C. V. Jawahar
Attend to what I say: Highlighting relevant content on slides
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Imagine sitting in a presentation, trying to follow the speaker while simultaneously scanning the slides for relevant information. While the entire slide is visible, identifying the relevant regions can be challenging. As you focus on one part of the slide, the speaker moves on to a new sentence, leaving you scrambling to catch up visually. This constant back-and-forth creates a disconnect between what is being said and the most important visual elements, making it hard to absorb key details, especially in fast-paced or content-heavy presentations such as conference talks. This requires an understanding of slides, including text, graphics, and layout. We introduce a method that automatically identifies and highlights the most relevant slide regions based on the speaker's narrative. By analyzing spoken content and matching it with textual or graphical elements in the slides, our approach ensures better synchronization between what listeners hear and what they need to attend to. We explore different ways of solving this problem and assess their success and failure cases. Analyzing multimedia documents is emerging as a key requirement for seamless understanding of content-rich videos, such as educational videos and conference talks, by reducing cognitive strain and improving comprehension. Code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/meghamariamkm2002/Slide_Highlight
PhyEduVideo: A Benchmark for Evaluating Text-to-Video Models for Physics Education
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Generative AI models, particularly Text-to-Video (T2V) systems, offer a promising avenue for transforming science education by automating the creation of engaging and intuitive visual explanations. In this work, we take a first step toward evaluating their potential in physics education by introducing a dedicated benchmark for explanatory video generation. The benchmark is designed to assess how well T2V models can convey core physics concepts through visual illustrations. Each physics concept in our benchmark is decomposed into granular teaching points, with each point accompanied by a carefully crafted prompt intended for visual explanation of the teaching point. T2V models are evaluated on their ability to generate accurate videos in response to these prompts. Our aim is to systematically explore the feasibility of using T2V models to generate high-quality, curriculum-aligned educational content-paving the way toward scalable, accessible, and personalized learning experiences powered by AI. Our evaluation reveals that current models produce visually coherent videos with smooth motion and minimal flickering, yet their conceptual accuracy is less reliable. Performance in areas such as mechanics, fluids, and optics is encouraging, but models struggle with electromagnetism and thermodynamics, where abstract interactions are harder to depict. These findings underscore the gap between visual quality and conceptual correctness in educational video generation. We hope this benchmark helps the community close that gap and move toward T2V systems that can deliver accurate, curriculum-aligned physics content at scale. The benchmark and accompanying codebase are publicly available at https://github.com/meghamariamkm/PhyEduVideo.
NoTeS-Bank: Benchmarking Neural Transcription and Search for Scientific Notes Understanding
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Understanding and reasoning over academic handwritten notes remains a challenge in document AI, particularly for mathematical equations, diagrams, and scientific notations. Existing visual question answering (VQA) benchmarks focus on printed or structured handwritten text, limiting generalization to real-world note-taking. To address this, we introduce NoTeS-Bank, an evaluation benchmark for Neural Transcription and Search in note-based question answering. NoTeS-Bank comprises complex notes across multiple domains, requiring models to process unstructured and multimodal content. The benchmark defines two tasks: (1) Evidence-Based VQA, where models retrieve localized answers with bounding-box evidence, and (2) Open-Domain VQA, where models classify the domain before retrieving relevant documents and answers. Unlike classical Document VQA datasets relying on optical character recognition (OCR) and structured data, NoTeS-BANK demands vision-language fusion, retrieval, and multimodal reasoning. We benchmark state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and retrieval frameworks, exposing structured transcription and reasoning limitations. NoTeS-Bank provides a rigorous evaluation with NDCG@5, MRR, Recall@K, IoU, and ANLS, establishing a new standard for visual document understanding and reasoning.
Contrasting Low and High-Resolution Features for HER2 Scoring using Deep Learning
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Breast cancer, the most common malignancy among women, requires precise detection and classification for effective treatment. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) biomarkers like HER2, ER, and PR are critical for identifying breast cancer subtypes. However, traditional IHC classification relies on pathologists' expertise, making it labor-intensive and subject to significant inter-observer variability. To address these challenges, this study introduces the India Pathology Breast Cancer Dataset (IPD-Breast), comprising of 1,272 IHC slides (HER2, ER, and PR) aimed at automating receptor status classification. The primary focus is on developing predictive models for HER2 3-way classification (0, Low, High) to enhance prognosis. Evaluation of multiple deep learning models revealed that an end-to-end ConvNeXt network utilizing low-resolution IHC images achieved an AUC, F1, and accuracy of 91.79%, 83.52%, and 83.56%, respectively, for 3-way classification, outperforming patch-based methods by over 5.35% in F1 score. This study highlights the potential of simple yet effective deep learning techniques to significantly improve accuracy and reproducibility in breast cancer classification, supporting their integration into clinical workflows for better patient outcomes.
A Dataset for Semantic Segmentation in the Presence of Unknowns
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Before deployment in the real-world deep neural networks require thorough evaluation of how they handle both knowns, inputs represented in the training data, and unknowns (anomalies). This is especially important for scene understanding tasks with safety critical applications, such as in autonomous driving. Existing datasets allow evaluation of only knowns or unknowns - but not both, which is required to establish "in the wild" suitability of deep neural network models. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel anomaly segmentation dataset, ISSU, that features a diverse set of anomaly inputs from cluttered real-world environments. The dataset is twice larger than existing anomaly segmentation datasets, and provides a training, validation and test set for controlled in-domain evaluation. The test set consists of a static and temporal part, with the latter comprised of videos. The dataset provides annotations for both closed-set (knowns) and anomalies, enabling closed-set and open-set evaluation. The dataset covers diverse conditions, such as domain and cross-sensor shift, illumination variation and allows ablation of anomaly detection methods with respect to these variations. Evaluation results of current state-of-the-art methods confirm the need for improvements especially in domain-generalization, small and large object segmentation.
ICPR 2024 Competition on Rider Intention Prediction
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:The recent surge in the vehicle market has led to an alarming increase in road accidents. This underscores the critical importance of enhancing road safety measures, particularly for vulnerable road users like motorcyclists. Hence, we introduce the rider intention prediction (RIP) competition that aims to address challenges in rider safety by proactively predicting maneuvers before they occur, thereby strengthening rider safety. This capability enables the riders to react to the potential incorrect maneuvers flagged by advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). We collect a new dataset, namely, rider action anticipation dataset (RAAD) for the competition consisting of two tasks: single-view RIP and multi-view RIP. The dataset incorporates a spectrum of traffic conditions and challenging navigational maneuvers on roads with varying lighting conditions. For the competition, we received seventy-five registrations and five team submissions for inference of which we compared the methods of the top three performing teams on both the RIP tasks: one state-space model (Mamba2) and two learning-based approaches (SVM and CNN-LSTM). The results indicate that the state-space model outperformed the other methods across the entire dataset, providing a balanced performance across maneuver classes. The SVM-based RIP method showed the second-best performance when using random sampling and SMOTE. However, the CNN-LSTM method underperformed, primarily due to class imbalance issues, particularly struggling with minority classes. This paper details the proposed RAAD dataset and provides a summary of the submissions for the RIP 2024 competition.
Can Reasons Help Improve Pedestrian Intent Estimation? A Cross-Modal Approach
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:With the increased importance of autonomous navigation systems has come an increasing need to protect the safety of Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) such as pedestrians. Predicting pedestrian intent is one such challenging task, where prior work predicts the binary cross/no-cross intention with a fusion of visual and motion features. However, there has been no effort so far to hedge such predictions with human-understandable reasons. We address this issue by introducing a novel problem setting of exploring the intuitive reasoning behind a pedestrian's intent. In particular, we show that predicting the 'WHY' can be very useful in understanding the 'WHAT'. To this end, we propose a novel, reason-enriched PIE++ dataset consisting of multi-label textual explanations/reasons for pedestrian intent. We also introduce a novel multi-task learning framework called MINDREAD, which leverages a cross-modal representation learning framework for predicting pedestrian intent as well as the reason behind the intent. Our comprehensive experiments show significant improvement of 5.6% and 7% in accuracy and F1-score for the task of intent prediction on the PIE++ dataset using MINDREAD. We also achieved a 4.4% improvement in accuracy on a commonly used JAAD dataset. Extensive evaluation using quantitative/qualitative metrics and user studies shows the effectiveness of our approach.
Advancing Question Answering on Handwritten Documents: A State-of-the-Art Recognition-Based Model for HW-SQuAD
Jun 25, 2024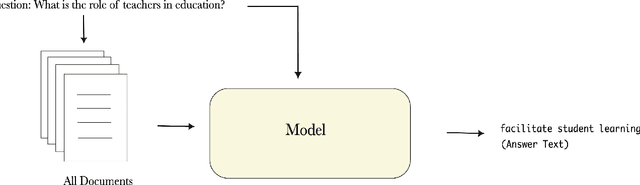
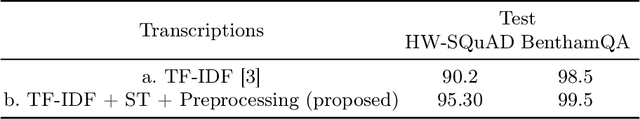
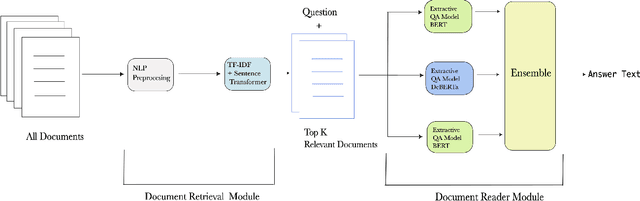
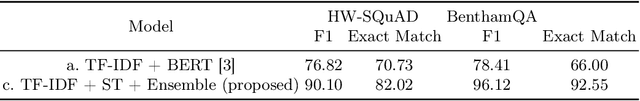
Abstract:Question-answering handwritten documents is a challenging task with numerous real-world applications. This paper proposes a novel recognition-based approach that improves upon the previous state-of-the-art on the HW-SQuAD and BenthamQA datasets. Our model incorporates transformer-based document retrieval and ensemble methods at the model level, achieving an Exact Match score of 82.02% and 92.55% in HW-SQuAD and BenthamQA datasets, respectively, surpassing the previous best recognition-based approach by 10.89% and 26%. We also enhance the document retrieval component, boosting the top-5 retrieval accuracy from 90% to 95.30%. Our results demonstrate the significance of our proposed approach in advancing question answering on handwritten documents. The code and trained models will be publicly available to facilitate future research in this critical area of natural language.
IDD-X: A Multi-View Dataset for Ego-relative Important Object Localization and Explanation in Dense and Unstructured Traffic
Apr 12, 2024Abstract:Intelligent vehicle systems require a deep understanding of the interplay between road conditions, surrounding entities, and the ego vehicle's driving behavior for safe and efficient navigation. This is particularly critical in developing countries where traffic situations are often dense and unstructured with heterogeneous road occupants. Existing datasets, predominantly geared towards structured and sparse traffic scenarios, fall short of capturing the complexity of driving in such environments. To fill this gap, we present IDD-X, a large-scale dual-view driving video dataset. With 697K bounding boxes, 9K important object tracks, and 1-12 objects per video, IDD-X offers comprehensive ego-relative annotations for multiple important road objects covering 10 categories and 19 explanation label categories. The dataset also incorporates rearview information to provide a more complete representation of the driving environment. We also introduce custom-designed deep networks aimed at multiple important object localization and per-object explanation prediction. Overall, our dataset and introduced prediction models form the foundation for studying how road conditions and surrounding entities affect driving behavior in complex traffic situations.
Multiple Instance Learning for Glioma Diagnosis using Hematoxylin and Eosin Whole Slide Images: An Indian Cohort Study
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:The effective management of brain tumors relies on precise typing, subtyping, and grading. This study advances patient care with findings from rigorous multiple instance learning experimentations across various feature extractors and aggregators in brain tumor histopathology. It establishes new performance benchmarks in glioma subtype classification across multiple datasets, including a novel dataset focused on the Indian demographic (IPD- Brain), providing a valuable resource for existing research. Using a ResNet-50, pretrained on histopathology datasets for feature extraction, combined with the Double-Tier Feature Distillation (DTFD) feature aggregator, our approach achieves state-of-the-art AUCs of 88.08 on IPD-Brain and 95.81 on the TCGA-Brain dataset, respectively, for three-way glioma subtype classification. Moreover, it establishes new benchmarks in grading and detecting IHC molecular biomarkers (IDH1R132H, TP53, ATRX, Ki-67) through H&E stained whole slide images for the IPD-Brain dataset. The work also highlights a significant correlation between the model decision-making processes and the diagnostic reasoning of pathologists, underscoring its capability to mimic professional diagnostic procedures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge