Yangxi Li
PathMind: A Retrieve-Prioritize-Reason Framework for Knowledge Graph Reasoning with Large Language Models
Nov 18, 2025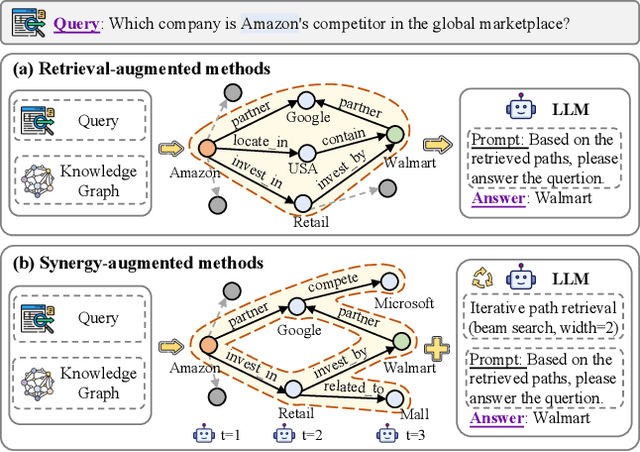
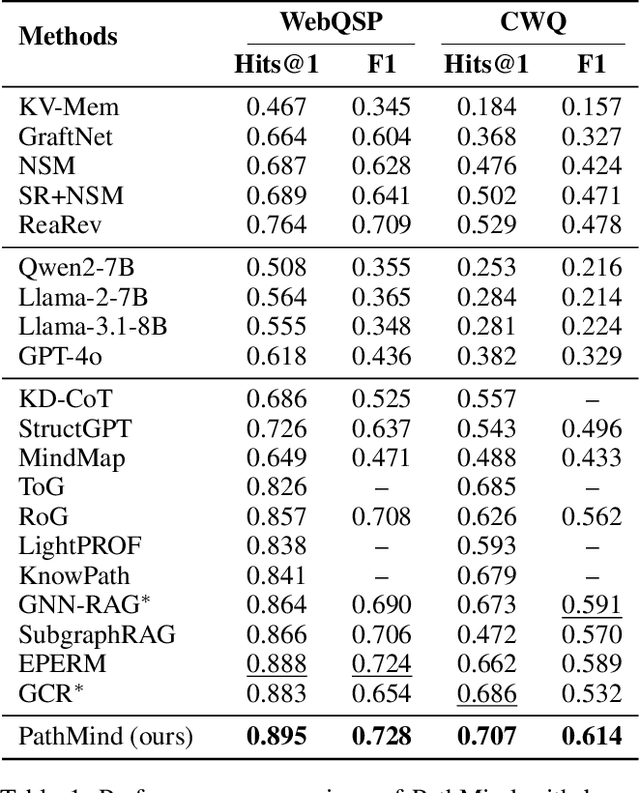
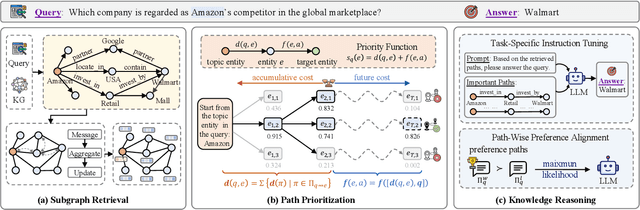
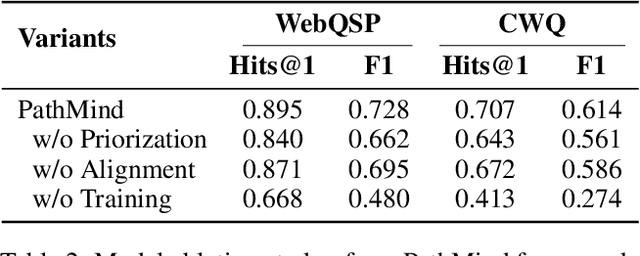
Abstract:Knowledge graph reasoning (KGR) is the task of inferring new knowledge by performing logical deductions on knowledge graphs. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in complex reasoning tasks. Despite promising success, current LLM-based KGR methods still face two critical limitations. First, existing methods often extract reasoning paths indiscriminately, without assessing their different importance, which may introduce irrelevant noise that misleads LLMs. Second, while many methods leverage LLMs to dynamically explore potential reasoning paths, they require high retrieval demands and frequent LLM calls. To address these limitations, we propose PathMind, a novel framework designed to enhance faithful and interpretable reasoning by selectively guiding LLMs with important reasoning paths. Specifically, PathMind follows a "Retrieve-Prioritize-Reason" paradigm. First, it retrieves a query subgraph from KG through the retrieval module. Next, it introduces a path prioritization mechanism that identifies important reasoning paths using a semantic-aware path priority function, which simultaneously considers the accumulative cost and the estimated future cost for reaching the target. Finally, PathMind generates accurate and logically consistent responses via a dual-phase training strategy, including task-specific instruction tuning and path-wise preference alignment. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that PathMind consistently outperforms competitive baselines, particularly on complex reasoning tasks with fewer input tokens, by identifying essential reasoning paths.
Reliably Bounding False Positives: A Zero-Shot Machine-Generated Text Detection Framework via Multiscaled Conformal Prediction
May 08, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models has raised significant concerns regarding their potential misuse by malicious actors. As a result, developing effective detectors to mitigate these risks has become a critical priority. However, most existing detection methods focus excessively on detection accuracy, often neglecting the societal risks posed by high false positive rates (FPRs). This paper addresses this issue by leveraging Conformal Prediction (CP), which effectively constrains the upper bound of FPRs. While directly applying CP constrains FPRs, it also leads to a significant reduction in detection performance. To overcome this trade-off, this paper proposes a Zero-Shot Machine-Generated Text Detection Framework via Multiscaled Conformal Prediction (MCP), which both enforces the FPR constraint and improves detection performance. This paper also introduces RealDet, a high-quality dataset that spans a wide range of domains, ensuring realistic calibration and enabling superior detection performance when combined with MCP. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that MCP effectively constrains FPRs, significantly enhances detection performance, and increases robustness against adversarial attacks across multiple detectors and datasets.
SelfMedHPM: Self Pre-training With Hard Patches Mining Masked Autoencoders For Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:In recent years, deep learning methods such as convolutional neural network (CNN) and transformers have made significant progress in CT multi-organ segmentation. However, CT multi-organ segmentation methods based on masked image modeling (MIM) are very limited. There are already methods using MAE for CT multi-organ segmentation task, we believe that the existing methods do not identify the most difficult areas to reconstruct. To this end, we propose a MIM self-training framework with hard patches mining masked autoencoders for CT multi-organ segmentation tasks (selfMedHPM). The method performs ViT self-pretraining on the training set of the target data and introduces an auxiliary loss predictor, which first predicts the patch loss and determines the location of the next mask. SelfMedHPM implementation is better than various competitive methods in abdominal CT multi-organ segmentation and body CT multi-organ segmentation. We have validated the performance of our method on the Multi Atlas Labeling Beyond The Cranial Vault (BTCV) dataset for abdomen mult-organ segmentation and the SinoMed Whole Body (SMWB) dataset for body multi-organ segmentation tasks.
LSP Framework: A Compensatory Model for Defeating Trigger Reverse Engineering via Label Smoothing Poisoning
Apr 19, 2024Abstract:Deep neural networks are vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Among the existing backdoor defense methods, trigger reverse engineering based approaches, which reconstruct the backdoor triggers via optimizations, are the most versatile and effective ones compared to other types of methods. In this paper, we summarize and construct a generic paradigm for the typical trigger reverse engineering process. Based on this paradigm, we propose a new perspective to defeat trigger reverse engineering by manipulating the classification confidence of backdoor samples. To determine the specific modifications of classification confidence, we propose a compensatory model to compute the lower bound of the modification. With proper modifications, the backdoor attack can easily bypass the trigger reverse engineering based methods. To achieve this objective, we propose a Label Smoothing Poisoning (LSP) framework, which leverages label smoothing to specifically manipulate the classification confidences of backdoor samples. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed work can defeat the state-of-the-art trigger reverse engineering based methods, and possess good compatibility with a variety of existing backdoor attacks.
Semi-Supervised Recognition under a Noisy and Fine-grained Dataset
Jun 18, 2020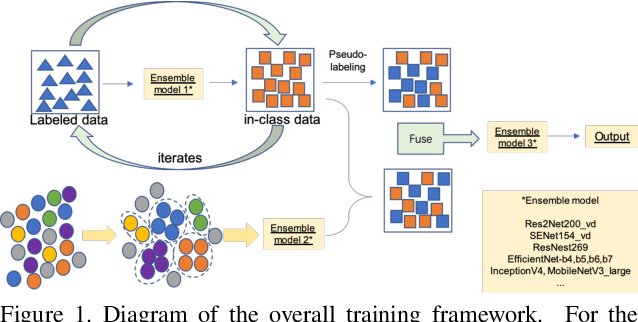
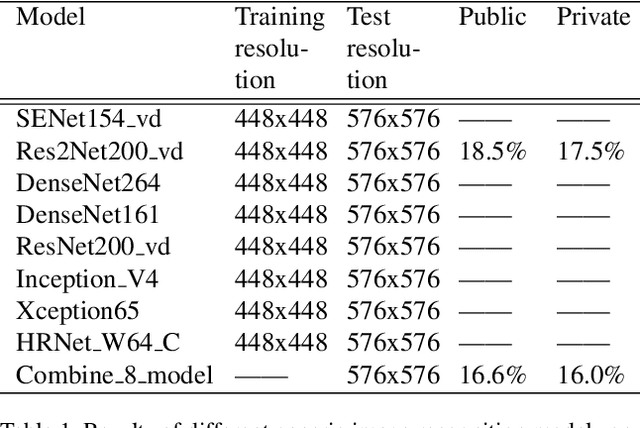
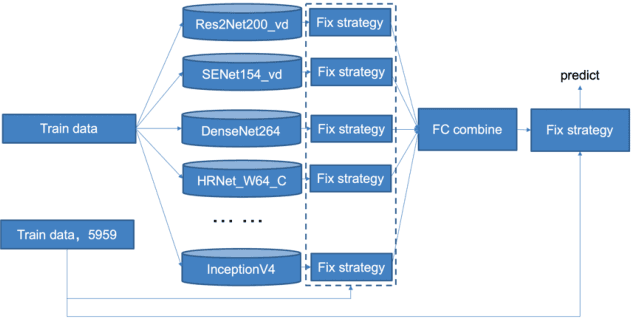
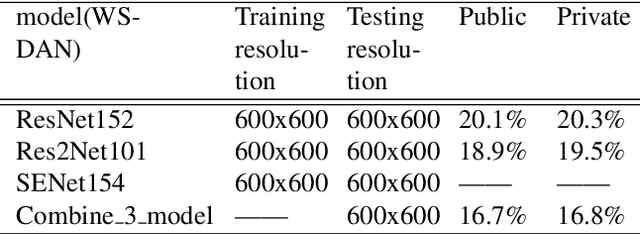
Abstract:Simi-Supervised Recognition Challenge-FGVC7 is a challenging fine-grained recognition competition. One of the difficulties of this competition is how to use unlabeled data. We adopted pseudo-tag data mining to increase the amount of training data. The other one is how to identify similar birds with a very small difference, especially those have a relatively tiny main-body in examples. We combined generic image recognition and fine-grained image recognition method to solve the problem. All generic image recognition models were training using PaddleClas . Using the combination of two different ways of deep recognition models, we finally won the third place in the competition.
Learning from Easy to Complex: Adaptive Multi-curricula Learning for Neural Dialogue Generation
Mar 16, 2020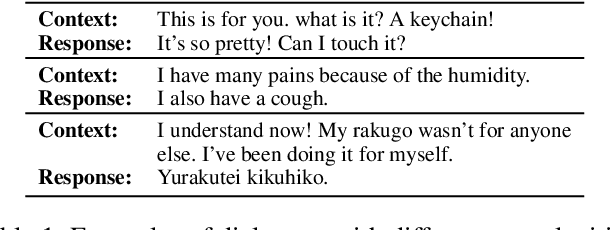
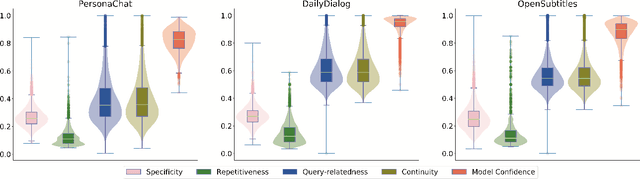
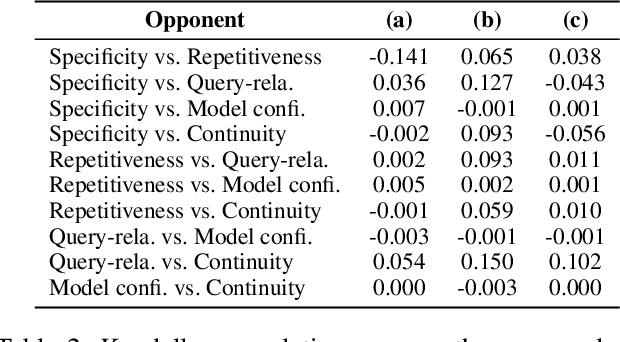
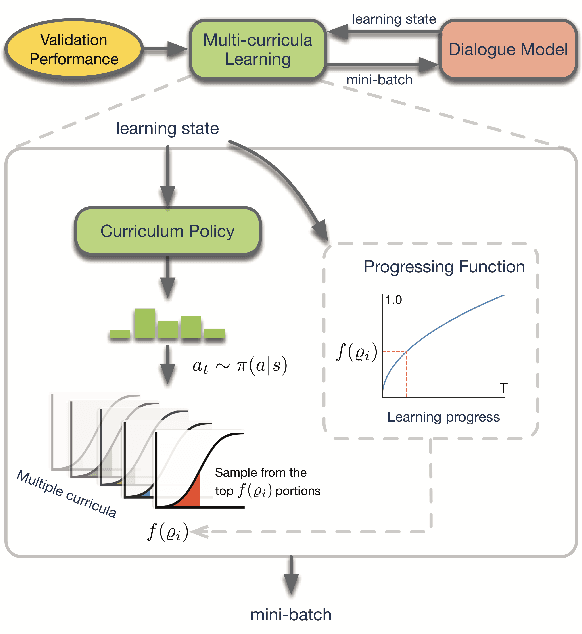
Abstract:Current state-of-the-art neural dialogue systems are mainly data-driven and are trained on human-generated responses. However, due to the subjectivity and open-ended nature of human conversations, the complexity of training dialogues varies greatly. The noise and uneven complexity of query-response pairs impede the learning efficiency and effects of the neural dialogue generation models. What is more, so far, there are no unified dialogue complexity measurements, and the dialogue complexity embodies multiple aspects of attributes---specificity, repetitiveness, relevance, etc. Inspired by human behaviors of learning to converse, where children learn from easy dialogues to complex ones and dynamically adjust their learning progress, in this paper, we first analyze five dialogue attributes to measure the dialogue complexity in multiple perspectives on three publicly available corpora. Then, we propose an adaptive multi-curricula learning framework to schedule a committee of the organized curricula. The framework is established upon the reinforcement learning paradigm, which automatically chooses different curricula at the evolving learning process according to the learning status of the neural dialogue generation model. Extensive experiments conducted on five state-of-the-art models demonstrate its learning efficiency and effectiveness with respect to 13 automatic evaluation metrics and human judgments.
RLINK: Deep Reinforcement Learning for User Identity Linkage
Oct 31, 2019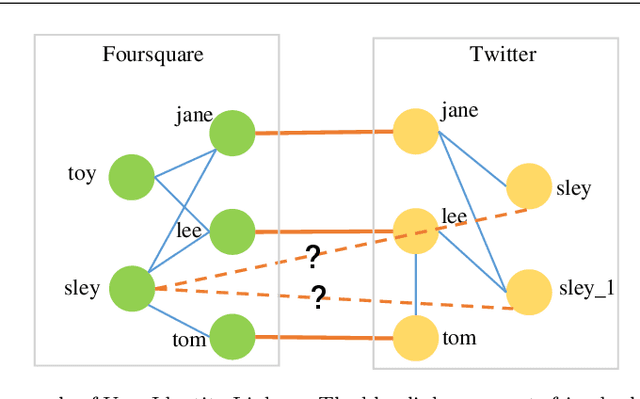
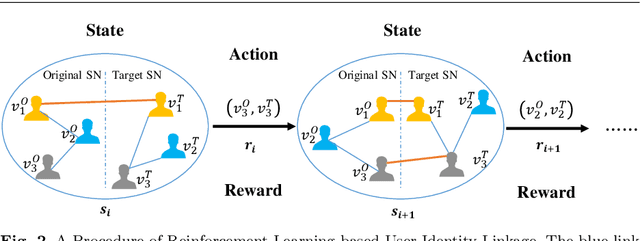
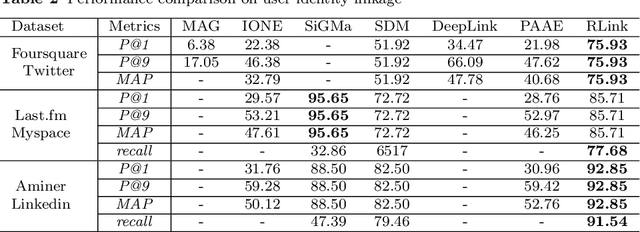
Abstract:User identity linkage is a task of recognizing the identities of the same user across different social networks (SN). Previous works tackle this problem via estimating the pairwise similarity between identities from different SN, predicting the label of identity pairs or selecting the most relevant identity pair based on the similarity scores. However, most of these methods ignore the results of previously matched identities, which could contribute to the linkage in following matching steps. To address this problem, we convert user identity linkage into a sequence decision problem and propose a reinforcement learning model to optimize the linkage strategy from the global perspective. Our method makes full use of both the social network structure and the history matched identities, and explores the long-term influence of current matching on subsequent decisions. We conduct experiments on different types of datasets, the results show that our method achieves better performance than other state-of-the-art methods.
Interaction-aware Spatio-temporal Pyramid Attention Networks for Action Classification
Aug 03, 2018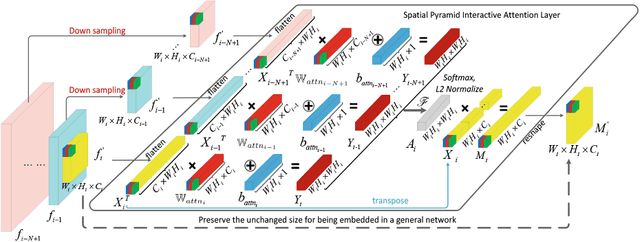
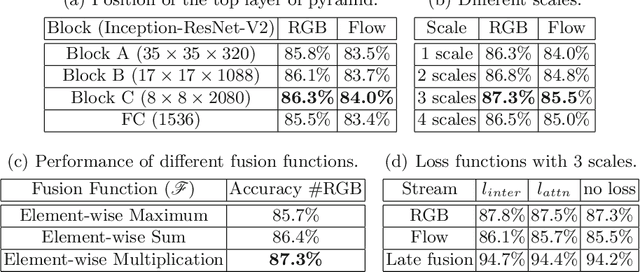
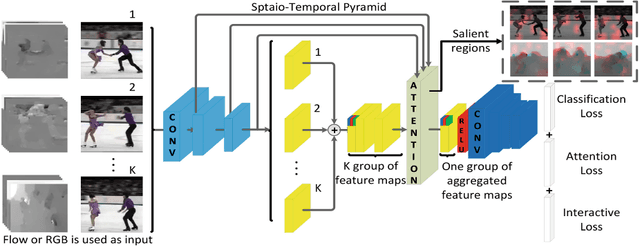
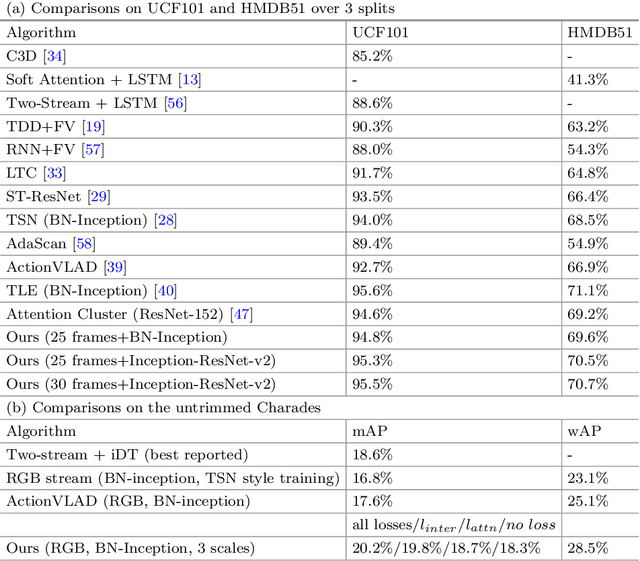
Abstract:Local features at neighboring spatial positions in feature maps have high correlation since their receptive fields are often overlapped. Self-attention usually uses the weighted sum (or other functions) with internal elements of each local feature to obtain its weight score, which ignores interactions among local features. To address this, we propose an effective interaction-aware self-attention model inspired by PCA to learn attention maps. Furthermore, since different layers in a deep network capture feature maps of different scales, we use these feature maps to construct a spatial pyramid and then utilize multi-scale information to obtain more accurate attention scores, which are used to weight the local features in all spatial positions of feature maps to calculate attention maps. Moreover, our spatial pyramid attention is unrestricted to the number of its input feature maps so it is easily extended to a spatio-temporal version. Finally, our model is embedded in general CNNs to form end-to-end attention networks for action classification. Experimental results show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art results on the UCF101, HMDB51 and untrimmed Charades.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge