Chi Xu
Self-Supervised Compression and Artifact Correction for Streaming Underwater Imaging Sonar
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Real-time imaging sonar has become an important tool for underwater monitoring in environments where optical sensing is unreliable. Its broader use is constrained by two coupled challenges: highly limited uplink bandwidth and severe sonar-specific artifacts (speckle, motion blur, reverberation, acoustic shadows) that affect up to 98% of frames. We present SCOPE, a self-supervised framework that jointly performs compression and artifact correction without clean-noise pairs or synthetic assumptions. SCOPE combines (i) Adaptive Codebook Compression (ACC), which learns frequency-encoded latent representations tailored to sonar, with (ii) Frequency-Aware Multiscale Segmentation (FAMS), which decomposes frames into low-frequency structure and sparse high-frequency dynamics while suppressing rapidly fluctuating artifacts. A hedging training strategy further guides frequency-aware learning using low-pass proxy pairs generated without labels. Evaluated on months of in-situ ARIS sonar data, SCOPE achieves a structural similarity index (SSIM) of 0.77, representing a 40% improvement over prior self-supervised denoising baselines, at bitrates down to <= 0.0118 bpp. It reduces uplink bandwidth by more than 80% while improving downstream detection. The system runs in real time, with 3.1 ms encoding on an embedded GPU and 97 ms full multi-layer decoding on the server end. SCOPE has been deployed for months in three Pacific Northwest rivers to support real-time salmon enumeration and environmental monitoring in the wild. Results demonstrate that learning frequency-structured latents enables practical, low-bitrate sonar streaming with preserved signal details under real-world deployment conditions.
VPHO: Joint Visual-Physical Cue Learning and Aggregation for Hand-Object Pose Estimation
Nov 15, 2025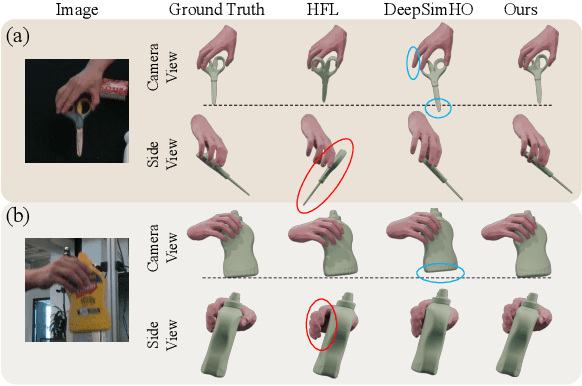
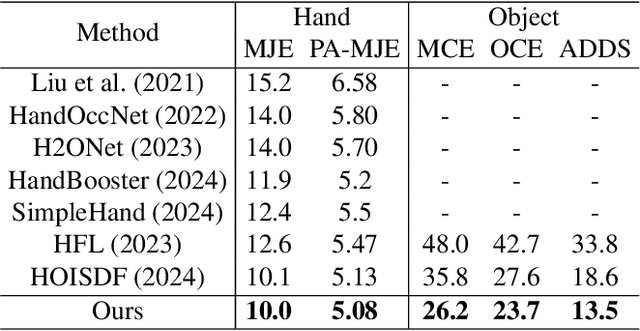
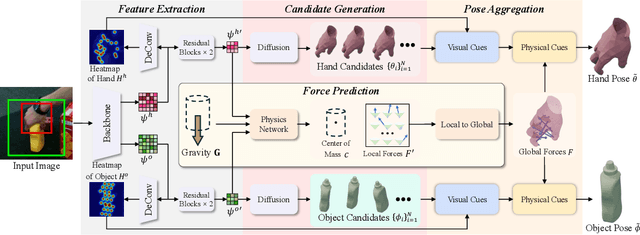
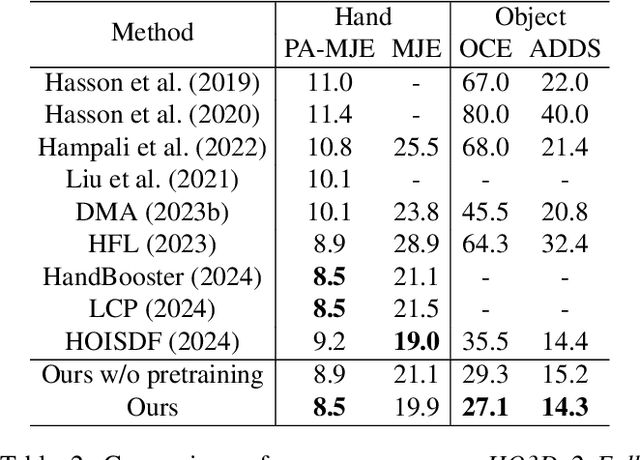
Abstract:Estimating the 3D poses of hands and objects from a single RGB image is a fundamental yet challenging problem, with broad applications in augmented reality and human-computer interaction. Existing methods largely rely on visual cues alone, often producing results that violate physical constraints such as interpenetration or non-contact. Recent efforts to incorporate physics reasoning typically depend on post-optimization or non-differentiable physics engines, which compromise visual consistency and end-to-end trainability. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel framework that jointly integrates visual and physical cues for hand-object pose estimation. This integration is achieved through two key ideas: 1) joint visual-physical cue learning: The model is trained to extract 2D visual cues and 3D physical cues, thereby enabling more comprehensive representation learning for hand-object interactions; 2) candidate pose aggregation: A novel refinement process that aggregates multiple diffusion-generated candidate poses by leveraging both visual and physical predictions, yielding a final estimate that is visually consistent and physically plausible. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in both pose accuracy and physical plausibility.
Explainable Image Classification with Reduced Overconfidence for Tissue Characterisation
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:The deployment of Machine Learning models intraoperatively for tissue characterisation can assist decision making and guide safe tumour resections. For image classification models, pixel attribution methods are popular to infer explainability. However, overconfidence in deep learning model's predictions translates to overconfidence in pixel attribution. In this paper, we propose the first approach which incorporates risk estimation into a pixel attribution method for improved image classification explainability. The proposed method iteratively applies a classification model with a pixel attribution method to create a volume of PA maps. This volume is used for the first time, to generate a pixel-wise distribution of PA values. We introduce a method to generate an enhanced PA map by estimating the expectation values of the pixel-wise distributions. In addition, the coefficient of variation (CV) is used to estimate pixel-wise risk of this enhanced PA map. Hence, the proposed method not only provides an improved PA map but also produces an estimation of risk on the output PA values. Performance evaluation on probe-based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (pCLE) data and ImageNet verifies that our improved explainability method outperforms the state-of-the-art.
SAMSA: Segment Anything Model Enhanced with Spectral Angles for Hyperspectral Interactive Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) provides rich spectral information for medical imaging, yet encounters significant challenges due to data limitations and hardware variations. We introduce SAMSA, a novel interactive segmentation framework that combines an RGB foundation model with spectral analysis. SAMSA efficiently utilizes user clicks to guide both RGB segmentation and spectral similarity computations. The method addresses key limitations in HSI segmentation through a unique spectral feature fusion strategy that operates independently of spectral band count and resolution. Performance evaluation on publicly available datasets has shown 81.0% 1-click and 93.4% 5-click DICE on a neurosurgical and 81.1% 1-click and 89.2% 5-click DICE on an intraoperative porcine hyperspectral dataset. Experimental results demonstrate SAMSA's effectiveness in few-shot and zero-shot learning scenarios and using minimal training examples. Our approach enables seamless integration of datasets with different spectral characteristics, providing a flexible framework for hyperspectral medical image analysis.
Exploring Multimodal Foundation AI and Expert-in-the-Loop for Sustainable Management of Wild Salmon Fisheries in Indigenous Rivers
May 10, 2025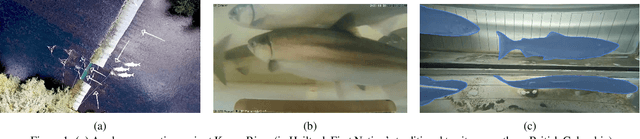

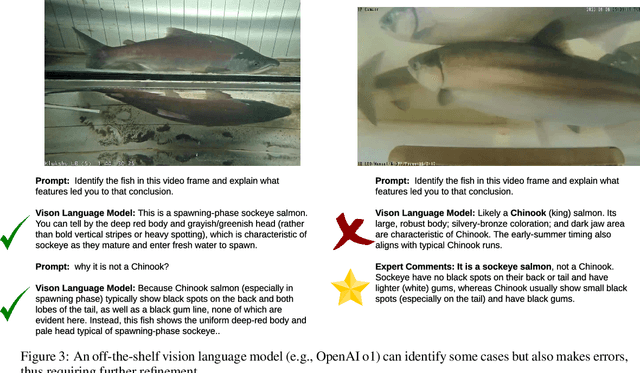
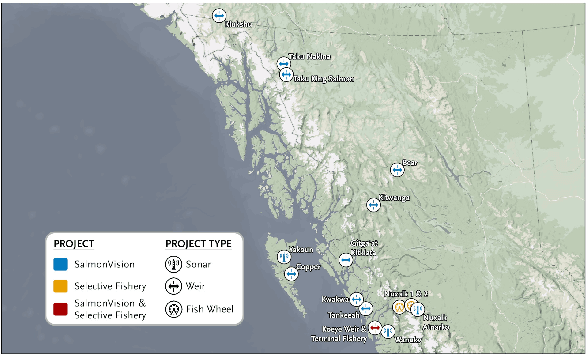
Abstract:Wild salmon are essential to the ecological, economic, and cultural sustainability of the North Pacific Rim. Yet climate variability, habitat loss, and data limitations in remote ecosystems that lack basic infrastructure support pose significant challenges to effective fisheries management. This project explores the integration of multimodal foundation AI and expert-in-the-loop frameworks to enhance wild salmon monitoring and sustainable fisheries management in Indigenous rivers across Pacific Northwest. By leveraging video and sonar-based monitoring, we develop AI-powered tools for automated species identification, counting, and length measurement, reducing manual effort, expediting delivery of results, and improving decision-making accuracy. Expert validation and active learning frameworks ensure ecological relevance while reducing annotation burdens. To address unique technical and societal challenges, we bring together a cross-domain, interdisciplinary team of university researchers, fisheries biologists, Indigenous stewardship practitioners, government agencies, and conservation organizations. Through these collaborations, our research fosters ethical AI co-development, open data sharing, and culturally informed fisheries management.
Towards Extreme Pruning of LLMs with Plug-and-Play Mixed Sparsity
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:N:M structured pruning is essential for large language models (LLMs) because it can remove less important network weights and reduce the memory and computation requirements. Existing pruning methods mainly focus on designing metrics to measure the importance of network components to guide pruning. Apart from the impact of these metrics, we observe that different layers have different sensitivities over the network performance. Thus, we propose an efficient method based on the trace of Fisher Information Matrix (FIM) to quantitatively measure and verify the different sensitivities across layers. Based on this, we propose Mixed Sparsity Pruning (MSP) which uses a pruning-oriented evolutionary algorithm (EA) to determine the optimal sparsity levels for different layers. To guarantee fast convergence and achieve promising performance, we utilize efficient FIM-inspired layer-wise sensitivity to initialize the population of EA. In addition, our MSP can work as a plug-and-play module, ready to be integrated into existing pruning methods. Extensive experiments on LLaMA and LLaMA-2 on language modeling and zero-shot tasks demonstrate our superior performance. In particular, in extreme pruning ratio (e.g. 75%), our method significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of perplexity (PPL) by orders of magnitude (Figure 1).
SurgRIPE challenge: Benchmark of Surgical Robot Instrument Pose Estimation
Jan 06, 2025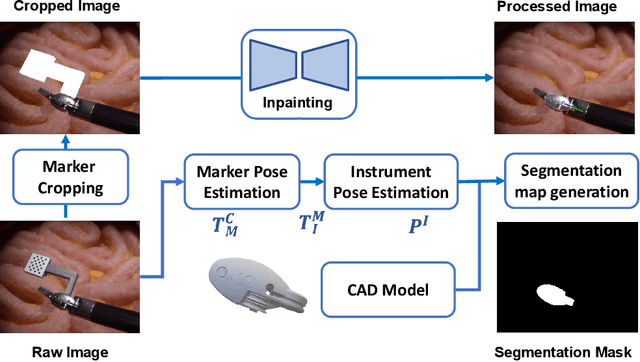
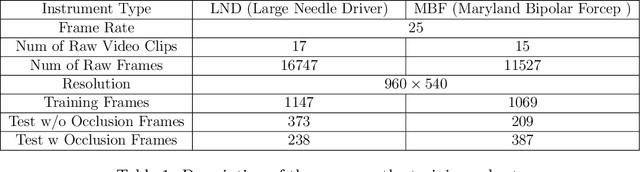
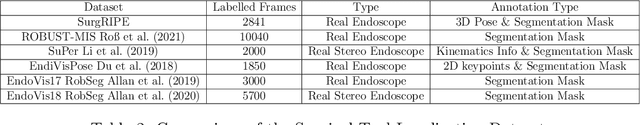
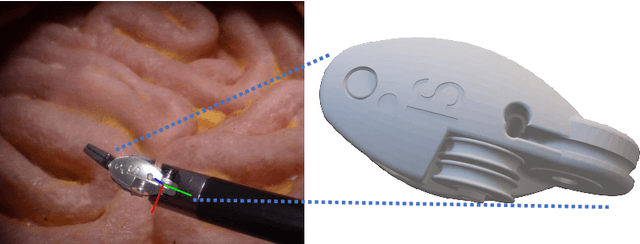
Abstract:Accurate instrument pose estimation is a crucial step towards the future of robotic surgery, enabling applications such as autonomous surgical task execution. Vision-based methods for surgical instrument pose estimation provide a practical approach to tool tracking, but they often require markers to be attached to the instruments. Recently, more research has focused on the development of marker-less methods based on deep learning. However, acquiring realistic surgical data, with ground truth instrument poses, required for deep learning training, is challenging. To address the issues in surgical instrument pose estimation, we introduce the Surgical Robot Instrument Pose Estimation (SurgRIPE) challenge, hosted at the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) in 2023. The objectives of this challenge are: (1) to provide the surgical vision community with realistic surgical video data paired with ground truth instrument poses, and (2) to establish a benchmark for evaluating markerless pose estimation methods. The challenge led to the development of several novel algorithms that showcased improved accuracy and robustness over existing methods. The performance evaluation study on the SurgRIPE dataset highlights the potential of these advanced algorithms to be integrated into robotic surgery systems, paving the way for more precise and autonomous surgical procedures. The SurgRIPE challenge has successfully established a new benchmark for the field, encouraging further research and development in surgical robot instrument pose estimation.
In-situ Self-optimization of Quantum Dot Emission for Lasers by Machine-Learning Assisted Epitaxy
Nov 01, 2024Abstract:Traditional methods for optimizing light source emissions rely on a time-consuming trial-and-error approach. While in-situ optimization of light source gain media emission during growth is ideal, it has yet to be realized. In this work, we integrate in-situ reflection high-energy electron diffraction (RHEED) with machine learning (ML) to correlate the surface reconstruction with the photoluminescence (PL) of InAs/GaAs quantum dots (QDs), which serve as the active region of lasers. A lightweight ResNet-GLAM model is employed for the real-time processing of RHEED data as input, enabling effective identification of optical performance. This approach guides the dynamic optimization of growth parameters, allowing real-time feedback control to adjust the QDs emission for lasers. We successfully optimized InAs QDs on GaAs substrates, with a 3.2-fold increase in PL intensity and a reduction in full width at half maximum (FWHM) from 36.69 meV to 28.17 meV under initially suboptimal growth conditions. Our automated, in-situ self-optimized lasers with 5-layer InAs QDs achieved electrically pumped continuous-wave operation at 1240 nm with a low threshold current of 150 A/cm2 at room temperature, an excellent performance comparable to samples grown through traditional manual multi-parameter optimization methods. These results mark a significant step toward intelligent, low-cost, and reproductive light emitters production.
SCALM: Towards Semantic Caching for Automated Chat Services with Large Language Models
May 24, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become increasingly popular, transforming a wide range of applications across various domains. However, the real-world effectiveness of their query cache systems has not been thoroughly investigated. In this work, we for the first time conducted an analysis on real-world human-to-LLM interaction data, identifying key challenges in existing caching solutions for LLM-based chat services. Our findings reveal that current caching methods fail to leverage semantic connections, leading to inefficient cache performance and extra token costs. To address these issues, we propose SCALM, a new cache architecture that emphasizes semantic analysis and identifies significant cache entries and patterns. We also detail the implementations of the corresponding cache storage and eviction strategies. Our evaluations show that SCALM increases cache hit ratios and reduces operational costs for LLMChat services. Compared with other state-of-the-art solutions in GPTCache, SCALM shows, on average, a relative increase of 63% in cache hit ratio and a relative improvement of 77% in tokens savings.
MVMoE: Multi-Task Vehicle Routing Solver with Mixture-of-Experts
May 02, 2024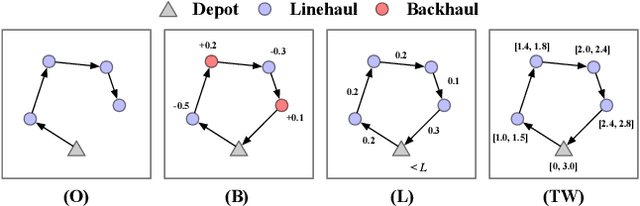
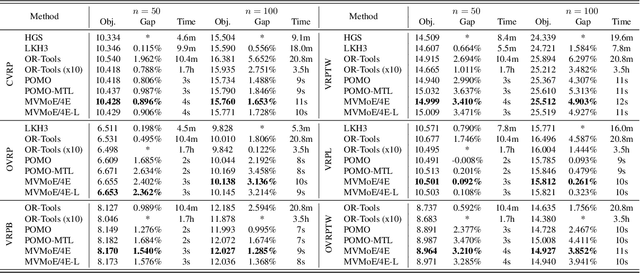
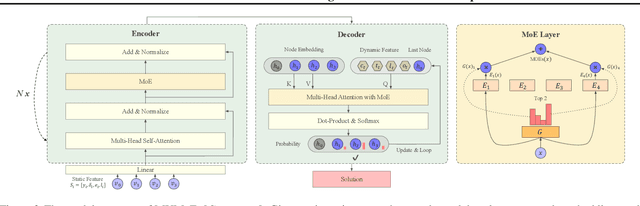
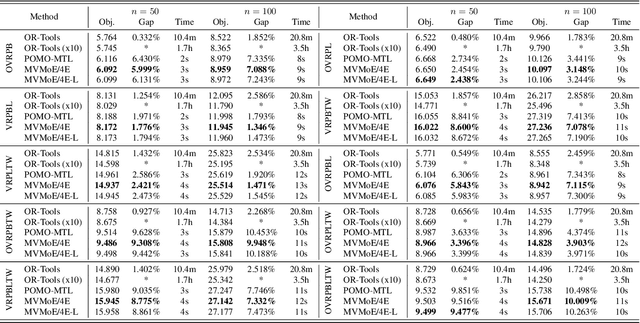
Abstract:Learning to solve vehicle routing problems (VRPs) has garnered much attention. However, most neural solvers are only structured and trained independently on a specific problem, making them less generic and practical. In this paper, we aim to develop a unified neural solver that can cope with a range of VRP variants simultaneously. Specifically, we propose a multi-task vehicle routing solver with mixture-of-experts (MVMoE), which greatly enhances the model capacity without a proportional increase in computation. We further develop a hierarchical gating mechanism for the MVMoE, delivering a good trade-off between empirical performance and computational complexity. Experimentally, our method significantly promotes the zero-shot generalization performance on 10 unseen VRP variants, and showcases decent results on the few-shot setting and real-world benchmark instances. We further provide extensive studies on the effect of MoE configurations in solving VRPs. Surprisingly, the hierarchical gating can achieve much better out-of-distribution generalization performance. The source code is available at: https://github.com/RoyalSkye/Routing-MVMoE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge