Ravi Kiran Sarvadevabhatla
Unveiling Text in Challenging Stone Inscriptions: A Character-Context-Aware Patching Strategy for Binarization
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Binarization is a popular first step towards text extraction in historical artifacts. Stone inscription images pose severe challenges for binarization due to poor contrast between etched characters and the stone background, non-uniform surface degradation, distracting artifacts, and highly variable text density and layouts. These conditions frequently cause existing binarization techniques to fail and struggle to isolate coherent character regions. Many approaches sub-divide the image into patches to improve text fragment resolution and improve binarization performance. With this in mind, we present a robust and adaptive patching strategy to binarize challenging Indic inscriptions. The patches from our approach are used to train an Attention U-Net for binarization. The attention mechanism allows the model to focus on subtle structural cues, while our dynamic sampling and patch selection method ensures that the model learns to overcome surface noise and layout irregularities. We also introduce a carefully annotated, pixel-precise dataset of Indic stone inscriptions at the character-fragment level. We demonstrate that our novel patching mechanism significantly boosts binarization performance across classical and deep learning baselines. Despite training only on single script Indic dataset, our model exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to other Indic and non-indic scripts, highlighting its robustness and script-agnostic generalization capabilities. By producing clean, structured representations of inscription content, our method lays the foundation for downstream tasks such as script identification, OCR, and historical text analysis. Project page: https://ihdia.iiit.ac.in/shilalekhya-binarization/
IndicDLP: A Foundational Dataset for Multi-Lingual and Multi-Domain Document Layout Parsing
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Document layout analysis is essential for downstream tasks such as information retrieval, extraction, OCR, and digitization. However, existing large-scale datasets like PubLayNet and DocBank lack fine-grained region labels and multilingual diversity, making them insufficient for representing complex document layouts. In contrast, human-annotated datasets such as M6Doc and D4LA offer richer labels and greater domain diversity, but are too small to train robust models and lack adequate multilingual coverage. This gap is especially pronounced for Indic documents, which encompass diverse scripts yet remain underrepresented in current datasets, further limiting progress in this space. To address these shortcomings, we introduce IndicDLP, a large-scale foundational document layout dataset spanning 11 representative Indic languages alongside English and 12 common document domains. Additionally, we curate UED-mini, a dataset derived from DocLayNet and M6Doc, to enhance pretraining and provide a solid foundation for Indic layout models. Our experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning existing English models on IndicDLP significantly boosts performance, validating its effectiveness. Moreover, models trained on IndicDLP generalize well beyond Indic layouts, making it a valuable resource for document digitization. This work bridges gaps in scale, diversity, and annotation granularity, driving inclusive and efficient document understanding.
STRinGS: Selective Text Refinement in Gaussian Splatting
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Text as signs, labels, or instructions is a critical element of real-world scenes as they can convey important contextual information. 3D representations such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) struggle to preserve fine-grained text details, while achieving high visual fidelity. Small errors in textual element reconstruction can lead to significant semantic loss. We propose STRinGS, a text-aware, selective refinement framework to address this issue for 3DGS reconstruction. Our method treats text and non-text regions separately, refining text regions first and merging them with non-text regions later for full-scene optimization. STRinGS produces sharp, readable text even in challenging configurations. We introduce a text readability measure OCR Character Error Rate (CER) to evaluate the efficacy on text regions. STRinGS results in a 63.6% relative improvement over 3DGS at just 7K iterations. We also introduce a curated dataset STRinGS-360 with diverse text scenarios to evaluate text readability in 3D reconstruction. Our method and dataset together push the boundaries of 3D scene understanding in text-rich environments, paving the way for more robust text-aware reconstruction methods.
TexTAR : Textual Attribute Recognition in Multi-domain and Multi-lingual Document Images
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Recognizing textual attributes such as bold, italic, underline and strikeout is essential for understanding text semantics, structure, and visual presentation. These attributes highlight key information, making them crucial for document analysis. Existing methods struggle with computational efficiency or adaptability in noisy, multilingual settings. To address this, we introduce TexTAR, a multi-task, context-aware Transformer for Textual Attribute Recognition (TAR). Our novel data selection pipeline enhances context awareness, and our architecture employs a 2D RoPE (Rotary Positional Embedding)-style mechanism to incorporate input context for more accurate attribute predictions. We also introduce MMTAD, a diverse, multilingual, multi-domain dataset annotated with text attributes across real-world documents such as legal records, notices, and textbooks. Extensive evaluations show TexTAR outperforms existing methods, demonstrating that contextual awareness contributes to state-of-the-art TAR performance.
RoadSocial: A Diverse VideoQA Dataset and Benchmark for Road Event Understanding from Social Video Narratives
Mar 27, 2025
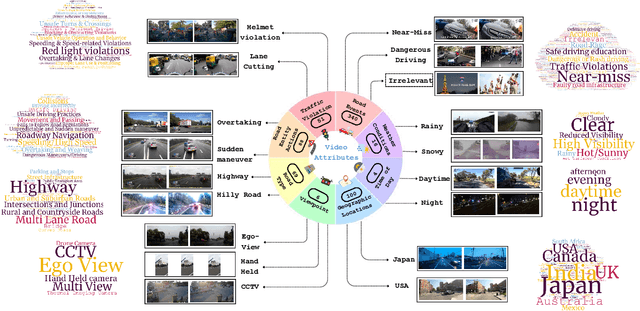
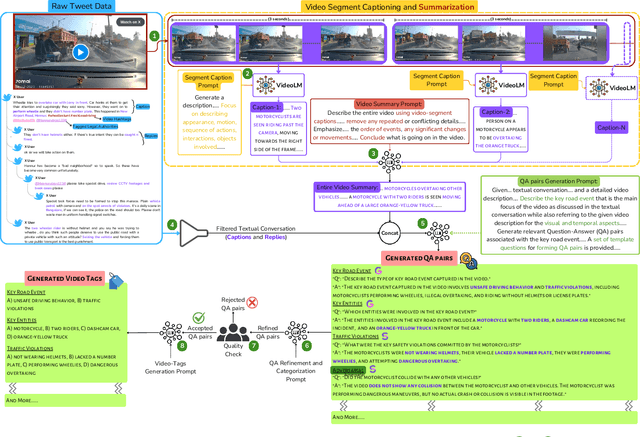
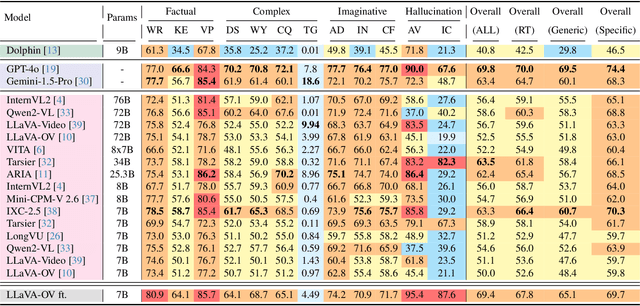
Abstract:We introduce RoadSocial, a large-scale, diverse VideoQA dataset tailored for generic road event understanding from social media narratives. Unlike existing datasets limited by regional bias, viewpoint bias and expert-driven annotations, RoadSocial captures the global complexity of road events with varied geographies, camera viewpoints (CCTV, handheld, drones) and rich social discourse. Our scalable semi-automatic annotation framework leverages Text LLMs and Video LLMs to generate comprehensive question-answer pairs across 12 challenging QA tasks, pushing the boundaries of road event understanding. RoadSocial is derived from social media videos spanning 14M frames and 414K social comments, resulting in a dataset with 13.2K videos, 674 tags and 260K high-quality QA pairs. We evaluate 18 Video LLMs (open-source and proprietary, driving-specific and general-purpose) on our road event understanding benchmark. We also demonstrate RoadSocial's utility in improving road event understanding capabilities of general-purpose Video LLMs.
CrackUDA: Incremental Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Improved Crack Segmentation in Civil Structures
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Crack segmentation plays a crucial role in ensuring the structural integrity and seismic safety of civil structures. However, existing crack segmentation algorithms encounter challenges in maintaining accuracy with domain shifts across datasets. To address this issue, we propose a novel deep network that employs incremental training with unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) using adversarial learning, without a significant drop in accuracy in the source domain. Our approach leverages an encoder-decoder architecture, consisting of both domain-invariant and domain-specific parameters. The encoder learns shared crack features across all domains, ensuring robustness to domain variations. Simultaneously, the decoder's domain-specific parameters capture domain-specific features unique to each domain. By combining these components, our model achieves improved crack segmentation performance. Furthermore, we introduce BuildCrack, a new crack dataset comparable to sub-datasets of the well-established CrackSeg9K dataset in terms of image count and crack percentage. We evaluate our proposed approach against state-of-the-art UDA methods using different sub-datasets of CrackSeg9K and our custom dataset. Our experimental results demonstrate a significant improvement in crack segmentation accuracy and generalization across target domains compared to other UDA methods - specifically, an improvement of 0.65 and 2.7 mIoU on source and target domains respectively.
MoRAG -- Multi-Fusion Retrieval Augmented Generation for Human Motion
Sep 18, 2024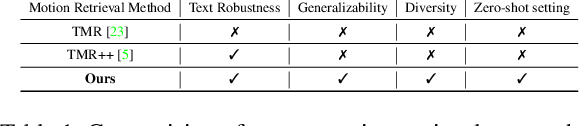
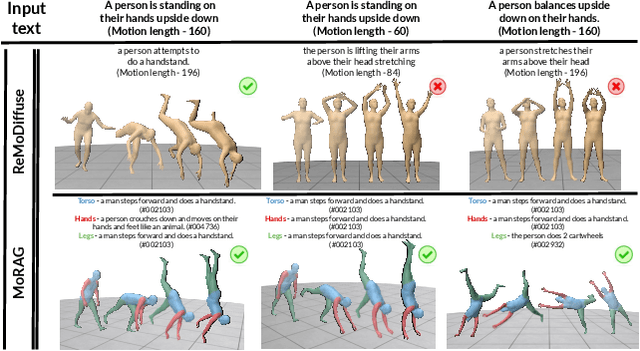
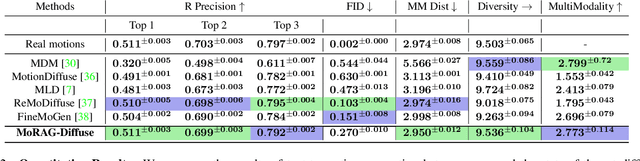
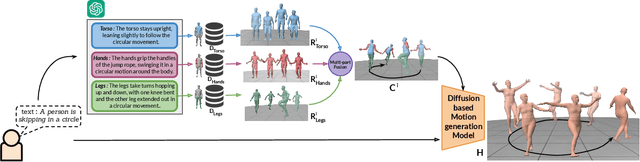
Abstract:We introduce MoRAG, a novel multi-part fusion based retrieval-augmented generation strategy for text-based human motion generation. The method enhances motion diffusion models by leveraging additional knowledge obtained through an improved motion retrieval process. By effectively prompting large language models (LLMs), we address spelling errors and rephrasing issues in motion retrieval. Our approach utilizes a multi-part retrieval strategy to improve the generalizability of motion retrieval across the language space. We create diverse samples through the spatial composition of the retrieved motions. Furthermore, by utilizing low-level, part-specific motion information, we can construct motion samples for unseen text descriptions. Our experiments demonstrate that our framework can serve as a plug-and-play module, improving the performance of motion diffusion models. Code, pretrained models and sample videos will be made available at: https://motion-rag.github.io/
Transfer-LMR: Heavy-Tail Driving Behavior Recognition in Diverse Traffic Scenarios
May 08, 2024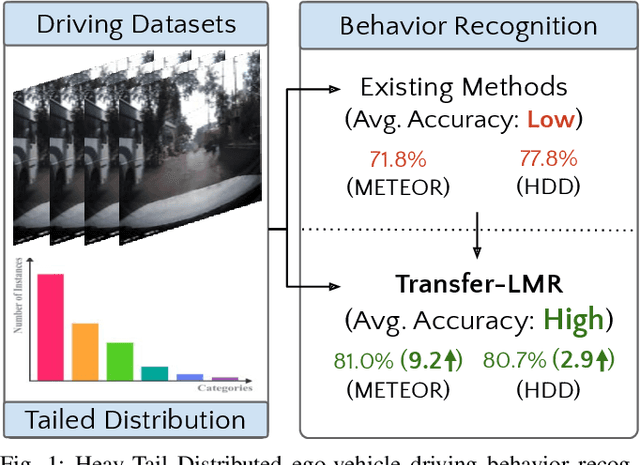
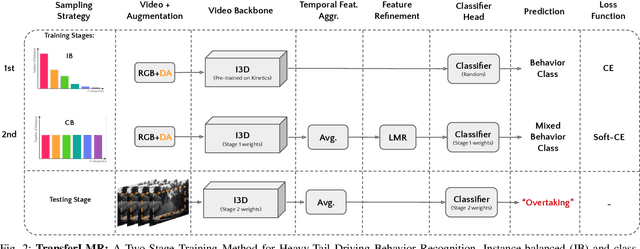
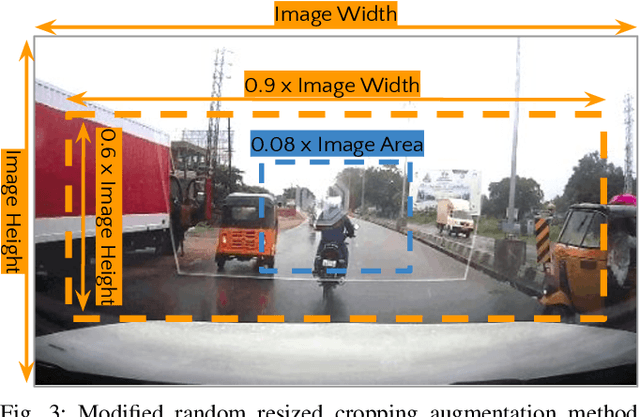
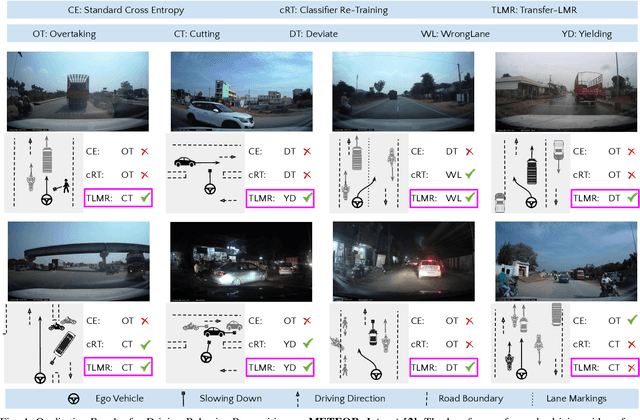
Abstract:Recognizing driving behaviors is important for downstream tasks such as reasoning, planning, and navigation. Existing video recognition approaches work well for common behaviors (e.g. "drive straight", "brake", "turn left/right"). However, the performance is sub-par for underrepresented/rare behaviors typically found in tail of the behavior class distribution. To address this shortcoming, we propose Transfer-LMR, a modular training routine for improving the recognition performance across all driving behavior classes. We extensively evaluate our approach on METEOR and HDD datasets that contain rich yet heavy-tailed distribution of driving behaviors and span diverse traffic scenarios. The experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our approach, especially for recognizing underrepresented/rare driving behaviors.
IDD-X: A Multi-View Dataset for Ego-relative Important Object Localization and Explanation in Dense and Unstructured Traffic
Apr 12, 2024Abstract:Intelligent vehicle systems require a deep understanding of the interplay between road conditions, surrounding entities, and the ego vehicle's driving behavior for safe and efficient navigation. This is particularly critical in developing countries where traffic situations are often dense and unstructured with heterogeneous road occupants. Existing datasets, predominantly geared towards structured and sparse traffic scenarios, fall short of capturing the complexity of driving in such environments. To fill this gap, we present IDD-X, a large-scale dual-view driving video dataset. With 697K bounding boxes, 9K important object tracks, and 1-12 objects per video, IDD-X offers comprehensive ego-relative annotations for multiple important road objects covering 10 categories and 19 explanation label categories. The dataset also incorporates rearview information to provide a more complete representation of the driving environment. We also introduce custom-designed deep networks aimed at multiple important object localization and per-object explanation prediction. Overall, our dataset and introduced prediction models form the foundation for studying how road conditions and surrounding entities affect driving behavior in complex traffic situations.
A Fine-Grained Vehicle Detection Dataset for Unconstrained Roads
Dec 30, 2022
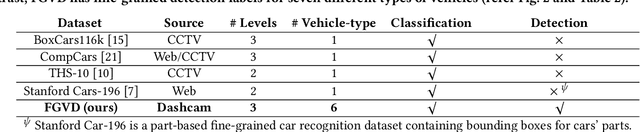

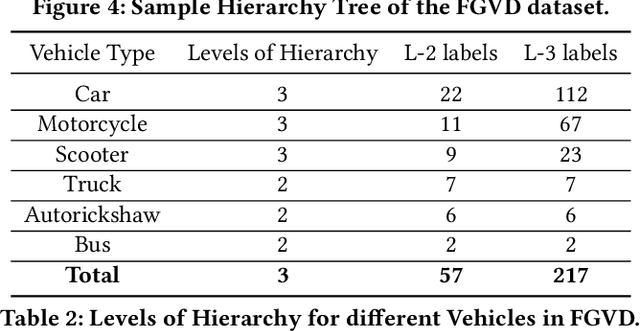
Abstract:The previous fine-grained datasets mainly focus on classification and are often captured in a controlled setup, with the camera focusing on the objects. We introduce the first Fine-Grained Vehicle Detection (FGVD) dataset in the wild, captured from a moving camera mounted on a car. It contains 5502 scene images with 210 unique fine-grained labels of multiple vehicle types organized in a three-level hierarchy. While previous classification datasets also include makes for different kinds of cars, the FGVD dataset introduces new class labels for categorizing two-wheelers, autorickshaws, and trucks. The FGVD dataset is challenging as it has vehicles in complex traffic scenarios with intra-class and inter-class variations in types, scale, pose, occlusion, and lighting conditions. The current object detectors like yolov5 and faster RCNN perform poorly on our dataset due to a lack of hierarchical modeling. Along with providing baseline results for existing object detectors on FGVD Dataset, we also present the results of a combination of an existing detector and the recent Hierarchical Residual Network (HRN) classifier for the FGVD task. Finally, we show that FGVD vehicle images are the most challenging to classify among the fine-grained datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge