Dimosthenis Karatzas
AVIR: Adaptive Visual In-Document Retrieval for Efficient Multi-Page Document Question Answering
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Multi-page Document Visual Question Answering (MP-DocVQA) remains challenging because long documents not only strain computational resources but also reduce the effectiveness of the attention mechanism in large vision-language models (LVLMs). We tackle these issues with an Adaptive Visual In-document Retrieval (AVIR) framework. A lightweight retrieval model first scores each page for question relevance. Pages are then clustered according to the score distribution to adaptively select relevant content. The clustered pages are screened again by Top-K to keep the context compact. However, for short documents, clustering reliability decreases, so we use a relevance probability threshold to select pages. The selected pages alone are fed to a frozen LVLM for answer generation, eliminating the need for model fine-tuning. The proposed AVIR framework reduces the average page count required for question answering by 70%, while achieving an ANLS of 84.58% on the MP-DocVQA dataset-surpassing previous methods with significantly lower computational cost. The effectiveness of the proposed AVIR is also verified on the SlideVQA and DUDE benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/Li-yachuan/AVIR.
TRIM: A Self-Supervised Video Summarization Framework Maximizing Temporal Relative Information and Representativeness
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:The increasing ubiquity of video content and the corresponding demand for efficient access to meaningful information have elevated video summarization and video highlights as a vital research area. However, many state-of-the-art methods depend heavily either on supervised annotations or on attention-based models, which are computationally expensive and brittle in the face of distribution shifts that hinder cross-domain applicability across datasets. We introduce a pioneering self-supervised video summarization model that captures both spatial and temporal dependencies without the overhead of attention, RNNs, or transformers. Our framework integrates a novel set of Markov process-driven loss metrics and a two-stage self supervised learning paradigm that ensures both performance and efficiency. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the SUMME and TVSUM datasets, outperforming all existing unsupervised methods. It also rivals the best supervised models, demonstrating the potential for efficient, annotation-free architectures. This paves the way for more generalizable video summarization techniques and challenges the prevailing reliance on complex architectures.
LLM-Driven Medical Document Analysis: Enhancing Trustworthy Pathology and Differential Diagnosis
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Medical document analysis plays a crucial role in extracting essential clinical insights from unstructured healthcare records, supporting critical tasks such as differential diagnosis. Determining the most probable condition among overlapping symptoms requires precise evaluation and deep medical expertise. While recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced performance in medical document analysis, privacy concerns related to sensitive patient data limit the use of online LLMs services in clinical settings. To address these challenges, we propose a trustworthy medical document analysis platform that fine-tunes a LLaMA-v3 using low-rank adaptation, specifically optimized for differential diagnosis tasks. Our approach utilizes DDXPlus, the largest benchmark dataset for differential diagnosis, and demonstrates superior performance in pathology prediction and variable-length differential diagnosis compared to existing methods. The developed web-based platform allows users to submit their own unstructured medical documents and receive accurate, explainable diagnostic results. By incorporating advanced explainability techniques, the system ensures transparent and reliable predictions, fostering user trust and confidence. Extensive evaluations confirm that the proposed method surpasses current state-of-the-art models in predictive accuracy while offering practical utility in clinical settings. This work addresses the urgent need for reliable, explainable, and privacy-preserving artificial intelligence solutions, representing a significant advancement in intelligent medical document analysis for real-world healthcare applications. The code can be found at \href{https://github.com/leitro/Differential-Diagnosis-LoRA}{https://github.com/leitro/Differential-Diagnosis-LoRA}.
DocVXQA: Context-Aware Visual Explanations for Document Question Answering
May 12, 2025Abstract:We propose DocVXQA, a novel framework for visually self-explainable document question answering. The framework is designed not only to produce accurate answers to questions but also to learn visual heatmaps that highlight contextually critical regions, thereby offering interpretable justifications for the model's decisions. To integrate explanations into the learning process, we quantitatively formulate explainability principles as explicit learning objectives. Unlike conventional methods that emphasize only the regions pertinent to the answer, our framework delivers explanations that are \textit{contextually sufficient} while remaining \textit{representation-efficient}. This fosters user trust while achieving a balance between predictive performance and interpretability in DocVQA applications. Extensive experiments, including human evaluation, provide strong evidence supporting the effectiveness of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/dali92002/DocVXQA.
xLSTM-ECG: Multi-label ECG Classification via Feature Fusion with xLSTM
Apr 14, 2025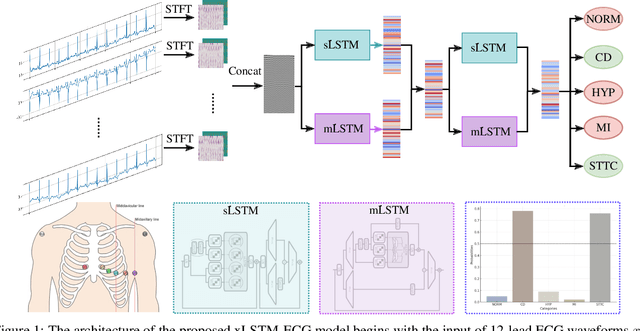
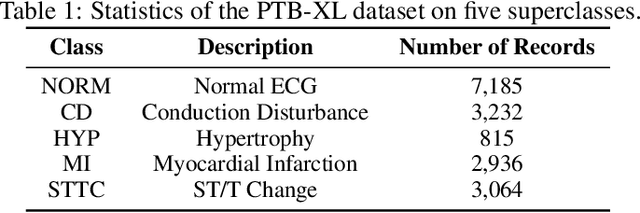
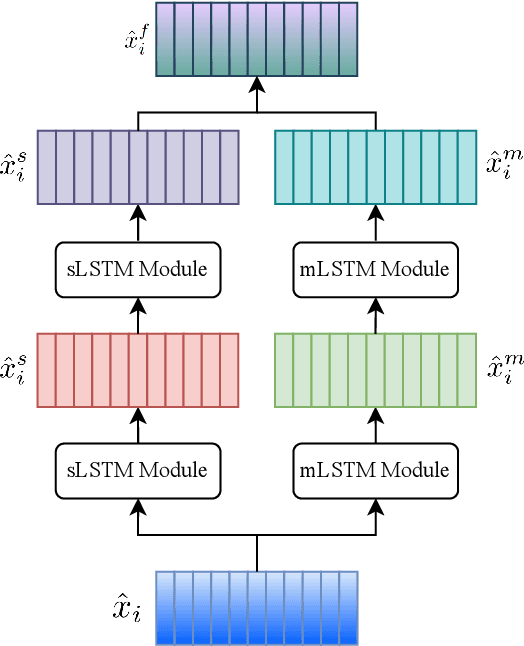
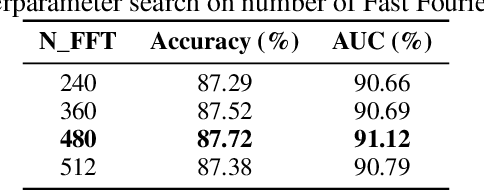
Abstract:Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of mortality worldwide, highlighting the critical need for efficient and accurate diagnostic tools. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are indispensable in diagnosing various heart conditions; however, their manual interpretation is time-consuming and error-prone. In this paper, we propose xLSTM-ECG, a novel approach that leverages an extended Long Short-Term Memory (xLSTM) network for multi-label classification of ECG signals, using the PTB-XL dataset. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first design and application of xLSTM modules specifically adapted for multi-label ECG classification. Our method employs a Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) to convert time-series ECG waveforms into the frequency domain, thereby enhancing feature extraction. The xLSTM architecture is specifically tailored to address the complexities of 12-lead ECG recordings by capturing both local and global signal features. Comprehensive experiments on the PTB-XL dataset reveal that our model achieves strong multi-label classification performance, while additional tests on the Georgia 12-Lead dataset underscore its robustness and efficiency. This approach significantly improves ECG classification accuracy, thereby advancing clinical diagnostics and patient care. The code will be publicly available upon acceptance.
NoTeS-Bank: Benchmarking Neural Transcription and Search for Scientific Notes Understanding
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Understanding and reasoning over academic handwritten notes remains a challenge in document AI, particularly for mathematical equations, diagrams, and scientific notations. Existing visual question answering (VQA) benchmarks focus on printed or structured handwritten text, limiting generalization to real-world note-taking. To address this, we introduce NoTeS-Bank, an evaluation benchmark for Neural Transcription and Search in note-based question answering. NoTeS-Bank comprises complex notes across multiple domains, requiring models to process unstructured and multimodal content. The benchmark defines two tasks: (1) Evidence-Based VQA, where models retrieve localized answers with bounding-box evidence, and (2) Open-Domain VQA, where models classify the domain before retrieving relevant documents and answers. Unlike classical Document VQA datasets relying on optical character recognition (OCR) and structured data, NoTeS-BANK demands vision-language fusion, retrieval, and multimodal reasoning. We benchmark state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and retrieval frameworks, exposing structured transcription and reasoning limitations. NoTeS-Bank provides a rigorous evaluation with NDCG@5, MRR, Recall@K, IoU, and ANLS, establishing a new standard for visual document understanding and reasoning.
Preserving Privacy Without Compromising Accuracy: Machine Unlearning for Handwritten Text Recognition
Apr 11, 2025



Abstract:Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR) is essential for document analysis and digitization. However, handwritten data often contains user-identifiable information, such as unique handwriting styles and personal lexicon choices, which can compromise privacy and erode trust in AI services. Legislation like the ``right to be forgotten'' underscores the necessity for methods that can expunge sensitive information from trained models. Machine unlearning addresses this by selectively removing specific data from models without necessitating complete retraining. Yet, it frequently encounters a privacy-accuracy tradeoff, where safeguarding privacy leads to diminished model performance. In this paper, we introduce a novel two-stage unlearning strategy for a multi-head transformer-based HTR model, integrating pruning and random labeling. Our proposed method utilizes a writer classification head both as an indicator and a trigger for unlearning, while maintaining the efficacy of the recognition head. To our knowledge, this represents the first comprehensive exploration of machine unlearning within HTR tasks. We further employ Membership Inference Attacks (MIA) to evaluate the effectiveness of unlearning user-identifiable information. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach effectively preserves privacy while maintaining model accuracy, paving the way for new research directions in the document analysis community. Our code will be publicly available upon acceptance.
ComicsPAP: understanding comic strips by picking the correct panel
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have made impressive strides in image captioning, VQA, and video comprehension, yet they still struggle with the intricate temporal and spatial cues found in comics. To address this gap, we introduce ComicsPAP, a large-scale benchmark designed for comic strip understanding. Comprising over 100k samples and organized into 5 subtasks under a Pick-a-Panel framework, ComicsPAP demands models to identify the missing panel in a sequence. Our evaluations, conducted under both multi-image and single-image protocols, reveal that current state-of-the-art LMMs perform near chance on these tasks, underscoring significant limitations in capturing sequential and contextual dependencies. To close the gap, we adapted LMMs for comic strip understanding, obtaining better results on ComicsPAP than 10x bigger models, demonstrating that ComicsPAP offers a robust resource to drive future research in multimodal comic comprehension.
DocMIA: Document-Level Membership Inference Attacks against DocVQA Models
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Document Visual Question Answering (DocVQA) has introduced a new paradigm for end-to-end document understanding, and quickly became one of the standard benchmarks for multimodal LLMs. Automating document processing workflows, driven by DocVQA models, presents significant potential for many business sectors. However, documents tend to contain highly sensitive information, raising concerns about privacy risks associated with training such DocVQA models. One significant privacy vulnerability, exploited by the membership inference attack, is the possibility for an adversary to determine if a particular record was part of the model's training data. In this paper, we introduce two novel membership inference attacks tailored specifically to DocVQA models. These attacks are designed for two different adversarial scenarios: a white-box setting, where the attacker has full access to the model architecture and parameters, and a black-box setting, where only the model's outputs are available. Notably, our attacks assume the adversary lacks access to auxiliary datasets, which is more realistic in practice but also more challenging. Our unsupervised methods outperform existing state-of-the-art membership inference attacks across a variety of DocVQA models and datasets, demonstrating their effectiveness and highlighting the privacy risks in this domain.
NeurIPS 2023 Competition: Privacy Preserving Federated Learning Document VQA
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:The Privacy Preserving Federated Learning Document VQA (PFL-DocVQA) competition challenged the community to develop provably private and communication-efficient solutions in a federated setting for a real-life use case: invoice processing. The competition introduced a dataset of real invoice documents, along with associated questions and answers requiring information extraction and reasoning over the document images. Thereby, it brings together researchers and expertise from the document analysis, privacy, and federated learning communities. Participants fine-tuned a pre-trained, state-of-the-art Document Visual Question Answering model provided by the organizers for this new domain, mimicking a typical federated invoice processing setup. The base model is a multi-modal generative language model, and sensitive information could be exposed through either the visual or textual input modality. Participants proposed elegant solutions to reduce communication costs while maintaining a minimum utility threshold in track 1 and to protect all information from each document provider using differential privacy in track 2. The competition served as a new testbed for developing and testing private federated learning methods, simultaneously raising awareness about privacy within the document image analysis and recognition community. Ultimately, the competition analysis provides best practices and recommendations for successfully running privacy-focused federated learning challenges in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge