Yanbing Liu
CRAFT: Calibrated Reasoning with Answer-Faithful Traces via Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Hop Question Answering
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is widely used to ground Large Language Models (LLMs) for multi-hop question answering. Recent work mainly focused on improving answer accuracy via fine-tuning and structured or reinforcement-based optimization. However, reliable reasoning in response generation faces three challenges: 1) Reasoning Collapse. Reasoning in multi-hop QA is inherently complex due to multi-hop composition and is further destabilized by noisy retrieval. 2) Reasoning-answer inconsistency. Due to the intrinsic uncertainty of LLM generation and exposure to evidence--distractor mixtures, models may produce correct answers that are not faithfully supported by their intermediate reasoning or evidence. 3) Loss of format control. Traditional chain-of-thought generation often deviates from required structured output formats, leading to incomplete or malformed structured content. To address these challenges, we propose CRAFT (Calibrated Reasoning with Answer-Faithful Traces), a Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) based reinforcement learning framework that trains models to perform faithful reasoning during response generation. CRAFT employs dual reward mechanisms to optimize multi-hop reasoning: deterministic rewards ensure structural correctness while judge-based rewards verify semantic faithfulness. This optimization framework supports controllable trace variants that enable systematic analysis of how structure and scale affect reasoning performance and faithfulness. Experiments on three multi-hop QA benchmarks show that CRAFT improves both answer accuracy and reasoning faithfulness across model scales, with the CRAFT 7B model achieving competitive performance with closed-source LLMs across multiple reasoning trace settings.
Beyond Accuracy: A Cognitive Load Framework for Mapping the Capability Boundaries of Tool-use Agents
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to use external tools unlocks powerful real-world interactions, making rigorous evaluation essential. However, current benchmarks primarily report final accuracy, revealing what models can do but obscuring the cognitive bottlenecks that define their true capability boundaries. To move from simple performance scoring to a diagnostic tool, we introduce a framework grounded in Cognitive Load Theory. Our framework deconstructs task complexity into two quantifiable components: Intrinsic Load, the inherent structural complexity of the solution path, formalized with a novel Tool Interaction Graph; and Extraneous Load, the difficulty arising from ambiguous task presentation. To enable controlled experiments, we construct ToolLoad-Bench, the first benchmark with parametrically adjustable cognitive load. Our evaluation reveals distinct performance cliffs as cognitive load increases, allowing us to precisely map each model's capability boundary. We validate that our framework's predictions are highly calibrated with empirical results, establishing a principled methodology for understanding an agent's limits and a practical foundation for building more efficient systems.
MuVaC: AVariational Causal Framework for Multimodal Sarcasm Understanding in Dialogues
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The prevalence of sarcasm in multimodal dialogues on the social platforms presents a crucial yet challenging task for understanding the true intent behind online content. Comprehensive sarcasm analysis requires two key aspects: Multimodal Sarcasm Detection (MSD) and Multimodal Sarcasm Explanation (MuSE). Intuitively, the act of detection is the result of the reasoning process that explains the sarcasm. Current research predominantly focuses on addressing either MSD or MuSE as a single task. Even though some recent work has attempted to integrate these tasks, their inherent causal dependency is often overlooked. To bridge this gap, we propose MuVaC, a variational causal inference framework that mimics human cognitive mechanisms for understanding sarcasm, enabling robust multimodal feature learning to jointly optimize MSD and MuSE. Specifically, we first model MSD and MuSE from the perspective of structural causal models, establishing variational causal pathways to define the objectives for joint optimization. Next, we design an alignment-then-fusion approach to integrate multimodal features, providing robust fusion representations for sarcasm detection and explanation generation. Finally, we enhance the reasoning trustworthiness by ensuring consistency between detection results and explanations. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of MuVaC in public datasets, offering a new perspective for understanding multimodal sarcasm.
PEARL: Plan Exploration and Adaptive Reinforcement Learning for Multihop Tool Use
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models show great potential with external tools, but face significant challenges in complex, multi-turn tool invocation. They often exhibit weak planning, tool hallucination, erroneous parameter generation, and struggle with robust interaction. To tackle these issues, we present PEARL, a novel framework to enhance LLM planning and execution for sophisticated tool use. PEARL adopts a two-stage approach: an offline phase where the agent explores tools to learn valid usage patterns and failure conditions, and an online reinforcement learning phase. In the online phase, a dedicated Planner is trained via group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with a carefully designed reward function that provides distinct signals for planning quality. Experiments on the ToolHop and T-Eval benchmarks show PEARL significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving a new state-of-the-art success rate of \textbf{56.5\%} on ToolHop while maintaining a low invocation error rate. Our work marks a key advance in addressing the complex planning challenges of tool use, contributing to the development of more robust and reliable LLM-based agents.
MemGovern: Enhancing Code Agents through Learning from Governed Human Experiences
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:While autonomous software engineering (SWE) agents are reshaping programming paradigms, they currently suffer from a "closed-world" limitation: they attempt to fix bugs from scratch or solely using local context, ignoring the immense historical human experience available on platforms like GitHub. Accessing this open-world experience is hindered by the unstructured and fragmented nature of real-world issue-tracking data. In this paper, we introduce MemGovern, a framework designed to govern and transform raw GitHub data into actionable experiential memory for agents. MemGovern employs experience governance to convert human experience into agent-friendly experience cards and introduces an agentic experience search strategy that enables logic-driven retrieval of human expertise. By producing 135K governed experience cards, MemGovern achieves a significant performance boost, improving resolution rates on the SWE-bench Verified by 4.65%. As a plug-in approach, MemGovern provides a solution for agent-friendly memory infrastructure.
LitVISTA: A Benchmark for Narrative Orchestration in Literary Text
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Computational narrative analysis aims to capture rhythm, tension, and emotional dynamics in literary texts. Existing large language models can generate long stories but overly focus on causal coherence, neglecting the complex story arcs and orchestration inherent in human narratives. This creates a structural misalignment between model- and human-generated narratives. We propose VISTA Space, a high-dimensional representational framework for narrative orchestration that unifies human and model narrative perspectives. We further introduce LitVISTA, a structurally annotated benchmark grounded in literary texts, enabling systematic evaluation of models' narrative orchestration capabilities. We conduct oracle evaluations on a diverse selection of frontier LLMs, including GPT, Claude, Grok, and Gemini. Results reveal systematic deficiencies: existing models fail to construct a unified global narrative view, struggling to jointly capture narrative function and structure. Furthermore, even advanced thinking modes yield only limited gains for such literary narrative understanding.
FaithSCAN: Model-Driven Single-Pass Hallucination Detection for Faithful Visual Question Answering
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Faithfulness hallucinations in VQA occur when vision-language models produce fluent yet visually ungrounded answers, severely undermining their reliability in safety-critical applications. Existing detection methods mainly fall into two categories: external verification approaches relying on auxiliary models or knowledge bases, and uncertainty-driven approaches using repeated sampling or uncertainty estimates. The former suffer from high computational overhead and are limited by external resource quality, while the latter capture only limited facets of model uncertainty and fail to sufficiently explore the rich internal signals associated with the diverse failure modes. Both paradigms thus have inherent limitations in efficiency, robustness, and detection performance. To address these challenges, we propose FaithSCAN: a lightweight network that detects hallucinations by exploiting rich internal signals of VLMs, including token-level decoding uncertainty, intermediate visual representations, and cross-modal alignment features. These signals are fused via branch-wise evidence encoding and uncertainty-aware attention. We also extend the LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm to VQA hallucination and propose a low-cost strategy to automatically generate model-dependent supervision signals, enabling supervised training without costly human labels while maintaining high detection accuracy. Experiments on multiple VQA benchmarks show that FaithSCAN significantly outperforms existing methods in both effectiveness and efficiency. In-depth analysis shows hallucinations arise from systematic internal state variations in visual perception, cross-modal reasoning, and language decoding. Different internal signals provide complementary diagnostic cues, and hallucination patterns vary across VLM architectures, offering new insights into the underlying causes of multimodal hallucinations.
HaluNet: Multi-Granular Uncertainty Modeling for Efficient Hallucination Detection in LLM Question Answering
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at question answering (QA) but often generate hallucinations, including factual errors or fabricated content. Detecting hallucinations from internal uncertainty signals is attractive due to its scalability and independence from external resources. Existing methods often aim to accurately capture a single type of uncertainty while overlooking the complementarity among different sources, particularly between token-level probability uncertainty and the uncertainty conveyed by internal semantic representations, which provide complementary views on model reliability. We present \textbf{HaluNet}, a lightweight and trainable neural framework that integrates multi granular token level uncertainties by combining semantic embeddings with probabilistic confidence and distributional uncertainty. Its multi branch architecture adaptively fuses what the model knows with the uncertainty expressed in its outputs, enabling efficient one pass hallucination detection. Experiments on SQuAD, TriviaQA, and Natural Questions show that HaluNet delivers strong detection performance and favorable computational efficiency, with or without access to context, highlighting its potential for real time hallucination detection in LLM based QA systems.
Emotion Transfer with Enhanced Prototype for Unseen Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Aug 27, 2025
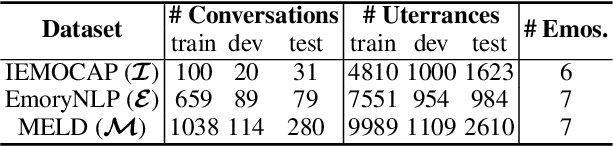

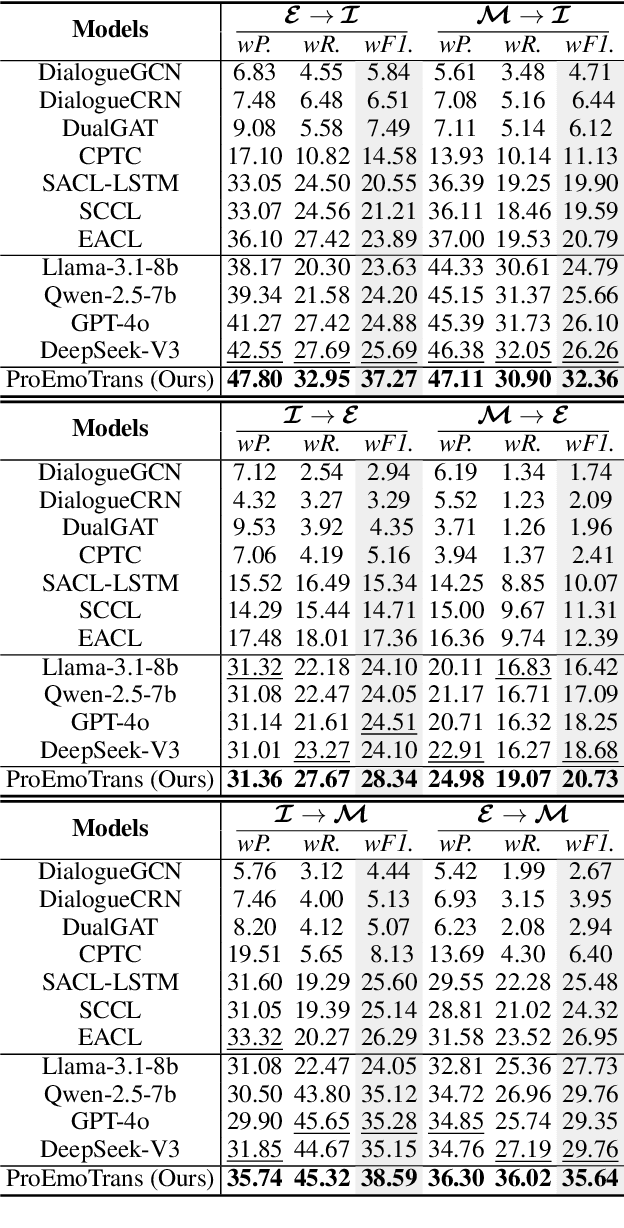
Abstract:Current Emotion Recognition in Conversation (ERC) research follows a closed-domain assumption. However, there is no clear consensus on emotion classification in psychology, which presents a challenge for models when it comes to recognizing previously unseen emotions in real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we introduce the Unseen Emotion Recognition in Conversation (UERC) task for the first time and propose ProEmoTrans, a solid prototype-based emotion transfer framework. This prototype-based approach shows promise but still faces key challenges: First, implicit expressions complicate emotion definition, which we address by proposing an LLM-enhanced description approach. Second, utterance encoding in long conversations is difficult, which we tackle with a proposed parameter-free mechanism for efficient encoding and overfitting prevention. Finally, the Markovian flow nature of emotions is hard to transfer, which we address with an improved Attention Viterbi Decoding (AVD) method to transfer seen emotion transitions to unseen emotions. Extensive experiments on three datasets show that our method serves as a strong baseline for preliminary exploration in this new area.
Dialogues Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Extraction via Structural Entropy Minimization Partitioning
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Dialogues Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Extraction (DiaASQ) aims to extract all target-aspect-opinion-sentiment quadruples from a given multi-round, multi-participant dialogue. Existing methods typically learn word relations across entire dialogues, assuming a uniform distribution of sentiment elements. However, we find that dialogues often contain multiple semantically independent sub-dialogues without clear dependencies between them. Therefore, learning word relationships across the entire dialogue inevitably introduces additional noise into the extraction process. To address this, our method focuses on partitioning dialogues into semantically independent sub-dialogues. Achieving completeness while minimizing these sub-dialogues presents a significant challenge. Simply partitioning based on reply relationships is ineffective. Instead, we propose utilizing a structural entropy minimization algorithm to partition the dialogues. This approach aims to preserve relevant utterances while distinguishing irrelevant ones as much as possible. Furthermore, we introduce a two-step framework for quadruple extraction: first extracting individual sentiment elements at the utterance level, then matching quadruples at the sub-dialogue level. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in DiaASQ with much lower computational costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge