Gwen Legate
Small Vocabularies, Big Gains: Pretraining and Tokenization in Time Series Models
Nov 06, 2025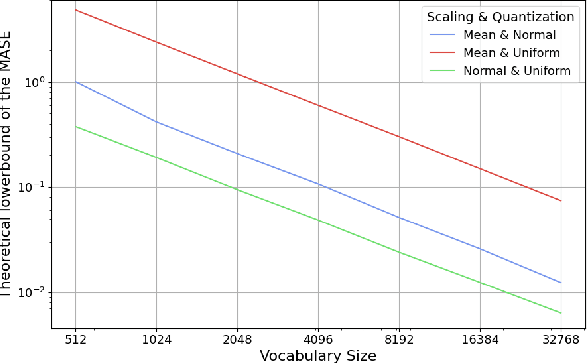
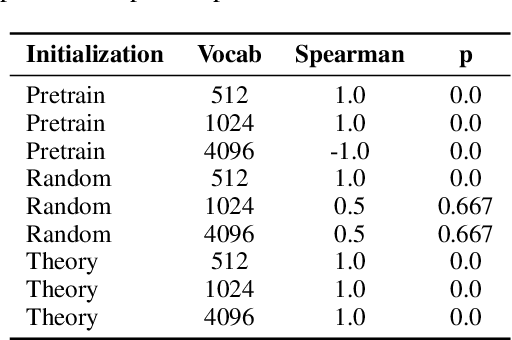
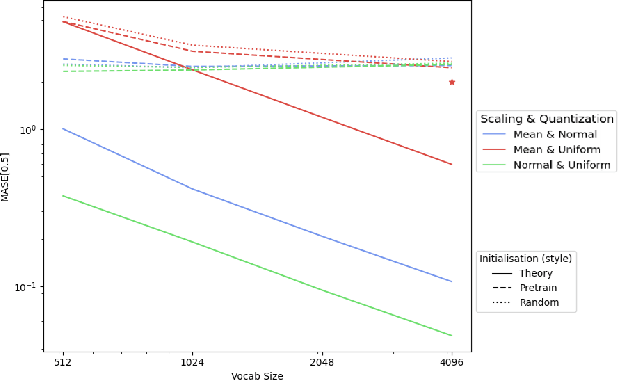
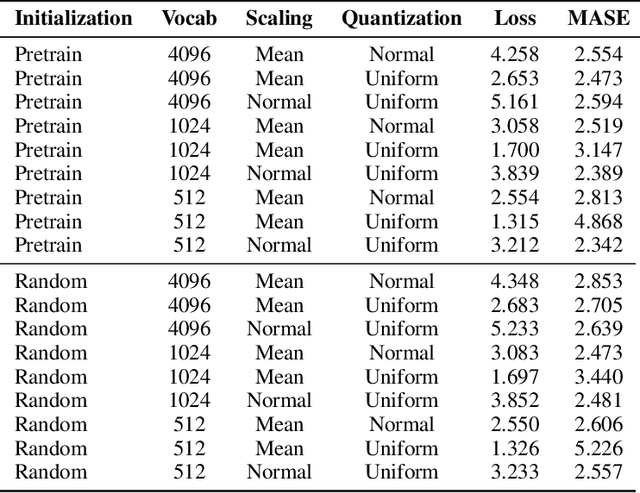
Abstract:Tokenization and transfer learning are two critical components in building state of the art time series foundation models for forecasting. In this work, we systematically study the effect of tokenizer design, specifically scaling and quantization strategies, on model performance, alongside the impact of pretraining versus random initialization. We show that tokenizer configuration primarily governs the representational capacity and stability of the model, while transfer learning influences optimization efficiency and alignment. Using a combination of empirical training experiments and theoretical analyses, we demonstrate that pretrained models consistently leverage well-designed tokenizers more effectively, particularly at smaller vocabulary sizes. Conversely, misaligned tokenization can diminish or even invert the benefits of pretraining. These findings highlight the importance of careful tokenization in time series modeling and suggest that combining small, efficient vocabularies with pretrained weights is especially advantageous in multi-modal forecasting settings, where the overall vocabulary must be shared across modalities. Our results provide concrete guidance for designing tokenizers and leveraging transfer learning in discrete representation learning for continuous signals.
Warming Up for Zeroth-Order Federated Pre-Training with Low Resource Clients
Sep 03, 2025Abstract:Federated learning enables collaborative model training across numerous edge devices without requiring participants to share data; however, memory and communication constraints on these edge devices may preclude their participation in training. We consider a setting in which a subset of edge devices are below a critical memory or communication threshold required to conduct model updates. Under typical federated optimization algorithms, these devices are excluded from training which renders their data inaccessible and increases system induced bias. We are inspired by MeZO, a zeroth-order method used for memory-efficient fine-tuning. The increased variance inherent to zeroth-order gradient approximations has relegated previous zeroth-order optimizers exclusively to the domain of fine tuning; a limitation we seek to correct. We devise a federated, memory-efficient zeroth-order optimizer, ZOWarmUp that permits zeroth-order training from a random initialization. ZOWarmUp leverages differing client capabilities and careful variance reduction techniques to facilitate participation of under-represented, low-resource clients in model training. Like other federated zeroth-order methods, ZOWarmUp eliminates the need for edge devices to transmit their full gradients to the server and instead relies on only a small set of random seeds, rendering the up-link communication cost negligible. We present experiments using various datasets and model architectures to show that ZOWarmUp is a robust algorithm that can can be applied under a wide variety of circumstances. For systems with a high proportion of edge devices that would otherwise be excluded from training, this algorithm provides access to a greater volume and diversity of data, thus improving training outcomes.
Guiding The Last Layer in Federated Learning with Pre-Trained Models
Jun 06, 2023



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is an emerging paradigm that allows a model to be trained across a number of participants without sharing data. Recent works have begun to consider the effects of using pre-trained models as an initialization point for existing FL algorithms; however, these approaches ignore the vast body of efficient transfer learning literature from the centralized learning setting. Here we revisit the problem of FL from a pre-trained model considered in prior work and expand it to a set of computer vision transfer learning problems. We first observe that simply fitting a linear classification head can be efficient and effective in many cases. We then show that in the FL setting, fitting a classifier using the Nearest Class Means (NCM) can be done exactly and orders of magnitude more efficiently than existing proposals, while obtaining strong performance. Finally, we demonstrate that using a two-phase approach of obtaining the classifier and then fine-tuning the model can yield rapid convergence and improved generalization in the federated setting. We demonstrate the potential our method has to reduce communication and compute costs while achieving better model performance.
Re-Weighted Softmax Cross-Entropy to Control Forgetting in Federated Learning
Apr 11, 2023Abstract:In Federated Learning, a global model is learned by aggregating model updates computed at a set of independent client nodes, to reduce communication costs multiple gradient steps are performed at each node prior to aggregation. A key challenge in this setting is data heterogeneity across clients resulting in differing local objectives which can lead clients to overly minimize their own local objective, diverging from the global solution. We demonstrate that individual client models experience a catastrophic forgetting with respect to data from other clients and propose an efficient approach that modifies the cross-entropy objective on a per-client basis by re-weighting the softmax logits prior to computing the loss. This approach shields classes outside a client's label set from abrupt representation change and we empirically demonstrate it can alleviate client forgetting and provide consistent improvements to standard federated learning algorithms. Our method is particularly beneficial under the most challenging federated learning settings where data heterogeneity is high and client participation in each round is low.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge