Andrey Barsky
Prototype Augmented Hypernetworks for Continual Learning
May 13, 2025Abstract:Continual learning (CL) aims to learn a sequence of tasks without forgetting prior knowledge, but gradient updates for a new task often overwrite the weights learned earlier, causing catastrophic forgetting (CF). We propose Prototype-Augmented Hypernetworks (PAH), a framework where a single hypernetwork, conditioned on learnable task prototypes, dynamically generates task-specific classifier heads on demand. To mitigate forgetting, PAH combines cross-entropy with dual distillation losses, one to align logits and another to align prototypes, ensuring stable feature representations across tasks. Evaluations on Split-CIFAR100 and TinyImageNet demonstrate that PAH achieves state-of-the-art performance, reaching 74.5 % and 63.7 % accuracy with only 1.7 % and 4.4 % forgetting, respectively, surpassing prior methods without storing samples or heads.
DocVXQA: Context-Aware Visual Explanations for Document Question Answering
May 12, 2025Abstract:We propose DocVXQA, a novel framework for visually self-explainable document question answering. The framework is designed not only to produce accurate answers to questions but also to learn visual heatmaps that highlight contextually critical regions, thereby offering interpretable justifications for the model's decisions. To integrate explanations into the learning process, we quantitatively formulate explainability principles as explicit learning objectives. Unlike conventional methods that emphasize only the regions pertinent to the answer, our framework delivers explanations that are \textit{contextually sufficient} while remaining \textit{representation-efficient}. This fosters user trust while achieving a balance between predictive performance and interpretability in DocVQA applications. Extensive experiments, including human evaluation, provide strong evidence supporting the effectiveness of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/dali92002/DocVXQA.
NeurIPS 2023 Competition: Privacy Preserving Federated Learning Document VQA
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:The Privacy Preserving Federated Learning Document VQA (PFL-DocVQA) competition challenged the community to develop provably private and communication-efficient solutions in a federated setting for a real-life use case: invoice processing. The competition introduced a dataset of real invoice documents, along with associated questions and answers requiring information extraction and reasoning over the document images. Thereby, it brings together researchers and expertise from the document analysis, privacy, and federated learning communities. Participants fine-tuned a pre-trained, state-of-the-art Document Visual Question Answering model provided by the organizers for this new domain, mimicking a typical federated invoice processing setup. The base model is a multi-modal generative language model, and sensitive information could be exposed through either the visual or textual input modality. Participants proposed elegant solutions to reduce communication costs while maintaining a minimum utility threshold in track 1 and to protect all information from each document provider using differential privacy in track 2. The competition served as a new testbed for developing and testing private federated learning methods, simultaneously raising awareness about privacy within the document image analysis and recognition community. Ultimately, the competition analysis provides best practices and recommendations for successfully running privacy-focused federated learning challenges in the future.
One missing piece in Vision and Language: A Survey on Comics Understanding
Sep 14, 2024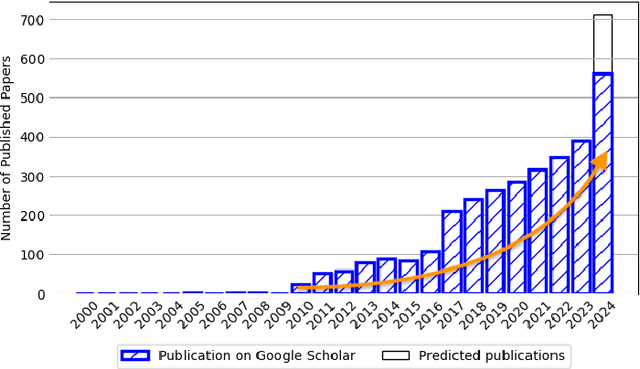
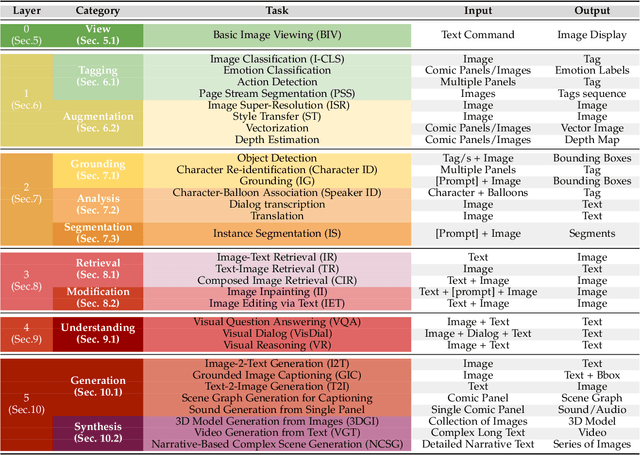
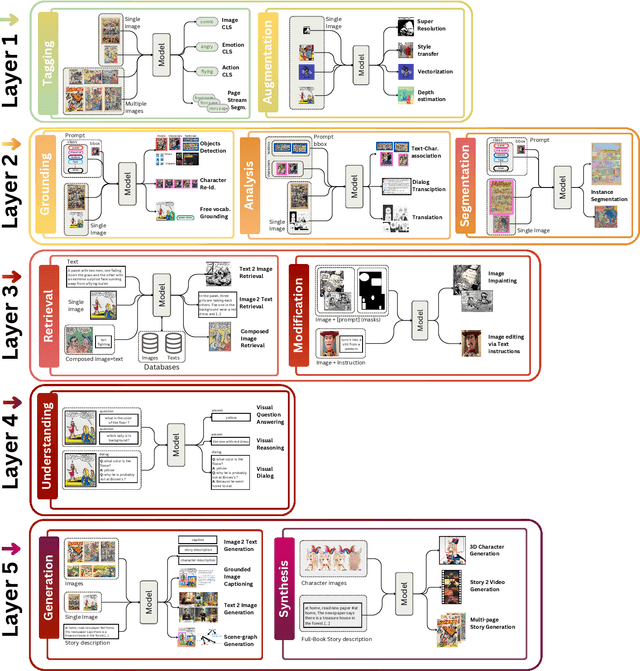
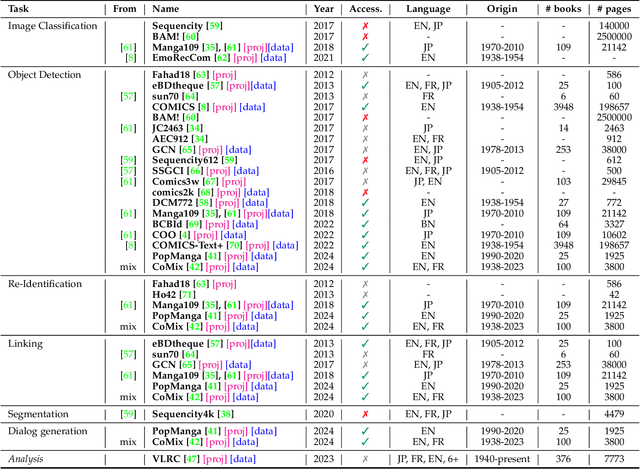
Abstract:Vision-language models have recently evolved into versatile systems capable of high performance across a range of tasks, such as document understanding, visual question answering, and grounding, often in zero-shot settings. Comics Understanding, a complex and multifaceted field, stands to greatly benefit from these advances. Comics, as a medium, combine rich visual and textual narratives, challenging AI models with tasks that span image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, and deeper narrative comprehension through sequential panels. However, the unique structure of comics -- characterized by creative variations in style, reading order, and non-linear storytelling -- presents a set of challenges distinct from those in other visual-language domains. In this survey, we present a comprehensive review of Comics Understanding from both dataset and task perspectives. Our contributions are fivefold: (1) We analyze the structure of the comics medium, detailing its distinctive compositional elements; (2) We survey the widely used datasets and tasks in comics research, emphasizing their role in advancing the field; (3) We introduce the Layer of Comics Understanding (LoCU) framework, a novel taxonomy that redefines vision-language tasks within comics and lays the foundation for future work; (4) We provide a detailed review and categorization of existing methods following the LoCU framework; (5) Finally, we highlight current research challenges and propose directions for future exploration, particularly in the context of vision-language models applied to comics. This survey is the first to propose a task-oriented framework for comics intelligence and aims to guide future research by addressing critical gaps in data availability and task definition. A project associated with this survey is available at https://github.com/emanuelevivoli/awesome-comics-understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge