Chi Jin
MUSIC: MUlti-Step Instruction Contrast for Multi-Turn Reward Models
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Evaluating the quality of multi-turn conversations is crucial for developing capable Large Language Models (LLMs), yet remains a significant challenge, often requiring costly human evaluation. Multi-turn reward models (RMs) offer a scalable alternative and can provide valuable signals for guiding LLM training. While recent work has advanced multi-turn \textit{training} techniques, effective automated \textit{evaluation} specifically for multi-turn interactions lags behind. We observe that standard preference datasets, typically contrasting responses based only on the final conversational turn, provide insufficient signal to capture the nuances of multi-turn interactions. Instead, we find that incorporating contrasts spanning \textit{multiple} turns is critical for building robust multi-turn RMs. Motivated by this finding, we propose \textbf{MU}lti-\textbf{S}tep \textbf{I}nstruction \textbf{C}ontrast (MUSIC), an unsupervised data augmentation strategy that synthesizes contrastive conversation pairs exhibiting differences across multiple turns. Leveraging MUSIC on the Skywork preference dataset, we train a multi-turn RM based on the Gemma-2-9B-Instruct model. Empirical results demonstrate that our MUSIC-augmented RM outperforms baseline methods, achieving higher alignment with judgments from advanced proprietary LLM judges on multi-turn conversations, crucially, without compromising performance on standard single-turn RM benchmarks.
Recurrent Autoregressive Diffusion: Global Memory Meets Local Attention
Nov 17, 2025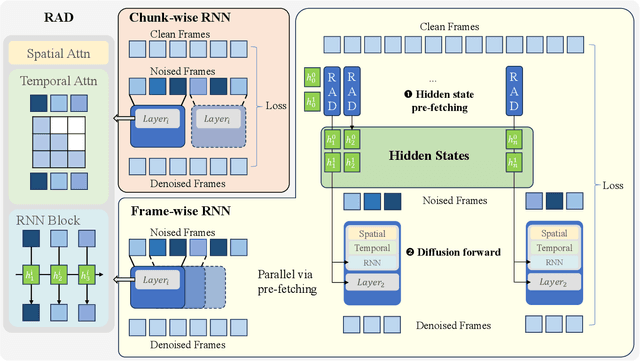
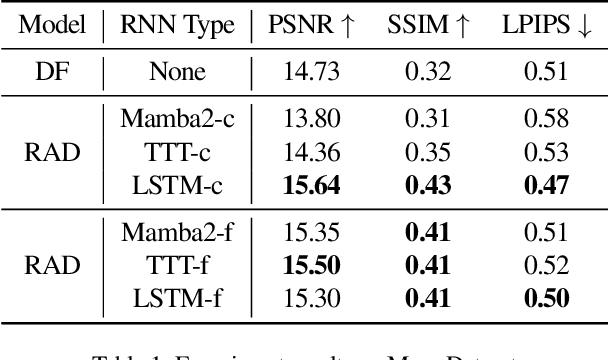
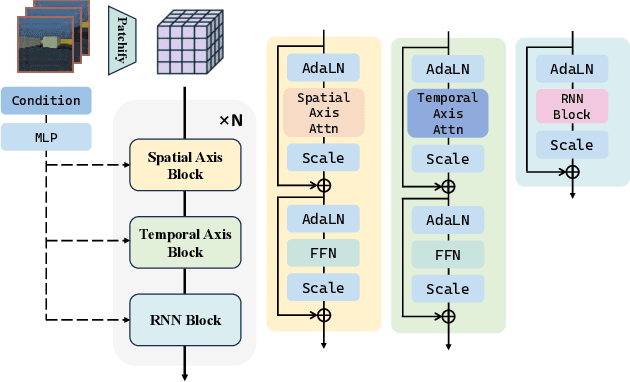
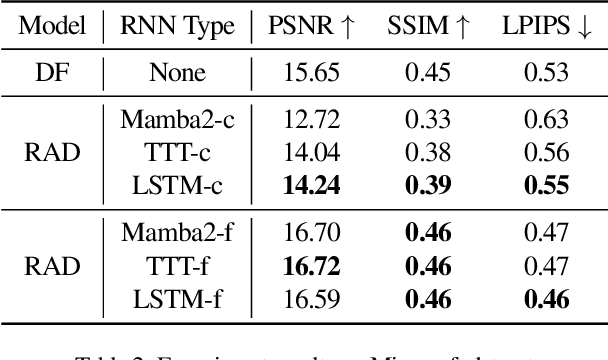
Abstract:Recent advancements in video generation have demonstrated the potential of using video diffusion models as world models, with autoregressive generation of infinitely long videos through masked conditioning. However, such models, usually with local full attention, lack effective memory compression and retrieval for long-term generation beyond the window size, leading to issues of forgetting and spatiotemporal inconsistencies. To enhance the retention of historical information within a fixed memory budget, we introduce a recurrent neural network (RNN) into the diffusion transformer framework. Specifically, a diffusion model incorporating LSTM with attention achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art RNN blocks, such as TTT and Mamba2. Moreover, existing diffusion-RNN approaches often suffer from performance degradation due to training-inference gap or the lack of overlap across windows. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Recurrent Autoregressive Diffusion (RAD) framework, which executes frame-wise autoregression for memory update and retrieval, consistently across training and inference time. Experiments on Memory Maze and Minecraft datasets demonstrate the superiority of RAD for long video generation, highlighting the efficiency of LSTM in sequence modeling.
Frontier LLMs Still Struggle with Simple Reasoning Tasks
Jul 09, 2025
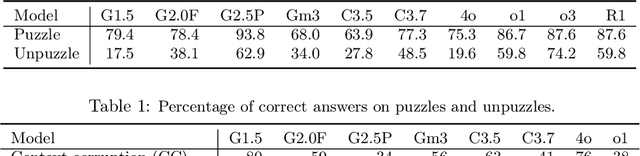
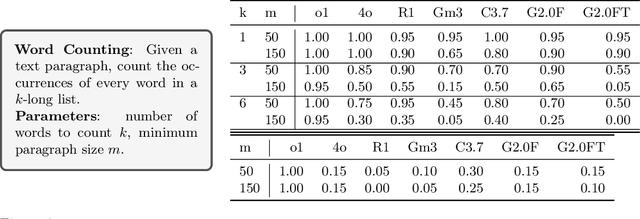
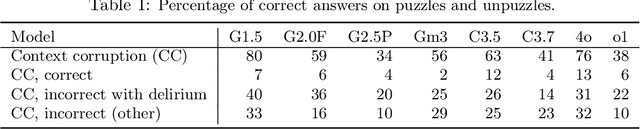
Abstract:While state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) demonstrate advanced reasoning capabilities-achieving remarkable performance on challenging competitive math and coding benchmarks-they also frequently fail on tasks that are easy for humans. This work studies the performance of frontier LLMs on a broad set of such "easy" reasoning problems. By extending previous work in the literature, we create a suite of procedurally generated simple reasoning tasks, including counting, first-order logic, proof trees, and travel planning, with changeable parameters (such as document length. or the number of variables in a math problem) that can arbitrarily increase the amount of computation required to produce the answer while preserving the fundamental difficulty. While previous work showed that traditional, non-thinking models can be made to fail on such problems, we demonstrate that even state-of-the-art thinking models consistently fail on such problems and for similar reasons (e.g. statistical shortcuts, errors in intermediate steps, and difficulties in processing long contexts). To further understand the behavior of the models, we introduce the unpuzzles dataset, a different "easy" benchmark consisting of trivialized versions of well-known math and logic puzzles. Interestingly, while modern LLMs excel at solving the original puzzles, they tend to fail on the trivialized versions, exhibiting several systematic failure patterns related to memorizing the originals. We show that this happens even if the models are otherwise able to solve problems with different descriptions but requiring the same logic. Our results highlight that out-of-distribution generalization is still problematic for frontier language models and the new generation of thinking models, even for simple reasoning tasks, and making tasks easier does not necessarily imply improved performance.
Learning World Models for Interactive Video Generation
May 28, 2025Abstract:Foundational world models must be both interactive and preserve spatiotemporal coherence for effective future planning with action choices. However, present models for long video generation have limited inherent world modeling capabilities due to two main challenges: compounding errors and insufficient memory mechanisms. We enhance image-to-video models with interactive capabilities through additional action conditioning and autoregressive framework, and reveal that compounding error is inherently irreducible in autoregressive video generation, while insufficient memory mechanism leads to incoherence of world models. We propose video retrieval augmented generation (VRAG) with explicit global state conditioning, which significantly reduces long-term compounding errors and increases spatiotemporal consistency of world models. In contrast, naive autoregressive generation with extended context windows and retrieval-augmented generation prove less effective for video generation, primarily due to the limited in-context learning capabilities of current video models. Our work illuminates the fundamental challenges in video world models and establishes a comprehensive benchmark for improving video generation models with internal world modeling capabilities.
Principled Out-of-Distribution Generalization via Simplicity
May 28, 2025Abstract:Modern foundation models exhibit remarkable out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization, solving tasks far beyond the support of their training data. However, the theoretical principles underpinning this phenomenon remain elusive. This paper investigates this problem by examining the compositional generalization abilities of diffusion models in image generation. Our analysis reveals that while neural network architectures are expressive enough to represent a wide range of models -- including many with undesirable behavior on OOD inputs -- the true, generalizable model that aligns with human expectations typically corresponds to the simplest among those consistent with the training data. Motivated by this observation, we develop a theoretical framework for OOD generalization via simplicity, quantified using a predefined simplicity metric. We analyze two key regimes: (1) the constant-gap setting, where the true model is strictly simpler than all spurious alternatives by a fixed gap, and (2) the vanishing-gap setting, where the fixed gap is replaced by a smoothness condition ensuring that models close in simplicity to the true model yield similar predictions. For both regimes, we study the regularized maximum likelihood estimator and establish the first sharp sample complexity guarantees for learning the true, generalizable, simple model.
Ineq-Comp: Benchmarking Human-Intuitive Compositional Reasoning in Automated Theorem Proving on Inequalities
May 19, 2025Abstract:LLM-based formal proof assistants (e.g., in Lean) hold great promise for automating mathematical discovery. But beyond syntactic correctness, do these systems truly understand mathematical structure as humans do? We investigate this question through the lens of mathematical inequalities -- a fundamental tool across many domains. While modern provers can solve basic inequalities, we probe their ability to handle human-intuitive compositionality. We introduce Ineq-Comp, a benchmark built from elementary inequalities through systematic transformations, including variable duplication, algebraic rewriting, and multi-step composition. Although these problems remain easy for humans, we find that most provers -- including Goedel, STP, and Kimina-7B -- struggle significantly. DeepSeek-Prover-V2-7B shows relative robustness -- possibly because it is trained to decompose the problems into sub-problems -- but still suffers a 20\% performance drop (pass@32). Strikingly, performance remains poor for all models even when formal proofs of the constituent parts are provided in context, revealing that the source of weakness is indeed in compositional reasoning. Our results expose a persisting gap between the generalization behavior of current AI provers and human mathematical intuition.
PokéChamp: an Expert-level Minimax Language Agent
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce Pok\'eChamp, a minimax agent powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) for Pok\'emon battles. Built on a general framework for two-player competitive games, Pok\'eChamp leverages the generalist capabilities of LLMs to enhance minimax tree search. Specifically, LLMs replace three key modules: (1) player action sampling, (2) opponent modeling, and (3) value function estimation, enabling the agent to effectively utilize gameplay history and human knowledge to reduce the search space and address partial observability. Notably, our framework requires no additional LLM training. We evaluate Pok\'eChamp in the popular Gen 9 OU format. When powered by GPT-4o, it achieves a win rate of 76% against the best existing LLM-based bot and 84% against the strongest rule-based bot, demonstrating its superior performance. Even with an open-source 8-billion-parameter Llama 3.1 model, Pok\'eChamp consistently outperforms the previous best LLM-based bot, Pok\'ellmon powered by GPT-4o, with a 64% win rate. Pok\'eChamp attains a projected Elo of 1300-1500 on the Pok\'emon Showdown online ladder, placing it among the top 30%-10% of human players. In addition, this work compiles the largest real-player Pok\'emon battle dataset, featuring over 3 million games, including more than 500k high-Elo matches. Based on this dataset, we establish a series of battle benchmarks and puzzles to evaluate specific battling skills. We further provide key updates to the local game engine. We hope this work fosters further research that leverage Pok\'emon battle as benchmark to integrate LLM technologies with game-theoretic algorithms addressing general multiagent problems. Videos, code, and dataset available at https://sites.google.com/view/pokechamp-llm.
Goedel-Prover: A Frontier Model for Open-Source Automated Theorem Proving
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce Goedel-Prover, an open-source large language model (LLM) that achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in automated formal proof generation for mathematical problems. The key challenge in this field is the scarcity of formalized math statements and proofs, which we tackle in the following ways. We train statement formalizers to translate the natural language math problems from Numina into formal language (Lean 4), creating a dataset of 1.64 million formal statements. LLMs are used to check that the formal statements accurately preserve the content of the original natural language problems. We then iteratively build a large dataset of formal proofs by training a series of provers. Each prover succeeds in proving many statements that the previous ones could not, and these new proofs are added to the training set for the next prover. The final prover outperforms all existing open-source models in whole-proof generation. On the miniF2F benchmark, it achieves a 57.6% success rate (Pass@32), exceeding the previous best open-source model by 7.6%. On PutnamBench, Goedel-Prover successfully solves 7 problems (Pass@512), ranking first on the leaderboard. Furthermore, it generates 29.7K formal proofs for Lean Workbook problems, nearly doubling the 15.7K produced by earlier works.
MATH-Perturb: Benchmarking LLMs' Math Reasoning Abilities against Hard Perturbations
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Large language models have demonstrated impressive performance on challenging mathematical reasoning tasks, which has triggered the discussion of whether the performance is achieved by true reasoning capability or memorization. To investigate this question, prior work has constructed mathematical benchmarks when questions undergo simple perturbations -- modifications that still preserve the underlying reasoning patterns of the solutions. However, no work has explored hard perturbations, which fundamentally change the nature of the problem so that the original solution steps do not apply. To bridge the gap, we construct MATH-P-Simple and MATH-P-Hard via simple perturbation and hard perturbation, respectively. Each consists of 279 perturbed math problems derived from level-5 (hardest) problems in the MATH dataset (Hendrycksmath et. al., 2021). We observe significant performance drops on MATH-P-Hard across various models, including o1-mini (-16.49%) and gemini-2.0-flash-thinking (-12.9%). We also raise concerns about a novel form of memorization where models blindly apply learned problem-solving skills without assessing their applicability to modified contexts. This issue is amplified when using original problems for in-context learning. We call for research efforts to address this challenge, which is critical for developing more robust and reliable reasoning models.
Generative Diffusion Modeling: A Practical Handbook
Dec 22, 2024Abstract:This handbook offers a unified perspective on diffusion models, encompassing diffusion probabilistic models, score-based generative models, consistency models, rectified flow, and related methods. By standardizing notations and aligning them with code implementations, it aims to bridge the "paper-to-code" gap and facilitate robust implementations and fair comparisons. The content encompasses the fundamentals of diffusion models, the pre-training process, and various post-training methods. Post-training techniques include model distillation and reward-based fine-tuning. Designed as a practical guide, it emphasizes clarity and usability over theoretical depth, focusing on widely adopted approaches in generative modeling with diffusion models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge