Qian Li
Beihang University
Reasoning to Rank: An End-to-End Solution for Exploiting Large Language Models for Recommendation
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Recommender systems are tasked to infer users' evolving preferences and rank items aligned with their intents, which calls for in-depth reasoning beyond pattern-based scoring. Recent efforts start to leverage large language models (LLMs) for recommendation, but how to effectively optimize the model for improved recommendation utility is still under explored. In this work, we propose Reasoning to Rank, an end-to-end training framework that internalizes recommendation utility optimization into the learning of step-by-step reasoning in LLMs. To avoid position bias in LLM reasoning and enable direct optimization of the reasoning process, our framework performs reasoning at the user-item level and employs reinforcement learning for end-to-end training of the LLM. Experiments on three Amazon datasets and a large-scale industrial dataset showed consistent gains over strong conventional and LLM-based solutions. Extensive in-depth analyses validate the necessity of the key components in the proposed framework and shed lights on the future developments of this line of work.
S-GRec: Personalized Semantic-Aware Generative Recommendation with Asymmetric Advantage
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Generative recommendation models sequence generation to produce items end-to-end, but training from behavioral logs often provides weak supervision on underlying user intent. Although Large Language Models (LLMs) offer rich semantic priors that could supply such supervision, direct adoption in industrial recommendation is hindered by two obstacles: semantic signals can conflict with platform business objectives, and LLM inference is prohibitively expensive at scale. This paper presents S-GRec, a semantic-aware framework that decouples an online lightweight generator from an offline LLM-based semantic judge for train-time supervision. S-GRec introduces a two-stage Personalized Semantic Judge (PSJ) that produces interpretable aspect evidence and learns user-conditional aggregation from pairwise feedback, yielding stable semantic rewards. To prevent semantic supervision from deviating from business goals, Asymmetric Advantage Policy Optimization (A2PO) anchors optimization on business rewards (e.g., eCPM) and injects semantic advantages only when they are consistent. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks and a large-scale production system validate both effectiveness and scalability, including statistically significant gains in CTR and a 1.19\% lift in GMV in online A/B tests, without requiring real-time LLM inference.
Internalizing Multi-Agent Reasoning for Accurate and Efficient LLM-based Recommendation
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping recommender systems by leveraging extensive world knowledge and semantic reasoning to interpret user intent. However, effectively integrating these capabilities with collaborative signals while avoiding prohibitive inference latency remains a critical bottleneck. To address this, we propose a trajectory-driven internalization framework to develop a Single-agent Trajectory-Aligned Recommender (STAR). Specifically, to internalize complex reasoning capabilities into a single efficient model, we first design a multi-agent teacher system capable of multi-turn tool usage and reflection. This teacher utilizes a Collaborative Signal Translation mechanism to explicitly convert latent behavioral patterns into descriptive natural language evidence to enhance reasoning accuracy. Subsequently, a trajectory-driven distillation pipeline transfers this agentic logic, including planning, tool usage, and self-reflection, into the compact STAR model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that STAR surpasses its teacher by 8.7% to 39.5% while eliminating iterative latency, paving the way for real-time, reasoning-enhanced recommendation.
DiffuReason: Bridging Latent Reasoning and Generative Refinement for Sequential Recommendation
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Latent reasoning has emerged as a promising paradigm for sequential recommendation, enabling models to capture complex user intent through multi-step deliberation. Yet existing approaches often rely on deterministic latent chains that accumulate noise and overlook the uncertainty inherent in user intent, and they are typically trained in staged pipelines that hinder joint optimization and exploration. To address these challenges, we propose DiffuReason, a unified "Think-then-Diffuse" framework for sequential recommendation. It integrates multi-step Thinking Tokens for latent reasoning, diffusion-based refinement for denoising intermediate representations, and end-to-end Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) alignment to optimize for ranking performance. In the Think stage, the model generates Thinking Tokens that reason over user history to form an initial intent hypothesis. In the Diffuse stage, rather than treating this hypothesis as the final output, we refine it through a diffusion process that models user intent as a probabilistic distribution, providing iterative denoising against reasoning noise. Finally, GRPO-based reinforcement learning enables the reasoning and refinement modules to co-evolve throughout training, without the constraints of staged optimization. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that DiffuReason consistently improves diverse backbone architectures. Online A/B tests on a large-scale industrial platform further validate its practical effectiveness.
ChainRec: An Agentic Recommender Learning to Route Tool Chains for Diverse and Evolving Interests
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated into recommender systems, motivating recent interest in agentic and reasoning-based recommendation. However, most existing approaches still rely on fixed workflows, applying the same reasoning procedure across diverse recommendation scenarios. In practice, user contexts vary substantially-for example, in cold-start settings or during interest shifts, so an agent should adaptively decide what evidence to gather next rather than following a scripted process. To address this, we propose ChainRec, an agentic recommender that uses a planner to dynamically select reasoning tools. ChainRec builds a standardized Tool Agent Library from expert trajectories. It then trains a planner using supervised fine-tuning and preference optimization to dynamically select tools, decide their order, and determine when to stop. Experiments on AgentRecBench across Amazon, Yelp, and Goodreads show that ChainRec consistently improves Avg HR@{1,3,5} over strong baselines, with especially notable gains in cold-start and evolving-interest scenarios. Ablation studies further validate the importance of tool standardization and preference-optimized planning.
UI-Venus-1.5 Technical Report
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:GUI agents have emerged as a powerful paradigm for automating interactions in digital environments, yet achieving both broad generality and consistently strong task performance remains challenging.In this report, we present UI-Venus-1.5, a unified, end-to-end GUI Agent designed for robust real-world applications.The proposed model family comprises two dense variants (2B and 8B) and one mixture-of-experts variant (30B-A3B) to meet various downstream application scenarios.Compared to our previous version, UI-Venus-1.5 introduces three key technical advances: (1) a comprehensive Mid-Training stage leveraging 10 billion tokens across 30+ datasets to establish foundational GUI semantics; (2) Online Reinforcement Learning with full-trajectory rollouts, aligning training objectives with long-horizon, dynamic navigation in large-scale environments; and (3) a single unified GUI Agent constructed via Model Merging, which synthesizes domain-specific models (grounding, web, and mobile) into one cohesive checkpoint. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that UI-Venus-1.5 establishes new state-of-the-art performance on benchmarks such as ScreenSpot-Pro (69.6%), VenusBench-GD (75.0%), and AndroidWorld (77.6%), significantly outperforming previous strong baselines. In addition, UI-Venus-1.5 demonstrates robust navigation capabilities across a variety of Chinese mobile apps, effectively executing user instructions in real-world scenarios. Code: https://github.com/inclusionAI/UI-Venus; Model: https://huggingface.co/collections/inclusionAI/ui-venus
FlyPrompt: Brain-Inspired Random-Expanded Routing with Temporal-Ensemble Experts for General Continual Learning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:General continual learning (GCL) challenges intelligent systems to learn from single-pass, non-stationary data streams without clear task boundaries. While recent advances in continual parameter-efficient tuning (PET) of pretrained models show promise, they typically rely on multiple training epochs and explicit task cues, limiting their effectiveness in GCL scenarios. Moreover, existing methods often lack targeted design and fail to address two fundamental challenges in continual PET: how to allocate expert parameters to evolving data distributions, and how to improve their representational capacity under limited supervision. Inspired by the fruit fly's hierarchical memory system characterized by sparse expansion and modular ensembles, we propose FlyPrompt, a brain-inspired framework that decomposes GCL into two subproblems: expert routing and expert competence improvement. FlyPrompt introduces a randomly expanded analytic router for instance-level expert activation and a temporal ensemble of output heads to dynamically adapt decision boundaries over time. Extensive theoretical and empirical evaluations demonstrate FlyPrompt's superior performance, achieving up to 11.23%, 12.43%, and 7.62% gains over state-of-the-art baselines on CIFAR-100, ImageNet-R, and CUB-200, respectively. Our source code is available at https://github.com/AnAppleCore/FlyGCL.
AMA: Adaptive Memory via Multi-Agent Collaboration
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The rapid evolution of Large Language Model (LLM) agents has necessitated robust memory systems to support cohesive long-term interaction and complex reasoning. Benefiting from the strong capabilities of LLMs, recent research focus has shifted from simple context extension to the development of dedicated agentic memory systems. However, existing approaches typically rely on rigid retrieval granularity, accumulation-heavy maintenance strategies, and coarse-grained update mechanisms. These design choices create a persistent mismatch between stored information and task-specific reasoning demands, while leading to the unchecked accumulation of logical inconsistencies over time. To address these challenges, we propose Adaptive Memory via Multi-Agent Collaboration (AMA), a novel framework that leverages coordinated agents to manage memory across multiple granularities. AMA employs a hierarchical memory design that dynamically aligns retrieval granularity with task complexity. Specifically, the Constructor and Retriever jointly enable multi-granularity memory construction and adaptive query routing. The Judge verifies the relevance and consistency of retrieved content, triggering iterative retrieval when evidence is insufficient or invoking the Refresher upon detecting logical conflicts. The Refresher then enforces memory consistency by performing targeted updates or removing outdated entries. Extensive experiments on challenging long-context benchmarks show that AMA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines while reducing token consumption by approximately 80% compared to full-context methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in maintaining retrieval precision and long-term memory consistency.
High-Rank Structured Modulation for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:As the number of model parameters increases, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) has become the go-to choice for tailoring pre-trained large language models. Low-rank Adaptation (LoRA) uses a low-rank update method to simulate full parameter fine-tuning, which is widely used to reduce resource requirements. However, decreasing the rank encounters challenges with limited representational capacity when compared to full parameter fine-tuning. We present \textbf{SMoA}, a high-rank \textbf{S}tructured \textbf{MO}dulation \textbf{A}dapter that uses fewer trainable parameters while maintaining a higher rank, thereby improving the model's representational capacity and offering improved performance potential. The core idea is to freeze the original pretrained weights and selectively amplify or suppress important features of the original weights across multiple subspaces. The subspace mechanism provides an efficient way to increase the capacity and complexity of a model. We conduct both theoretical analyses and empirical studies on various tasks. Experiment results show that SMoA outperforms LoRA and its variants on 10 tasks, with extensive ablation studies validating its effectiveness.
GPR: Towards a Generative Pre-trained One-Model Paradigm for Large-Scale Advertising Recommendation
Nov 13, 2025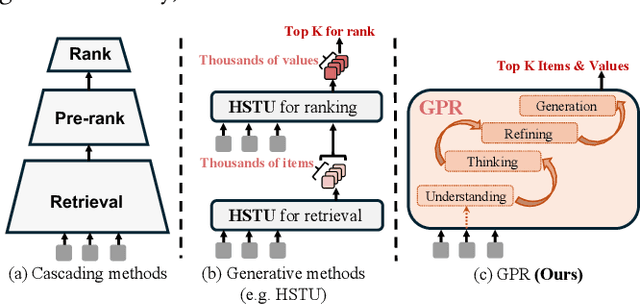
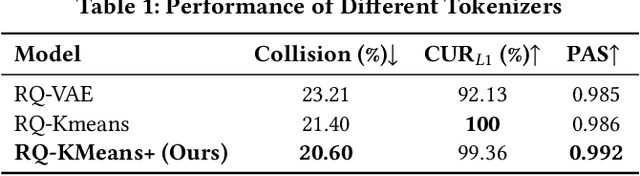
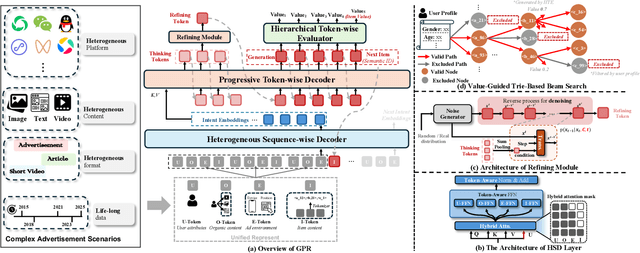
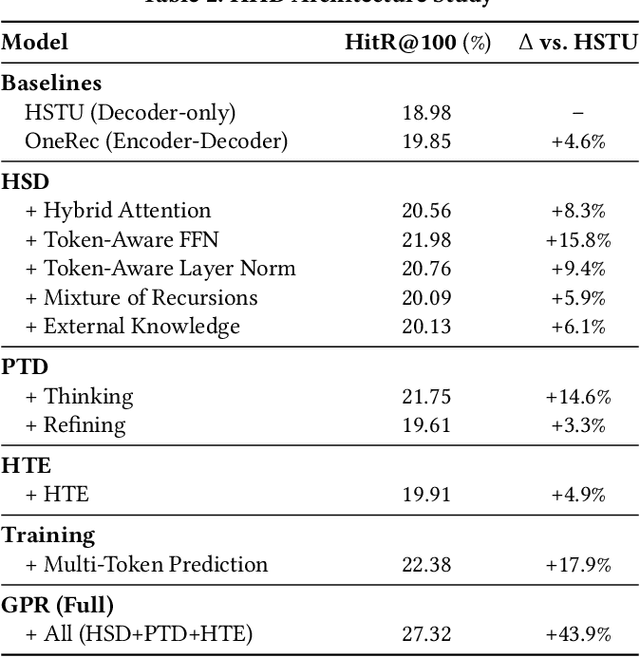
Abstract:As an intelligent infrastructure connecting users with commercial content, advertising recommendation systems play a central role in information flow and value creation within the digital economy. However, existing multi-stage advertising recommendation systems suffer from objective misalignment and error propagation, making it difficult to achieve global optimality, while unified generative recommendation models still struggle to meet the demands of practical industrial applications. To address these issues, we propose GPR (Generative Pre-trained Recommender), the first one-model framework that redefines advertising recommendation as an end-to-end generative task, replacing the traditional cascading paradigm with a unified generative approach. To realize GPR, we introduce three key innovations spanning unified representation, network architecture, and training strategy. First, we design a unified input schema and tokenization method tailored to advertising scenarios, mapping both ads and organic content into a shared multi-level semantic ID space, thereby enhancing semantic alignment and modeling consistency across heterogeneous data. Second, we develop the Heterogeneous Hierarchical Decoder (HHD), a dual-decoder architecture that decouples user intent modeling from ad generation, achieving a balance between training efficiency and inference flexibility while maintaining strong modeling capacity. Finally, we propose a multi-stage joint training strategy that integrates Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), Value-Aware Fine-Tuning and the Hierarchy Enhanced Policy Optimization (HEPO) algorithm, forming a complete generative recommendation pipeline that unifies interest modeling, value alignment, and policy optimization. GPR has been fully deployed in the Tencent Weixin Channels advertising system, delivering significant improvements in key business metrics including GMV and CTCVR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge