Cong Cao
CRAFT: Calibrated Reasoning with Answer-Faithful Traces via Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Hop Question Answering
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is widely used to ground Large Language Models (LLMs) for multi-hop question answering. Recent work mainly focused on improving answer accuracy via fine-tuning and structured or reinforcement-based optimization. However, reliable reasoning in response generation faces three challenges: 1) Reasoning Collapse. Reasoning in multi-hop QA is inherently complex due to multi-hop composition and is further destabilized by noisy retrieval. 2) Reasoning-answer inconsistency. Due to the intrinsic uncertainty of LLM generation and exposure to evidence--distractor mixtures, models may produce correct answers that are not faithfully supported by their intermediate reasoning or evidence. 3) Loss of format control. Traditional chain-of-thought generation often deviates from required structured output formats, leading to incomplete or malformed structured content. To address these challenges, we propose CRAFT (Calibrated Reasoning with Answer-Faithful Traces), a Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) based reinforcement learning framework that trains models to perform faithful reasoning during response generation. CRAFT employs dual reward mechanisms to optimize multi-hop reasoning: deterministic rewards ensure structural correctness while judge-based rewards verify semantic faithfulness. This optimization framework supports controllable trace variants that enable systematic analysis of how structure and scale affect reasoning performance and faithfulness. Experiments on three multi-hop QA benchmarks show that CRAFT improves both answer accuracy and reasoning faithfulness across model scales, with the CRAFT 7B model achieving competitive performance with closed-source LLMs across multiple reasoning trace settings.
MuVaC: AVariational Causal Framework for Multimodal Sarcasm Understanding in Dialogues
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The prevalence of sarcasm in multimodal dialogues on the social platforms presents a crucial yet challenging task for understanding the true intent behind online content. Comprehensive sarcasm analysis requires two key aspects: Multimodal Sarcasm Detection (MSD) and Multimodal Sarcasm Explanation (MuSE). Intuitively, the act of detection is the result of the reasoning process that explains the sarcasm. Current research predominantly focuses on addressing either MSD or MuSE as a single task. Even though some recent work has attempted to integrate these tasks, their inherent causal dependency is often overlooked. To bridge this gap, we propose MuVaC, a variational causal inference framework that mimics human cognitive mechanisms for understanding sarcasm, enabling robust multimodal feature learning to jointly optimize MSD and MuSE. Specifically, we first model MSD and MuSE from the perspective of structural causal models, establishing variational causal pathways to define the objectives for joint optimization. Next, we design an alignment-then-fusion approach to integrate multimodal features, providing robust fusion representations for sarcasm detection and explanation generation. Finally, we enhance the reasoning trustworthiness by ensuring consistency between detection results and explanations. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of MuVaC in public datasets, offering a new perspective for understanding multimodal sarcasm.
Learning Sewing Patterns via Latent Flow Matching of Implicit Fields
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Sewing patterns define the structural foundation of garments and are essential for applications such as fashion design, fabrication, and physical simulation. Despite progress in automated pattern generation, accurately modeling sewing patterns remains difficult due to the broad variability in panel geometry and seam arrangements. In this work, we introduce a sewing pattern modeling method based on an implicit representation. We represent each panel using a signed distance field that defines its boundary and an unsigned distance field that identifies seam endpoints, and encode these fields into a continuous latent space that enables differentiable meshing. A latent flow matching model learns distributions over panel combinations in this representation, and a stitching prediction module recovers seam relations from extracted edge segments. This formulation allows accurate modeling and generation of sewing patterns with complex structures. We further show that it can be used to estimate sewing patterns from images with improved accuracy relative to existing approaches, and supports applications such as pattern completion and refitting, providing a practical tool for digital fashion design.
Parameter-Efficient MoE LoRA for Few-Shot Multi-Style Editing
Nov 14, 2025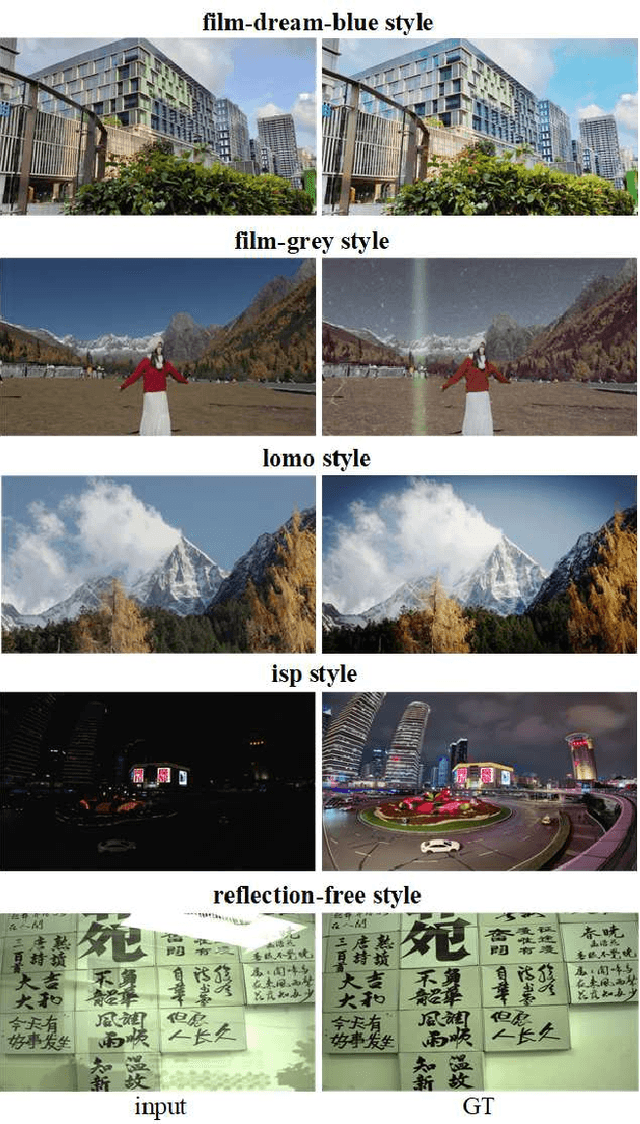
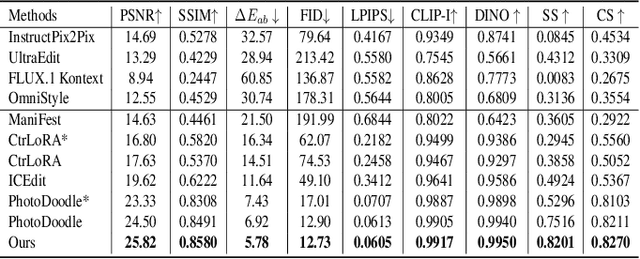

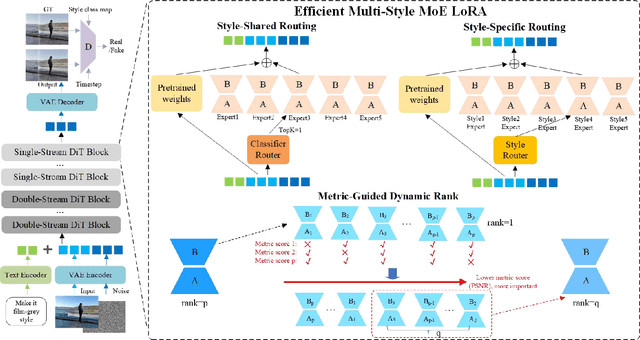
Abstract:In recent years, image editing has garnered growing attention. However, general image editing models often fail to produce satisfactory results when confronted with new styles. The challenge lies in how to effectively fine-tune general image editing models to new styles using only a limited amount of paired data. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel few-shot style editing framework. For this task, we construct a benchmark dataset that encompasses five distinct styles. Correspondingly, we propose a parameter-efficient multi-style Mixture-of-Experts Low-Rank Adaptation (MoE LoRA) with style-specific and style-shared routing mechanisms for jointly fine-tuning multiple styles. The style-specific routing ensures that different styles do not interfere with one another, while the style-shared routing adaptively allocates shared MoE LoRAs to learn common patterns. Our MoE LoRA can automatically determine the optimal ranks for each layer through a novel metric-guided approach that estimates the importance score of each single-rank component. Additionally, we explore the optimal location to insert LoRA within the Diffusion in Transformer (DiT) model and integrate adversarial learning and flow matching to guide the diffusion training process. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches with significantly fewer LoRA parameters.
LUIVITON: Learned Universal Interoperable VIrtual Try-ON
Sep 05, 2025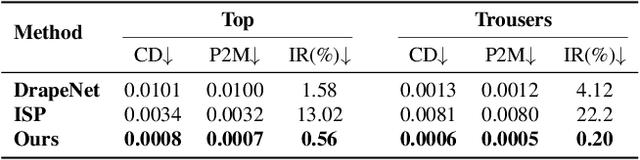
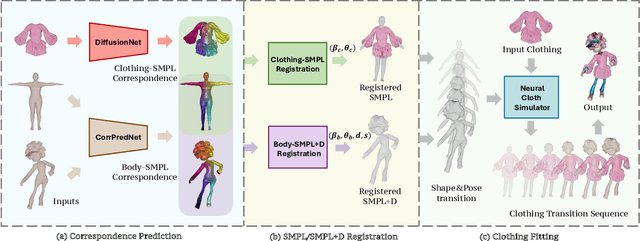
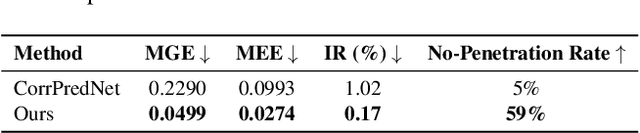
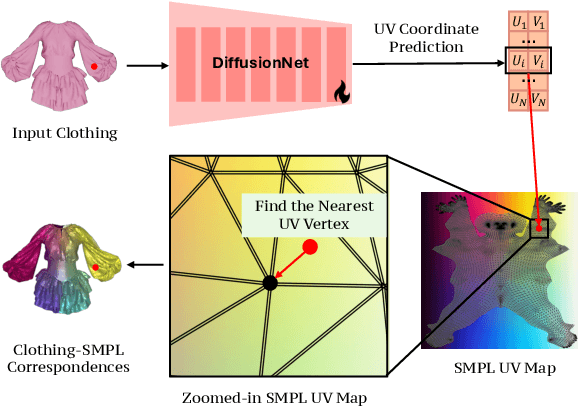
Abstract:We present LUIVITON, an end-to-end system for fully automated virtual try-on, capable of draping complex, multi-layer clothing onto diverse and arbitrarily posed humanoid characters. To address the challenge of aligning complex garments with arbitrary and highly diverse body shapes, we use SMPL as a proxy representation and separate the clothing-to-body draping problem into two correspondence tasks: 1) clothing-to-SMPL and 2) body-to-SMPL correspondence, where each has its unique challenges. While we address the clothing-to-SMPL fitting problem using a geometric learning-based approach for partial-to-complete shape correspondence prediction, we introduce a diffusion model-based approach for body-to-SMPL correspondence using multi-view consistent appearance features and a pre-trained 2D foundation model. Our method can handle complex geometries, non-manifold meshes, and generalizes effectively to a wide range of humanoid characters -- including humans, robots, cartoon subjects, creatures, and aliens, while maintaining computational efficiency for practical adoption. In addition to offering a fully automatic fitting solution, LUIVITON supports fast customization of clothing size, allowing users to adjust clothing sizes and material properties after they have been draped. We show that our system can produce high-quality 3D clothing fittings without any human labor, even when 2D clothing sewing patterns are not available.
Emotion Transfer with Enhanced Prototype for Unseen Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Aug 27, 2025
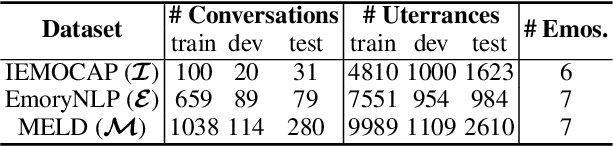

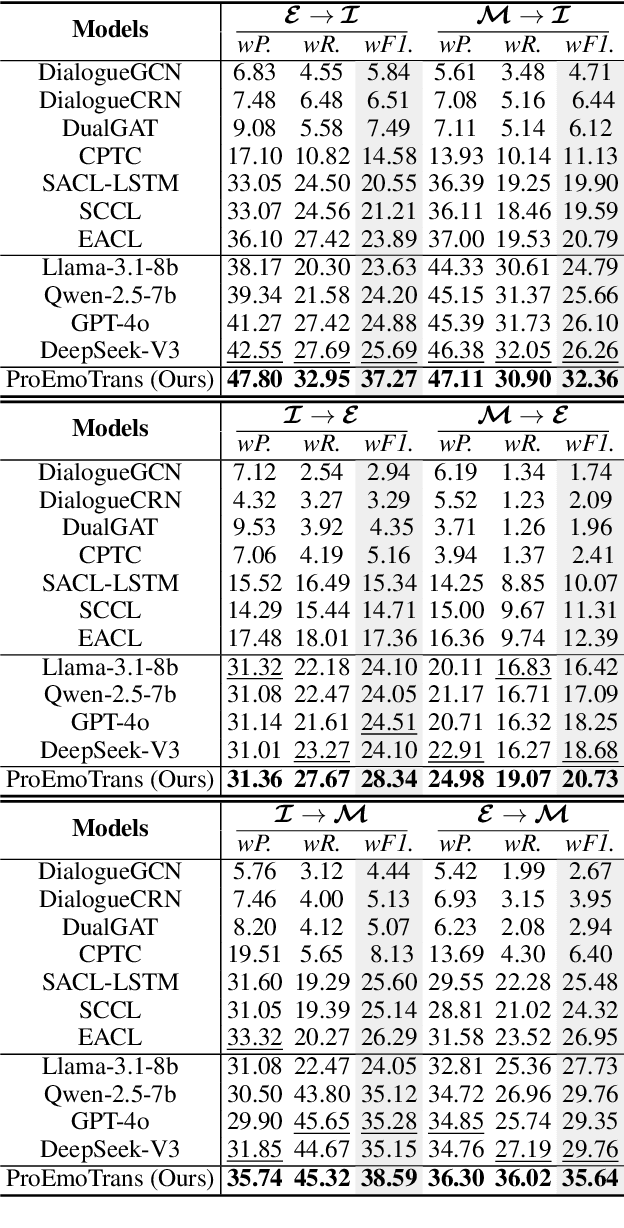
Abstract:Current Emotion Recognition in Conversation (ERC) research follows a closed-domain assumption. However, there is no clear consensus on emotion classification in psychology, which presents a challenge for models when it comes to recognizing previously unseen emotions in real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we introduce the Unseen Emotion Recognition in Conversation (UERC) task for the first time and propose ProEmoTrans, a solid prototype-based emotion transfer framework. This prototype-based approach shows promise but still faces key challenges: First, implicit expressions complicate emotion definition, which we address by proposing an LLM-enhanced description approach. Second, utterance encoding in long conversations is difficult, which we tackle with a proposed parameter-free mechanism for efficient encoding and overfitting prevention. Finally, the Markovian flow nature of emotions is hard to transfer, which we address with an improved Attention Viterbi Decoding (AVD) method to transfer seen emotion transitions to unseen emotions. Extensive experiments on three datasets show that our method serves as a strong baseline for preliminary exploration in this new area.
Dialogues Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Extraction via Structural Entropy Minimization Partitioning
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Dialogues Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Extraction (DiaASQ) aims to extract all target-aspect-opinion-sentiment quadruples from a given multi-round, multi-participant dialogue. Existing methods typically learn word relations across entire dialogues, assuming a uniform distribution of sentiment elements. However, we find that dialogues often contain multiple semantically independent sub-dialogues without clear dependencies between them. Therefore, learning word relationships across the entire dialogue inevitably introduces additional noise into the extraction process. To address this, our method focuses on partitioning dialogues into semantically independent sub-dialogues. Achieving completeness while minimizing these sub-dialogues presents a significant challenge. Simply partitioning based on reply relationships is ineffective. Instead, we propose utilizing a structural entropy minimization algorithm to partition the dialogues. This approach aims to preserve relevant utterances while distinguishing irrelevant ones as much as possible. Furthermore, we introduce a two-step framework for quadruple extraction: first extracting individual sentiment elements at the utterance level, then matching quadruples at the sub-dialogue level. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in DiaASQ with much lower computational costs.
T-T: Table Transformer for Tagging-based Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction
May 08, 2025Abstract:Aspect sentiment triplet extraction (ASTE) aims to extract triplets composed of aspect terms, opinion terms, and sentiment polarities from given sentences. The table tagging method is a popular approach to addressing this task, which encodes a sentence into a 2-dimensional table, allowing for the tagging of relations between any two words. Previous efforts have focused on designing various downstream relation learning modules to better capture interactions between tokens in the table, revealing that a stronger capability to capture relations can lead to greater improvements in the model. Motivated by this, we attempt to directly utilize transformer layers as downstream relation learning modules. Due to the powerful semantic modeling capability of transformers, it is foreseeable that this will lead to excellent improvement. However, owing to the quadratic relation between the length of the table and the length of the input sentence sequence, using transformers directly faces two challenges: overly long table sequences and unfair local attention interaction. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Table-Transformer (T-T) for the tagging-based ASTE method. Specifically, we introduce a stripe attention mechanism with a loop-shift strategy to tackle these challenges. The former modifies the global attention mechanism to only attend to a 2-dimensional local attention window, while the latter facilitates interaction between different attention windows. Extensive and comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the T-T, as a downstream relation learning module, achieves state-of-the-art performance with lower computational costs.
Single View Garment Reconstruction Using Diffusion Mapping Via Pattern Coordinates
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing 3D clothed humans from images is fundamental to applications like virtual try-on, avatar creation, and mixed reality. While recent advances have enhanced human body recovery, accurate reconstruction of garment geometry -- especially for loose-fitting clothing -- remains an open challenge. We present a novel method for high-fidelity 3D garment reconstruction from single images that bridges 2D and 3D representations. Our approach combines Implicit Sewing Patterns (ISP) with a generative diffusion model to learn rich garment shape priors in a 2D UV space. A key innovation is our mapping model that establishes correspondences between 2D image pixels, UV pattern coordinates, and 3D geometry, enabling joint optimization of both 3D garment meshes and the corresponding 2D patterns by aligning learned priors with image observations. Despite training exclusively on synthetically simulated cloth data, our method generalizes effectively to real-world images, outperforming existing approaches on both tight- and loose-fitting garments. The reconstructed garments maintain physical plausibility while capturing fine geometric details, enabling downstream applications including garment retargeting and texture manipulation.
Multi-View Incongruity Learning for Multimodal Sarcasm Detection
Dec 01, 2024Abstract:Multimodal sarcasm detection (MSD) is essential for various downstream tasks. Existing MSD methods tend to rely on spurious correlations. These methods often mistakenly prioritize non-essential features yet still make correct predictions, demonstrating poor generalizability beyond training environments. Regarding this phenomenon, this paper undertakes several initiatives. Firstly, we identify two primary causes that lead to the reliance of spurious correlations. Secondly, we address these challenges by proposing a novel method that integrate Multimodal Incongruities via Contrastive Learning (MICL) for multimodal sarcasm detection. Specifically, we first leverage incongruity to drive multi-view learning from three views: token-patch, entity-object, and sentiment. Then, we introduce extensive data augmentation to mitigate the biased learning of the textual modality. Additionally, we construct a test set, SPMSD, which consists potential spurious correlations to evaluate the the model's generalizability. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of MICL on benchmark datasets, along with the analyses showcasing MICL's advancement in mitigating the effect of spurious correlation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge