Daniel Vlasic
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
PaLI-3 Vision Language Models: Smaller, Faster, Stronger
Oct 17, 2023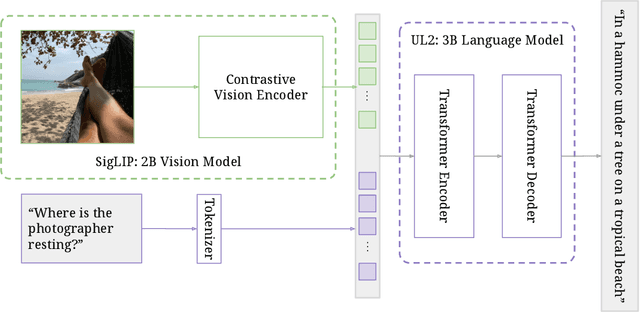
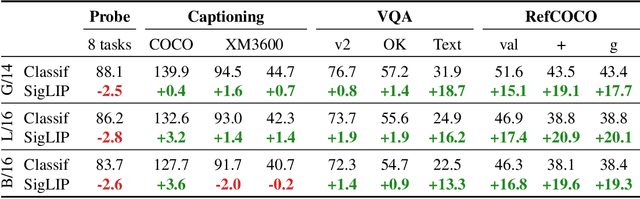
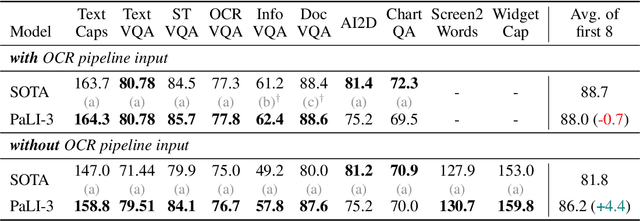
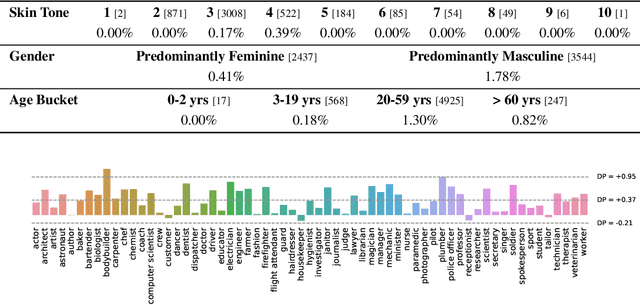
Abstract:This paper presents PaLI-3, a smaller, faster, and stronger vision language model (VLM) that compares favorably to similar models that are 10x larger. As part of arriving at this strong performance, we compare Vision Transformer (ViT) models pretrained using classification objectives to contrastively (SigLIP) pretrained ones. We find that, while slightly underperforming on standard image classification benchmarks, SigLIP-based PaLI shows superior performance across various multimodal benchmarks, especially on localization and visually-situated text understanding. We scale the SigLIP image encoder up to 2 billion parameters, and achieves a new state-of-the-art on multilingual cross-modal retrieval. We hope that PaLI-3, at only 5B parameters, rekindles research on fundamental pieces of complex VLMs, and could fuel a new generation of scaled-up models.
NAVI: Category-Agnostic Image Collections with High-Quality 3D Shape and Pose Annotations
Jun 15, 2023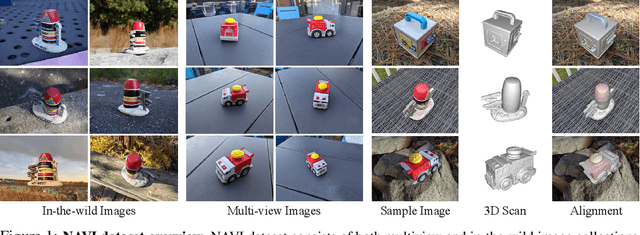


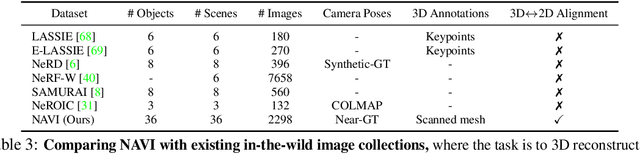
Abstract:Recent advances in neural reconstruction enable high-quality 3D object reconstruction from casually captured image collections. Current techniques mostly analyze their progress on relatively simple image collections where Structure-from-Motion (SfM) techniques can provide ground-truth (GT) camera poses. We note that SfM techniques tend to fail on in-the-wild image collections such as image search results with varying backgrounds and illuminations. To enable systematic research progress on 3D reconstruction from casual image captures, we propose NAVI: a new dataset of category-agnostic image collections of objects with high-quality 3D scans along with per-image 2D-3D alignments providing near-perfect GT camera parameters. These 2D-3D alignments allow us to extract accurate derivative annotations such as dense pixel correspondences, depth and segmentation maps. We demonstrate the use of NAVI image collections on different problem settings and show that NAVI enables more thorough evaluations that were not possible with existing datasets. We believe NAVI is beneficial for systematic research progress on 3D reconstruction and correspondence estimation. Project page: https://navidataset.github.io
Differentiable Surface Rendering via Non-Differentiable Sampling
Aug 10, 2021



Abstract:We present a method for differentiable rendering of 3D surfaces that supports both explicit and implicit representations, provides derivatives at occlusion boundaries, and is fast and simple to implement. The method first samples the surface using non-differentiable rasterization, then applies differentiable, depth-aware point splatting to produce the final image. Our approach requires no differentiable meshing or rasterization steps, making it efficient for large 3D models and applicable to isosurfaces extracted from implicit surface definitions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method for implicit-, mesh-, and parametric-surface-based inverse rendering and neural-network training applications. In particular, we show for the first time efficient, differentiable rendering of an isosurface extracted from a neural radiance field (NeRF), and demonstrate surface-based, rather than volume-based, rendering of a NeRF.
LASR: Learning Articulated Shape Reconstruction from a Monocular Video
May 06, 2021



Abstract:Remarkable progress has been made in 3D reconstruction of rigid structures from a video or a collection of images. However, it is still challenging to reconstruct nonrigid structures from RGB inputs, due to its under-constrained nature. While template-based approaches, such as parametric shape models, have achieved great success in modeling the "closed world" of known object categories, they cannot well handle the "open-world" of novel object categories or outlier shapes. In this work, we introduce a template-free approach to learn 3D shapes from a single video. It adopts an analysis-by-synthesis strategy that forward-renders object silhouette, optical flow, and pixel values to compare with video observations, which generates gradients to adjust the camera, shape and motion parameters. Without using a category-specific shape template, our method faithfully reconstructs nonrigid 3D structures from videos of human, animals, and objects of unknown classes. Code will be available at lasr-google.github.io .
AutoFlow: Learning a Better Training Set for Optical Flow
Apr 29, 2021



Abstract:Synthetic datasets play a critical role in pre-training CNN models for optical flow, but they are painstaking to generate and hard to adapt to new applications. To automate the process, we present AutoFlow, a simple and effective method to render training data for optical flow that optimizes the performance of a model on a target dataset. AutoFlow takes a layered approach to render synthetic data, where the motion, shape, and appearance of each layer are controlled by learnable hyperparameters. Experimental results show that AutoFlow achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in pre-training both PWC-Net and RAFT. Our code and data are available at https://autoflow-google.github.io .
Learning Shape Templates with Structured Implicit Functions
Apr 12, 2019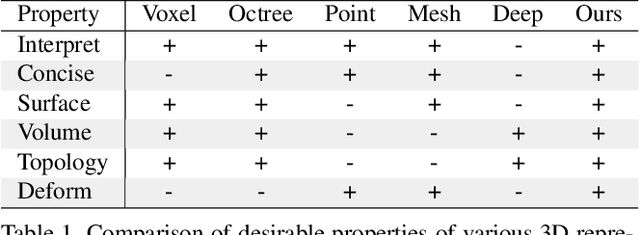
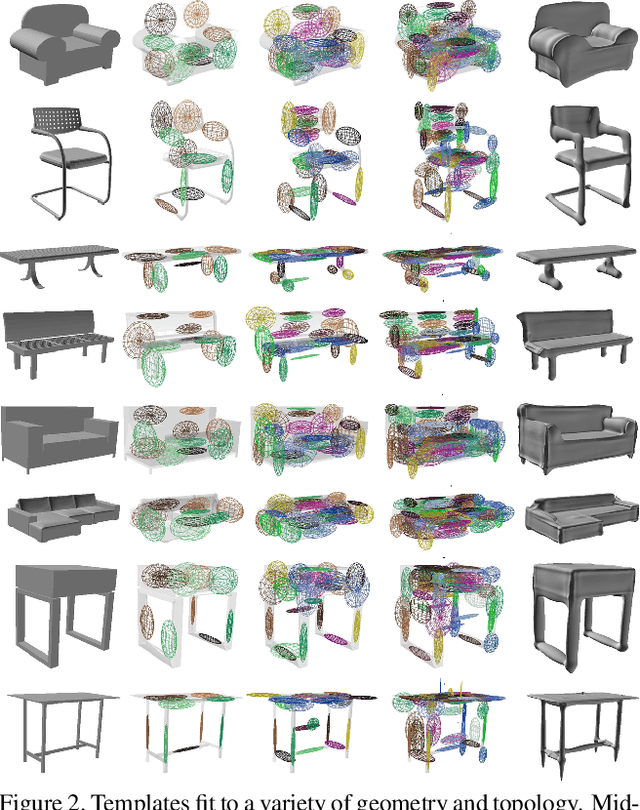
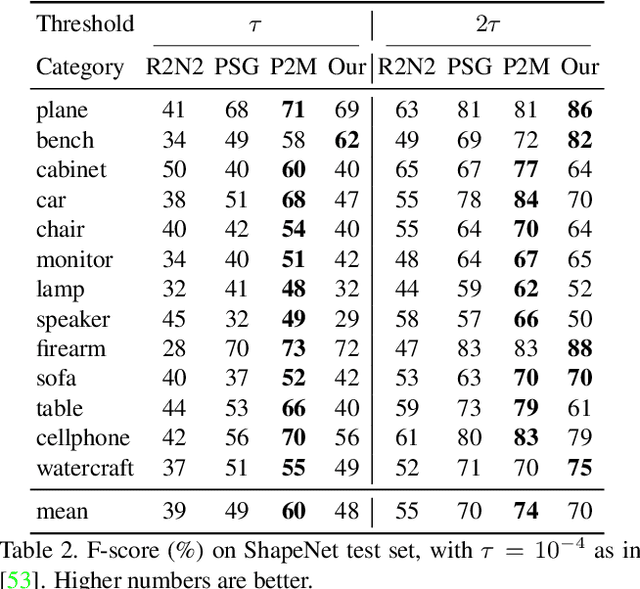
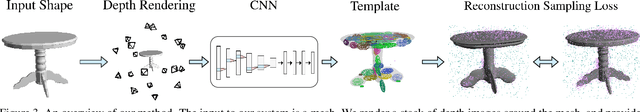
Abstract:Template 3D shapes are useful for many tasks in graphics and vision, including fitting observation data, analyzing shape collections, and transferring shape attributes. Because of the variety of geometry and topology of real-world shapes, previous methods generally use a library of hand-made templates. In this paper, we investigate learning a general shape template from data. To allow for widely varying geometry and topology, we choose an implicit surface representation based on composition of local shape elements. While long known to computer graphics, this representation has not yet been explored in the context of machine learning for vision. We show that structured implicit functions are suitable for learning and allow a network to smoothly and simultaneously fit multiple classes of shapes. The learned shape template supports applications such as shape exploration, correspondence, abstraction, interpolation, and semantic segmentation from an RGB image.
Unsupervised Training for 3D Morphable Model Regression
Jun 15, 2018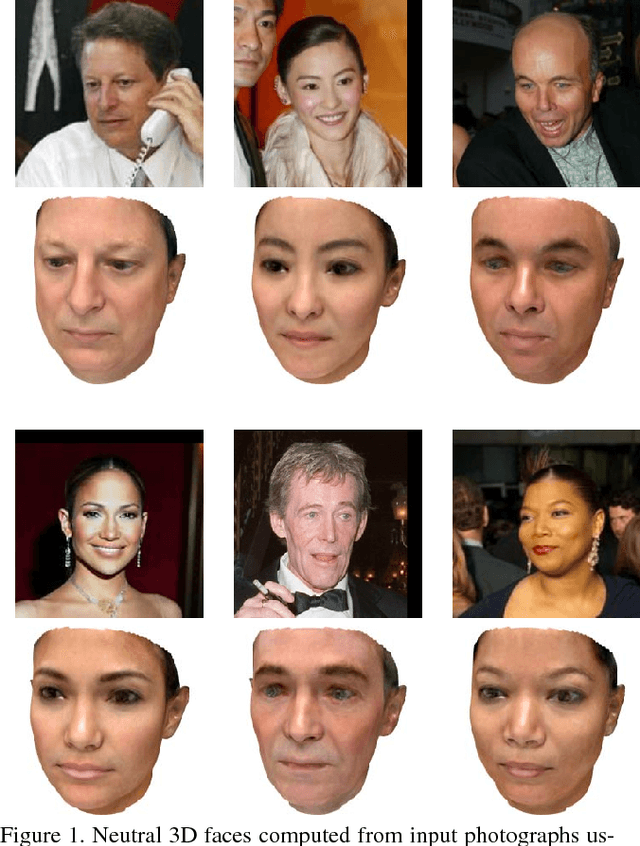
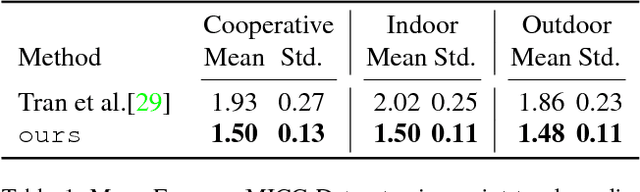
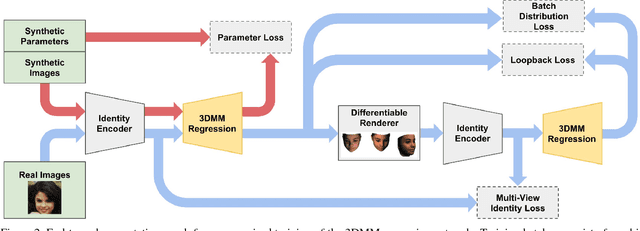
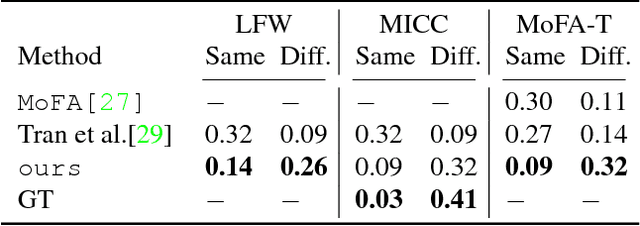
Abstract:We present a method for training a regression network from image pixels to 3D morphable model coordinates using only unlabeled photographs. The training loss is based on features from a facial recognition network, computed on-the-fly by rendering the predicted faces with a differentiable renderer. To make training from features feasible and avoid network fooling effects, we introduce three objectives: a batch distribution loss that encourages the output distribution to match the distribution of the morphable model, a loopback loss that ensures the network can correctly reinterpret its own output, and a multi-view identity loss that compares the features of the predicted 3D face and the input photograph from multiple viewing angles. We train a regression network using these objectives, a set of unlabeled photographs, and the morphable model itself, and demonstrate state-of-the-art results.
* CVPR 2018 version with supplemental material (http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/html/Genova_Unsupervised_Training_for_CVPR_2018_paper.html)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge