Daiyun Shen
BCRNet: Enhancing Landmark Detection in Laparoscopic Liver Surgery via Bezier Curve Refinement
Jun 18, 2025


Abstract:Laparoscopic liver surgery, while minimally invasive, poses significant challenges in accurately identifying critical anatomical structures. Augmented reality (AR) systems, integrating MRI/CT with laparoscopic images based on 2D-3D registration, offer a promising solution for enhancing surgical navigation. A vital aspect of the registration progress is the precise detection of curvilinear anatomical landmarks in laparoscopic images. In this paper, we propose BCRNet (Bezier Curve Refinement Net), a novel framework that significantly enhances landmark detection in laparoscopic liver surgery primarily via the Bezier curve refinement strategy. The framework starts with a Multi-modal Feature Extraction (MFE) module designed to robustly capture semantic features. Then we propose Adaptive Curve Proposal Initialization (ACPI) to generate pixel-aligned Bezier curves and confidence scores for reliable initial proposals. Additionally, we design the Hierarchical Curve Refinement (HCR) mechanism to enhance these proposals iteratively through a multi-stage process, capturing fine-grained contextual details from multi-scale pixel-level features for precise Bezier curve adjustment. Extensive evaluations on the L3D and P2ILF datasets demonstrate that BCRNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving significant performance improvements. Code will be available.
Instrument-Splatting: Controllable Photorealistic Reconstruction of Surgical Instruments Using Gaussian Splatting
Mar 06, 2025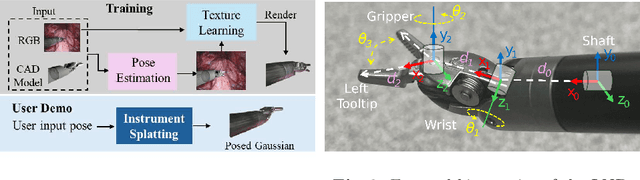
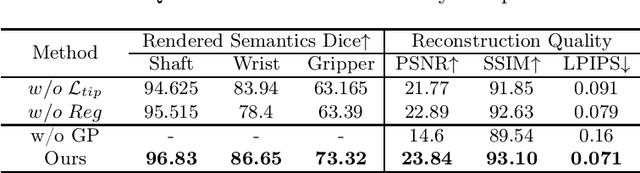
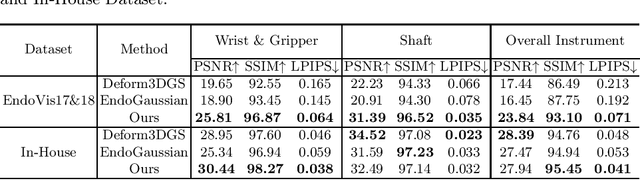
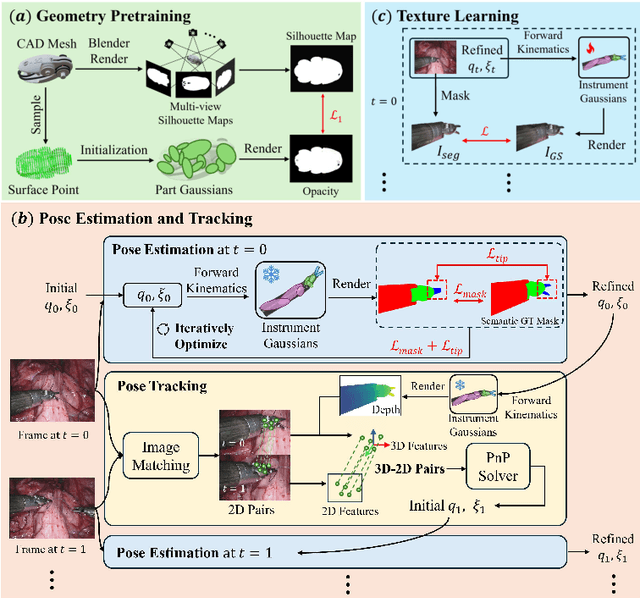
Abstract:Real2Sim is becoming increasingly important with the rapid development of surgical artificial intelligence (AI) and autonomy. In this work, we propose a novel Real2Sim methodology, \textit{Instrument-Splatting}, that leverages 3D Gaussian Splatting to provide fully controllable 3D reconstruction of surgical instruments from monocular surgical videos. To maintain both high visual fidelity and manipulability, we introduce a geometry pre-training to bind Gaussian point clouds on part mesh with accurate geometric priors and define a forward kinematics to control the Gaussians as flexible as real instruments. Afterward, to handle unposed videos, we design a novel instrument pose tracking method leveraging semantics-embedded Gaussians to robustly refine per-frame instrument poses and joint states in a render-and-compare manner, which allows our instrument Gaussian to accurately learn textures and reach photorealistic rendering. We validated our method on 2 publicly released surgical videos and 4 videos collected on ex vivo tissues and green screens. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.
SurgRIPE challenge: Benchmark of Surgical Robot Instrument Pose Estimation
Jan 06, 2025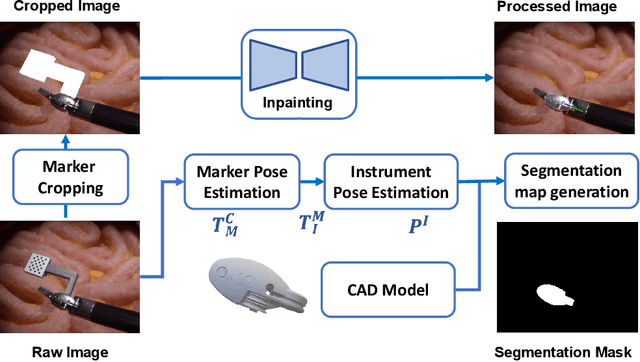
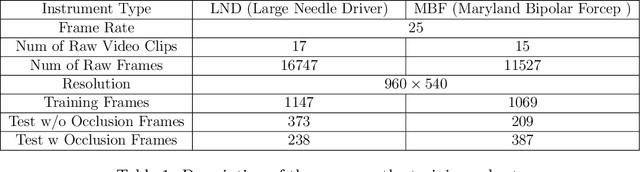
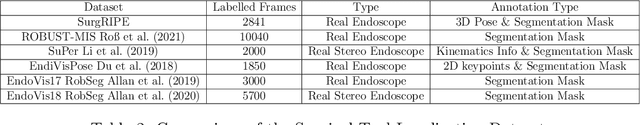
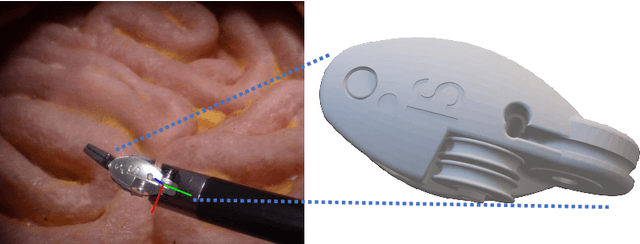
Abstract:Accurate instrument pose estimation is a crucial step towards the future of robotic surgery, enabling applications such as autonomous surgical task execution. Vision-based methods for surgical instrument pose estimation provide a practical approach to tool tracking, but they often require markers to be attached to the instruments. Recently, more research has focused on the development of marker-less methods based on deep learning. However, acquiring realistic surgical data, with ground truth instrument poses, required for deep learning training, is challenging. To address the issues in surgical instrument pose estimation, we introduce the Surgical Robot Instrument Pose Estimation (SurgRIPE) challenge, hosted at the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) in 2023. The objectives of this challenge are: (1) to provide the surgical vision community with realistic surgical video data paired with ground truth instrument poses, and (2) to establish a benchmark for evaluating markerless pose estimation methods. The challenge led to the development of several novel algorithms that showcased improved accuracy and robustness over existing methods. The performance evaluation study on the SurgRIPE dataset highlights the potential of these advanced algorithms to be integrated into robotic surgery systems, paving the way for more precise and autonomous surgical procedures. The SurgRIPE challenge has successfully established a new benchmark for the field, encouraging further research and development in surgical robot instrument pose estimation.
Free-DyGS: Camera-Pose-Free Scene Reconstruction based on Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Surgical Videos
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:Reconstructing endoscopic videos is crucial for high-fidelity visualization and the efficiency of surgical operations. Despite the importance, existing 3D reconstruction methods encounter several challenges, including stringent demands for accuracy, imprecise camera positioning, intricate dynamic scenes, and the necessity for rapid reconstruction. Addressing these issues, this paper presents the first camera-pose-free scene reconstruction framework, Free-DyGS, tailored for dynamic surgical videos, leveraging 3D Gaussian splatting technology. Our approach employs a frame-by-frame reconstruction strategy and is delineated into four distinct phases: Scene Initialization, Joint Learning, Scene Expansion, and Retrospective Learning. We introduce a Generalizable Gaussians Parameterization module within the Scene Initialization and Expansion phases to proficiently generate Gaussian attributes for each pixel from the RGBD frames. The Joint Learning phase is crafted to concurrently deduce scene deformation and camera pose, facilitated by an innovative flexible deformation module. In the scene expansion stage, the Gaussian points gradually grow as the camera moves. The Retrospective Learning phase is dedicated to enhancing the precision of scene deformation through the reassessment of prior frames. The efficacy of the proposed Free-DyGS is substantiated through experiments on two datasets: the StereoMIS and Hamlyn datasets. The experimental outcomes underscore that Free-DyGS surpasses conventional baseline models in both rendering fidelity and computational efficiency.
Deform3DGS: Flexible Deformation for Fast Surgical Scene Reconstruction with Gaussian Splatting
May 29, 2024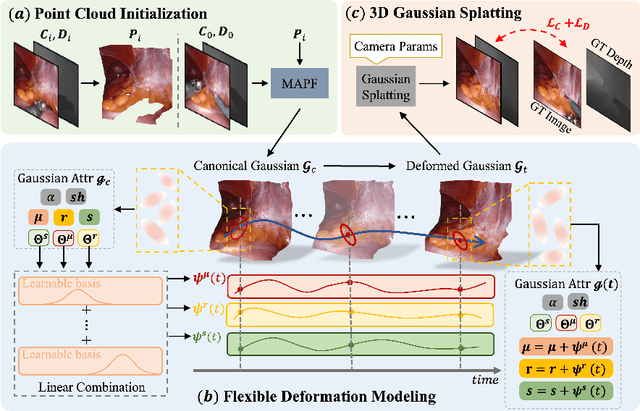
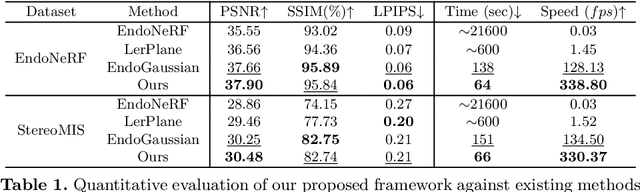
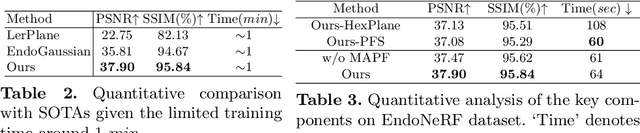
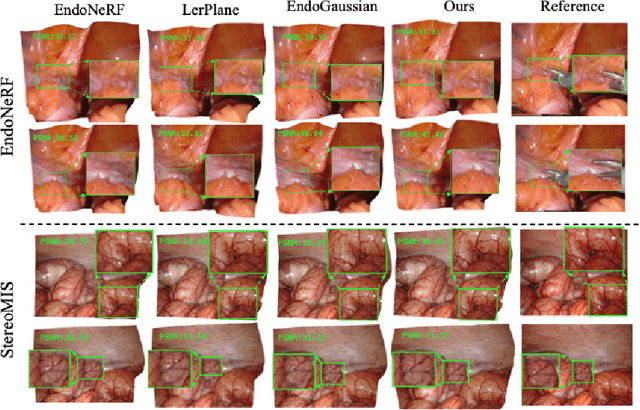
Abstract:Tissue deformation poses a key challenge for accurate surgical scene reconstruction. Despite yielding high reconstruction quality, existing methods suffer from slow rendering speeds and long training times, limiting their intraoperative applicability. Motivated by recent progress in 3D Gaussian Splatting, an emerging technology in real-time 3D rendering, this work presents a novel fast reconstruction framework, termed Deform3DGS, for deformable tissues during endoscopic surgery. Specifically, we introduce 3D GS into surgical scenes by integrating a point cloud initialization to improve reconstruction. Furthermore, we propose a novel flexible deformation modeling scheme (FDM) to learn tissue deformation dynamics at the level of individual Gaussians. Our FDM can model the surface deformation with efficient representations, allowing for real-time rendering performance. More importantly, FDM significantly accelerates surgical scene reconstruction, demonstrating considerable clinical values, particularly in intraoperative settings where time efficiency is crucial. Experiments on DaVinci robotic surgery videos indicate the efficacy of our approach, showcasing superior reconstruction fidelity PSNR: (37.90) and rendering speed (338.8 FPS) while substantially reducing training time to only 1 minute/scene.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge