Stamatia Giannarou
Explainable Image Classification with Reduced Overconfidence for Tissue Characterisation
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:The deployment of Machine Learning models intraoperatively for tissue characterisation can assist decision making and guide safe tumour resections. For image classification models, pixel attribution methods are popular to infer explainability. However, overconfidence in deep learning model's predictions translates to overconfidence in pixel attribution. In this paper, we propose the first approach which incorporates risk estimation into a pixel attribution method for improved image classification explainability. The proposed method iteratively applies a classification model with a pixel attribution method to create a volume of PA maps. This volume is used for the first time, to generate a pixel-wise distribution of PA values. We introduce a method to generate an enhanced PA map by estimating the expectation values of the pixel-wise distributions. In addition, the coefficient of variation (CV) is used to estimate pixel-wise risk of this enhanced PA map. Hence, the proposed method not only provides an improved PA map but also produces an estimation of risk on the output PA values. Performance evaluation on probe-based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (pCLE) data and ImageNet verifies that our improved explainability method outperforms the state-of-the-art.
SAMSA: Segment Anything Model Enhanced with Spectral Angles for Hyperspectral Interactive Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) provides rich spectral information for medical imaging, yet encounters significant challenges due to data limitations and hardware variations. We introduce SAMSA, a novel interactive segmentation framework that combines an RGB foundation model with spectral analysis. SAMSA efficiently utilizes user clicks to guide both RGB segmentation and spectral similarity computations. The method addresses key limitations in HSI segmentation through a unique spectral feature fusion strategy that operates independently of spectral band count and resolution. Performance evaluation on publicly available datasets has shown 81.0% 1-click and 93.4% 5-click DICE on a neurosurgical and 81.1% 1-click and 89.2% 5-click DICE on an intraoperative porcine hyperspectral dataset. Experimental results demonstrate SAMSA's effectiveness in few-shot and zero-shot learning scenarios and using minimal training examples. Our approach enables seamless integration of datasets with different spectral characteristics, providing a flexible framework for hyperspectral medical image analysis.
SurgPose: Generalisable Surgical Instrument Pose Estimation using Zero-Shot Learning and Stereo Vision
May 16, 2025



Abstract:Accurate pose estimation of surgical tools in Robot-assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery (RMIS) is essential for surgical navigation and robot control. While traditional marker-based methods offer accuracy, they face challenges with occlusions, reflections, and tool-specific designs. Similarly, supervised learning methods require extensive training on annotated datasets, limiting their adaptability to new tools. Despite their success in other domains, zero-shot pose estimation models remain unexplored in RMIS for pose estimation of surgical instruments, creating a gap in generalising to unseen surgical tools. This paper presents a novel 6 Degrees of Freedom (DoF) pose estimation pipeline for surgical instruments, leveraging state-of-the-art zero-shot RGB-D models like the FoundationPose and SAM-6D. We advanced these models by incorporating vision-based depth estimation using the RAFT-Stereo method, for robust depth estimation in reflective and textureless environments. Additionally, we enhanced SAM-6D by replacing its instance segmentation module, Segment Anything Model (SAM), with a fine-tuned Mask R-CNN, significantly boosting segmentation accuracy in occluded and complex conditions. Extensive validation reveals that our enhanced SAM-6D surpasses FoundationPose in zero-shot pose estimation of unseen surgical instruments, setting a new benchmark for zero-shot RGB-D pose estimation in RMIS. This work enhances the generalisability of pose estimation for unseen objects and pioneers the application of RGB-D zero-shot methods in RMIS.
Confidence-Based Annotation Of Brain Tumours In Ultrasound
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Purpose: An investigation of the challenge of annotating discrete segmentations of brain tumours in ultrasound, with a focus on the issue of aleatoric uncertainty along the tumour margin, particularly for diffuse tumours. A segmentation protocol and method is proposed that incorporates this margin-related uncertainty while minimising the interobserver variance through reduced subjectivity, thereby diminishing annotator epistemic uncertainty. Approach: A sparse confidence method for annotation is proposed, based on a protocol designed using computer vision and radiology theory. Results: Output annotations using the proposed method are compared with the corresponding professional discrete annotation variance between the observers. A linear relationship was measured within the tumour margin region, with a Pearson correlation of 0.8. The downstream application was explored, comparing training using confidence annotations as soft labels with using the best discrete annotations as hard labels. In all evaluation folds, the Brier score was superior for the soft-label trained network. Conclusion: A formal framework was constructed to demonstrate the infeasibility of discrete annotation of brain tumours in B-mode ultrasound. Subsequently, a method for sparse confidence-based annotation is proposed and evaluated. Keywords: Brain tumours, ultrasound, confidence, annotation.
Standardisation of Convex Ultrasound Data Through Geometric Analysis and Augmentation
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:The application of ultrasound in healthcare has seen increased diversity and importance. Unlike other medical imaging modalities, ultrasound research and development has historically lagged, particularly in the case of applications with data-driven algorithms. A significant issue with ultrasound is the extreme variability of the images, due to the number of different machines available and the possible combination of parameter settings. One outcome of this is the lack of standardised and benchmarking ultrasound datasets. The method proposed in this article is an approach to alleviating this issue of disorganisation. For this purpose, the issue of ultrasound data sparsity is examined and a novel perspective, approach, and solution is proposed; involving the extraction of the underlying ultrasound plane within the image and representing it using annulus sector geometry. An application of this methodology is proposed, which is the extraction of scan lines and the linearisation of convex planes. Validation of the robustness of the proposed method is performed on both private and public data. The impact of deformation and the invertibility of augmentation using the estimated annulus sector parameters is also studied. Keywords: Ultrasound, Annulus Sector, Augmentation, Linearisation.
SurgRIPE challenge: Benchmark of Surgical Robot Instrument Pose Estimation
Jan 06, 2025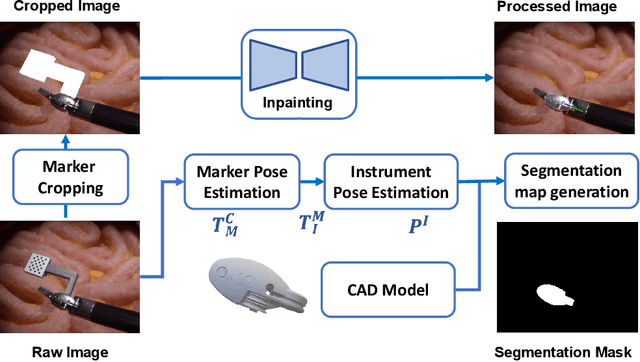
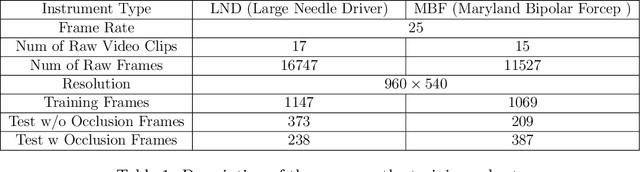
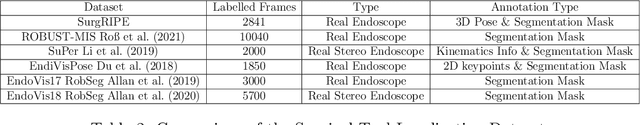
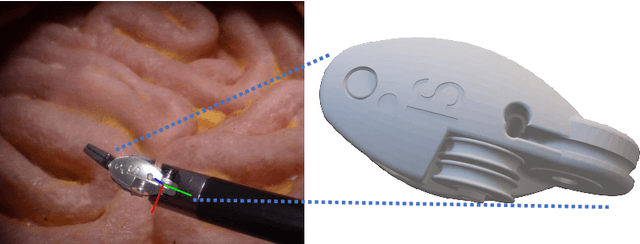
Abstract:Accurate instrument pose estimation is a crucial step towards the future of robotic surgery, enabling applications such as autonomous surgical task execution. Vision-based methods for surgical instrument pose estimation provide a practical approach to tool tracking, but they often require markers to be attached to the instruments. Recently, more research has focused on the development of marker-less methods based on deep learning. However, acquiring realistic surgical data, with ground truth instrument poses, required for deep learning training, is challenging. To address the issues in surgical instrument pose estimation, we introduce the Surgical Robot Instrument Pose Estimation (SurgRIPE) challenge, hosted at the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) in 2023. The objectives of this challenge are: (1) to provide the surgical vision community with realistic surgical video data paired with ground truth instrument poses, and (2) to establish a benchmark for evaluating markerless pose estimation methods. The challenge led to the development of several novel algorithms that showcased improved accuracy and robustness over existing methods. The performance evaluation study on the SurgRIPE dataset highlights the potential of these advanced algorithms to be integrated into robotic surgery systems, paving the way for more precise and autonomous surgical procedures. The SurgRIPE challenge has successfully established a new benchmark for the field, encouraging further research and development in surgical robot instrument pose estimation.
Image Synthesis with Class-Aware Semantic Diffusion Models for Surgical Scene Segmentation
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Surgical scene segmentation is essential for enhancing surgical precision, yet it is frequently compromised by the scarcity and imbalance of available data. To address these challenges, semantic image synthesis methods based on generative adversarial networks and diffusion models have been developed. However, these models often yield non-diverse images and fail to capture small, critical tissue classes, limiting their effectiveness. In response, we propose the Class-Aware Semantic Diffusion Model (CASDM), a novel approach which utilizes segmentation maps as conditions for image synthesis to tackle data scarcity and imbalance. Novel class-aware mean squared error and class-aware self-perceptual loss functions have been defined to prioritize critical, less visible classes, thereby enhancing image quality and relevance. Furthermore, to our knowledge, we are the first to generate multi-class segmentation maps using text prompts in a novel fashion to specify their contents. These maps are then used by CASDM to generate surgical scene images, enhancing datasets for training and validating segmentation models. Our evaluation, which assesses both image quality and downstream segmentation performance, demonstrates the strong effectiveness and generalisability of CASDM in producing realistic image-map pairs, significantly advancing surgical scene segmentation across diverse and challenging datasets.
Towards Safe and Collaborative Robotic Ultrasound Tissue Scanning in Neurosurgery
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:Intraoperative ultrasound imaging is used to facilitate safe brain tumour resection. However, due to challenges with image interpretation and the physical scanning, this tool has yet to achieve widespread adoption in neurosurgery. In this paper, we introduce the components and workflow of a novel, versatile robotic platform for intraoperative ultrasound tissue scanning in neurosurgery. An RGB-D camera attached to the robotic arm allows for automatic object localisation with ArUco markers, and 3D surface reconstruction as a triangular mesh using the ImFusion Suite software solution. Impedance controlled guidance of the US probe along arbitrary surfaces, represented as a mesh, enables collaborative US scanning, i.e., autonomous, teleoperated and hands-on guided data acquisition. A preliminary experiment evaluates the suitability of the conceptual workflow and system components for probe landing on a custom-made soft-tissue phantom. Further assessment in future experiments will be necessary to prove the effectiveness of the presented platform.
Dietary Assessment with Multimodal ChatGPT: A Systematic Analysis
Dec 14, 2023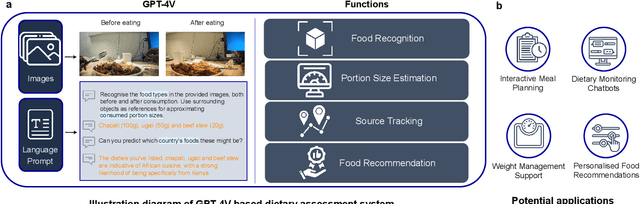

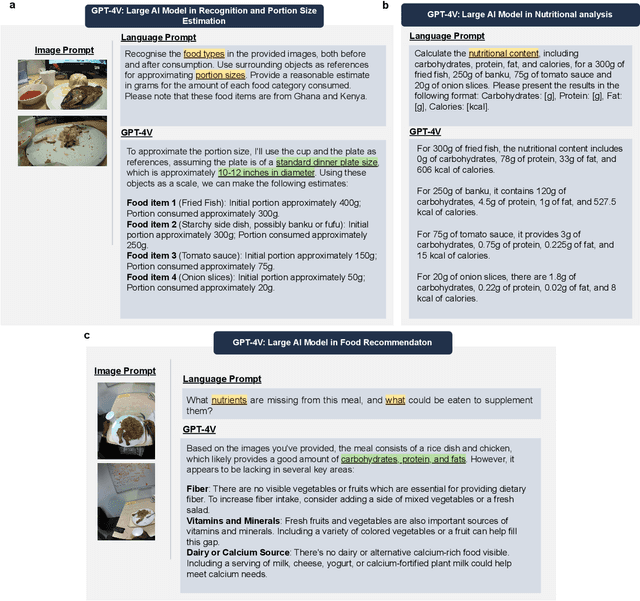

Abstract:Conventional approaches to dietary assessment are primarily grounded in self-reporting methods or structured interviews conducted under the supervision of dietitians. These methods, however, are often subjective, potentially inaccurate, and time-intensive. Although artificial intelligence (AI)-based solutions have been devised to automate the dietary assessment process, these prior AI methodologies encounter challenges in their ability to generalize across a diverse range of food types, dietary behaviors, and cultural contexts. This results in AI applications in the dietary field that possess a narrow specialization and limited accuracy. Recently, the emergence of multimodal foundation models such as GPT-4V powering the latest ChatGPT has exhibited transformative potential across a wide range of tasks (e.g., Scene understanding and image captioning) in numerous research domains. These models have demonstrated remarkable generalist intelligence and accuracy, capable of processing various data modalities. In this study, we explore the application of multimodal ChatGPT within the realm of dietary assessment. Our findings reveal that GPT-4V excels in food detection under challenging conditions with accuracy up to 87.5% without any fine-tuning or adaptation using food-specific datasets. By guiding the model with specific language prompts (e.g., African cuisine), it shifts from recognizing common staples like rice and bread to accurately identifying regional dishes like banku and ugali. Another GPT-4V's standout feature is its contextual awareness. GPT-4V can leverage surrounding objects as scale references to deduce the portion sizes of food items, further enhancing its accuracy in translating food weight into nutritional content. This alignment with the USDA National Nutrient Database underscores GPT-4V's potential to advance nutritional science and dietary assessment techniques.
Detecting the Sensing Area of A Laparoscopic Probe in Minimally Invasive Cancer Surgery
Jul 07, 2023



Abstract:In surgical oncology, it is challenging for surgeons to identify lymph nodes and completely resect cancer even with pre-operative imaging systems like PET and CT, because of the lack of reliable intraoperative visualization tools. Endoscopic radio-guided cancer detection and resection has recently been evaluated whereby a novel tethered laparoscopic gamma detector is used to localize a preoperatively injected radiotracer. This can both enhance the endoscopic imaging and complement preoperative nuclear imaging data. However, gamma activity visualization is challenging to present to the operator because the probe is non-imaging and it does not visibly indicate the activity origination on the tissue surface. Initial failed attempts used segmentation or geometric methods, but led to the discovery that it could be resolved by leveraging high-dimensional image features and probe position information. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this solution, we designed and implemented a simple regression network that successfully addressed the problem. To further validate the proposed solution, we acquired and publicly released two datasets captured using a custom-designed, portable stereo laparoscope system. Through intensive experimentation, we demonstrated that our method can successfully and effectively detect the sensing area, establishing a new performance benchmark. Code and data are available at https://github.com/br0202/Sensing_area_detection.git
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge