Jean-Baptiste Gaya
Sid
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
WorldSense: A Synthetic Benchmark for Grounded Reasoning in Large Language Models
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:We propose WorldSense, a benchmark designed to assess the extent to which LLMs are consistently able to sustain tacit world models, by testing how they draw simple inferences from descriptions of simple arrangements of entities. Worldsense is a synthetic benchmark with three problem types, each with their own trivial control, which explicitly avoids bias by decorrelating the abstract structure of problems from the vocabulary and expressions, and by decorrelating all problem subparts with the correct response. We run our benchmark on three state-of-the-art chat-LLMs (GPT3.5, GPT4 and Llama2-chat) and show that these models make errors even with as few as three objects. Furthermore, they have quite heavy response biases, preferring certain responses irrespective of the question. Errors persist even with chain-of-thought prompting and in-context learning. Lastly, we show that while finetuning on similar problems does result in substantial improvements -- within- and out-of-distribution -- the finetuned models do not generalise beyond a constraint problem space.
Rewarded soups: towards Pareto-optimal alignment by interpolating weights fine-tuned on diverse rewards
Jun 07, 2023



Abstract:Foundation models are first pre-trained on vast unsupervised datasets and then fine-tuned on labeled data. Reinforcement learning, notably from human feedback (RLHF), can further align the network with the intended usage. Yet the imperfections in the proxy reward may hinder the training and lead to suboptimal results; the diversity of objectives in real-world tasks and human opinions exacerbate the issue. This paper proposes embracing the heterogeneity of diverse rewards by following a multi-policy strategy. Rather than focusing on a single a priori reward, we aim for Pareto-optimal generalization across the entire space of preferences. To this end, we propose rewarded soup, first specializing multiple networks independently (one for each proxy reward) and then interpolating their weights linearly. This succeeds empirically because we show that the weights remain linearly connected when fine-tuned on diverse rewards from a shared pre-trained initialization. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach for text-to-text (summarization, Q&A, helpful assistant, review), text-image (image captioning, text-to-image generation, visual grounding, VQA), and control (locomotion) tasks. We hope to enhance the alignment of deep models, and how they interact with the world in all its diversity.
Building a Subspace of Policies for Scalable Continual Learning
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:The ability to continuously acquire new knowledge and skills is crucial for autonomous agents. Existing methods are typically based on either fixed-size models that struggle to learn a large number of diverse behaviors, or growing-size models that scale poorly with the number of tasks. In this work, we aim to strike a better balance between an agent's size and performance by designing a method that grows adaptively depending on the task sequence. We introduce Continual Subspace of Policies (CSP), a new approach that incrementally builds a subspace of policies for training a reinforcement learning agent on a sequence of tasks. The subspace's high expressivity allows CSP to perform well for many different tasks while growing sublinearly with the number of tasks. Our method does not suffer from forgetting and displays positive transfer to new tasks. CSP outperforms a number of popular baselines on a wide range of scenarios from two challenging domains, Brax (locomotion) and Continual World (manipulation).
SaLinA: Sequential Learning of Agents
Oct 15, 2021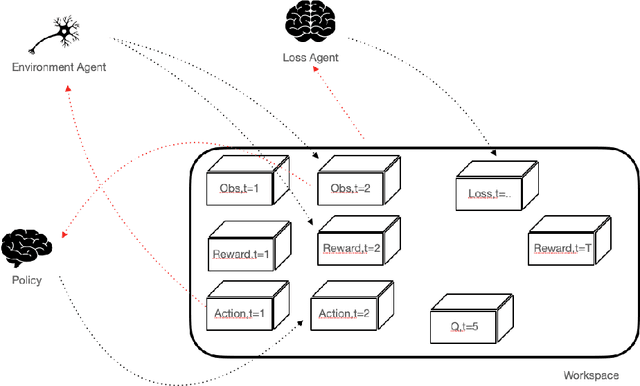


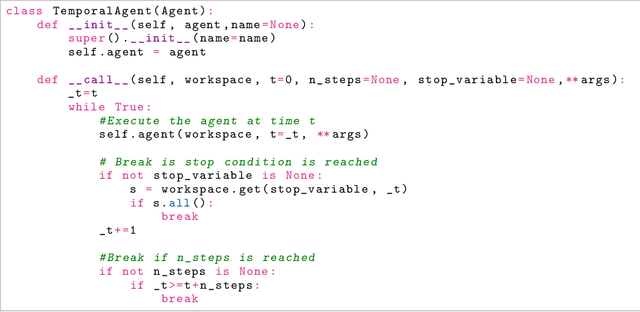
Abstract:SaLinA is a simple library that makes implementing complex sequential learning models easy, including reinforcement learning algorithms. It is built as an extension of PyTorch: algorithms coded with \SALINA{} can be understood in few minutes by PyTorch users and modified easily. Moreover, SaLinA naturally works with multiple CPUs and GPUs at train and test time, thus being a good fit for the large-scale training use cases. In comparison to existing RL libraries, SaLinA has a very low adoption cost and capture a large variety of settings (model-based RL, batch RL, hierarchical RL, multi-agent RL, etc.). But SaLinA does not only target RL practitioners, it aims at providing sequential learning capabilities to any deep learning programmer.
Learning a subspace of policies for online adaptation in Reinforcement Learning
Oct 11, 2021
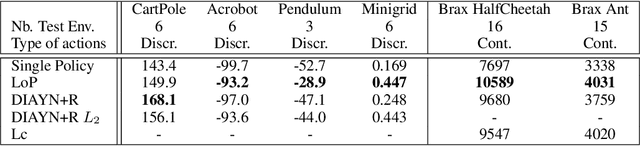
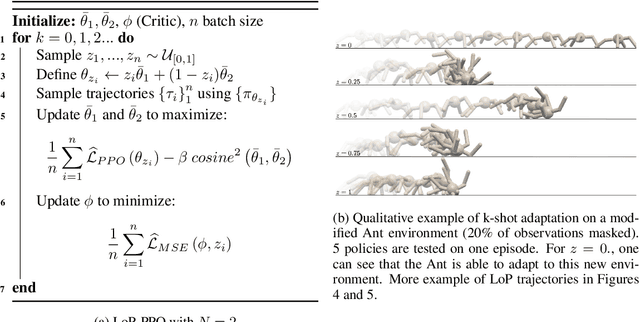
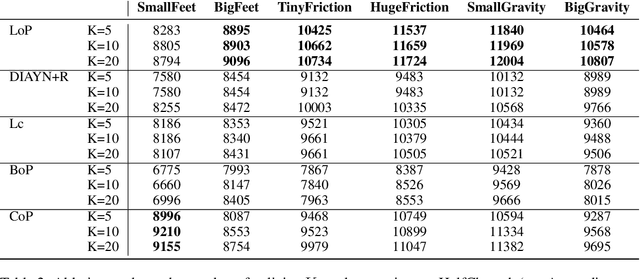
Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) is mainly studied in a setting where the training and the testing environments are similar. But in many practical applications, these environments may differ. For instance, in control systems, the robot(s) on which a policy is learned might differ from the robot(s) on which a policy will run. It can be caused by different internal factors (e.g., calibration issues, system attrition, defective modules) or also by external changes (e.g., weather conditions). There is a need to develop RL methods that generalize well to variations of the training conditions. In this article, we consider the simplest yet hard to tackle generalization setting where the test environment is unknown at train time, forcing the agent to adapt to the system's new dynamics. This online adaptation process can be computationally expensive (e.g., fine-tuning) and cannot rely on meta-RL techniques since there is just a single train environment. To do so, we propose an approach where we learn a subspace of policies within the parameter space. This subspace contains an infinite number of policies that are trained to solve the training environment while having different parameter values. As a consequence, two policies in that subspace process information differently and exhibit different behaviors when facing variations of the train environment. Our experiments carried out over a large variety of benchmarks compare our approach with baselines, including diversity-based methods. In comparison, our approach is simple to tune, does not need any extra component (e.g., discriminator) and learns policies able to gather a high reward on unseen environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge