interactive Debugging
Mar 27, 2025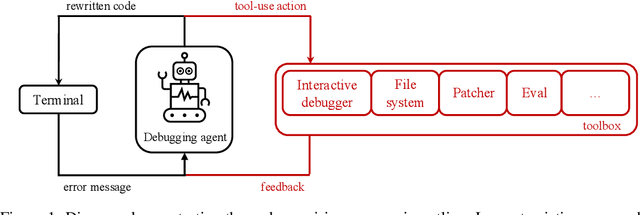
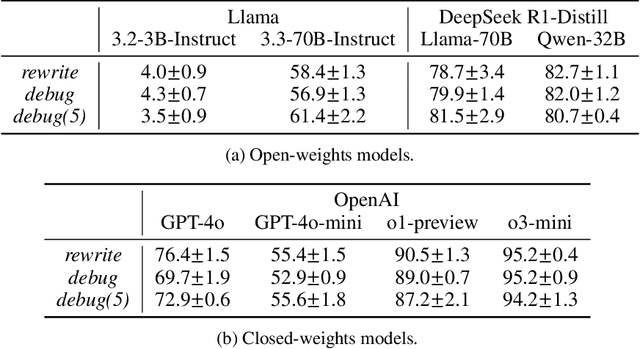
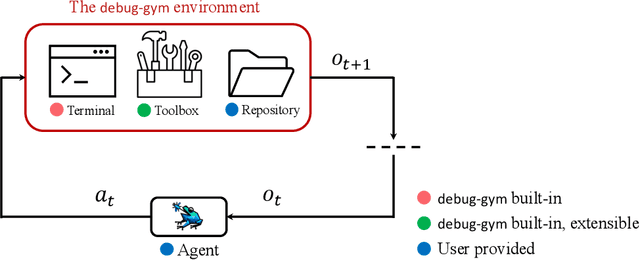
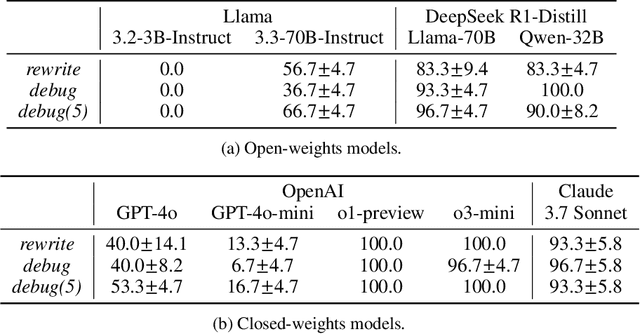
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly relied upon for coding tasks, yet in most scenarios it is assumed that all relevant information can be either accessed in context or matches their training data. We posit that LLMs can benefit from the ability to interactively explore a codebase to gather the information relevant to their task. To achieve this, we present a textual environment, namely debug-gym, for developing LLM-based agents in an interactive coding setting. Our environment is lightweight and provides a preset of useful tools, such as a Python debugger (pdb), designed to facilitate an LLM-based agent's interactive debugging. Beyond coding and debugging tasks, this approach can be generalized to other tasks that would benefit from information-seeking behavior by an LLM agent.
Training Plug-n-Play Knowledge Modules with Deep Context Distillation
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Dynamically integrating new or rapidly evolving information after (Large) Language Model pre-training remains challenging, particularly in low-data scenarios or when dealing with private and specialized documents. In-context learning and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) face limitations, including their high inference costs and their inability to capture global document information. In this paper, we propose a way of modularizing knowledge by training document-level Knowledge Modules (KMs). KMs are lightweight components implemented as parameter-efficient LoRA modules, which are trained to store information about new documents and can be easily plugged into models on demand. We show that next-token prediction performs poorly as the training objective for KMs. We instead propose Deep Context Distillation: we learn KMs parameters such as to simulate hidden states and logits of a teacher that takes the document in context. Our method outperforms standard next-token prediction and pre-instruction training techniques, across two datasets. Finally, we highlight synergies between KMs and retrieval-augmented generation.
Generative Modeling of Individual Behavior at Scale
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:There has been a growing interest in using AI to model human behavior, particularly in domains where humans interact with this technology. While most existing work models human behavior at an aggregate level, our goal is to model behavior at the individual level. Recent approaches to behavioral stylometry -- or the task of identifying a person from their actions alone -- have shown promise in domains like chess, but these approaches are either not scalable (e.g., fine-tune a separate model for each person) or not generative, in that they cannot generate actions. We address these limitations by framing behavioral stylometry as a multi-task learning problem -- where each task represents a distinct person -- and use parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods to learn an explicit style vector for each person. Style vectors are generative: they selectively activate shared "skill" parameters to generate actions in the style of each person. They also induce a latent space that we can interpret and manipulate algorithmically. In particular, we develop a general technique for style steering that allows us to steer a player's style vector towards a desired property. We apply our approach to two very different games, at unprecedented scales: chess (47,864 players) and Rocket League (2,000 players). We also show generality beyond gaming by applying our method to image generation, where we learn style vectors for 10,177 celebrities and use these vectors to steer their images.
A Survey on Model MoErging: Recycling and Routing Among Specialized Experts for Collaborative Learning
Aug 13, 2024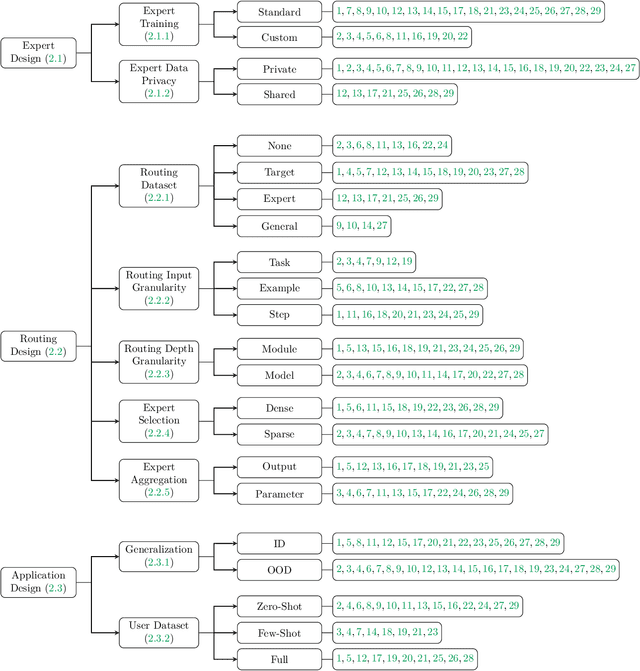
Abstract:The availability of performant pre-trained models has led to a proliferation of fine-tuned expert models that are specialized to a particular domain or task. Model MoErging methods aim to recycle expert models to create an aggregate system with improved performance or generalization. A key component of MoErging methods is the creation of a router that decides which expert model(s) to use for a particular input or application. The promise, effectiveness, and large design space of MoErging has spurred the development of many new methods over the past few years. This rapid pace of development has made it challenging to compare different MoErging methods, which are rarely compared to one another and are often validated in different experimental setups. To remedy such gaps, we present a comprehensive survey of MoErging methods that includes a novel taxonomy for cataloging key design choices and clarifying suitable applications for each method. Apart from surveying MoErging research, we inventory software tools and applications that make use of MoErging. We additionally discuss related fields of study such as model merging, multitask learning, and mixture-of-experts models. Taken as a whole, our survey provides a unified overview of existing MoErging methods and creates a solid foundation for future work in this burgeoning field.
Towards Modular LLMs by Building and Reusing a Library of LoRAs
May 18, 2024Abstract:The growing number of parameter-efficient adaptations of a base large language model (LLM) calls for studying whether we can reuse such trained adapters to improve performance for new tasks. We study how to best build a library of adapters given multi-task data and devise techniques for both zero-shot and supervised task generalization through routing in such library. We benchmark existing approaches to build this library and introduce model-based clustering, MBC, a method that groups tasks based on the similarity of their adapter parameters, indirectly optimizing for transfer across the multi-task dataset. To re-use the library, we present a novel zero-shot routing mechanism, Arrow, which enables dynamic selection of the most relevant adapters for new inputs without the need for retraining. We experiment with several LLMs, such as Phi-2 and Mistral, on a wide array of held-out tasks, verifying that MBC-based adapters and Arrow routing lead to superior generalization to new tasks. We make steps towards creating modular, adaptable LLMs that can match or outperform traditional joint training.
Guiding Language Model Reasoning with Planning Tokens
Oct 09, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently attracted considerable interest for their ability to perform complex reasoning tasks, such as chain-of-thought reasoning. However, most of the existing approaches to enhance this ability rely heavily on data-driven methods, while neglecting the structural aspects of the model's reasoning capacity. We find that while LLMs can manage individual reasoning steps well, they struggle with maintaining consistency across an entire reasoning chain. To solve this, we introduce 'planning tokens' at the start of each reasoning step, serving as a guide for the model. These token embeddings are then fine-tuned along with the rest of the model parameters. Our approach requires a negligible increase in trainable parameters (just 0.001%) and can be applied through either full fine-tuning or a more parameter-efficient scheme. We demonstrate our method's effectiveness by applying it to three different LLMs, showing notable accuracy improvements across three math word problem datasets w.r.t. plain chain-of-thought fine-tuning baselines.
Guiding The Last Layer in Federated Learning with Pre-Trained Models
Jun 06, 2023



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is an emerging paradigm that allows a model to be trained across a number of participants without sharing data. Recent works have begun to consider the effects of using pre-trained models as an initialization point for existing FL algorithms; however, these approaches ignore the vast body of efficient transfer learning literature from the centralized learning setting. Here we revisit the problem of FL from a pre-trained model considered in prior work and expand it to a set of computer vision transfer learning problems. We first observe that simply fitting a linear classification head can be efficient and effective in many cases. We then show that in the FL setting, fitting a classifier using the Nearest Class Means (NCM) can be done exactly and orders of magnitude more efficiently than existing proposals, while obtaining strong performance. Finally, we demonstrate that using a two-phase approach of obtaining the classifier and then fine-tuning the model can yield rapid convergence and improved generalization in the federated setting. We demonstrate the potential our method has to reduce communication and compute costs while achieving better model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge