Shubh Maheshwari
MoRAG -- Multi-Fusion Retrieval Augmented Generation for Human Motion
Sep 18, 2024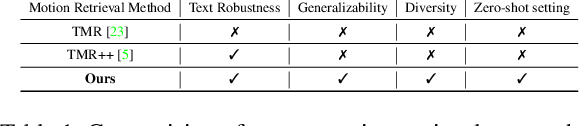
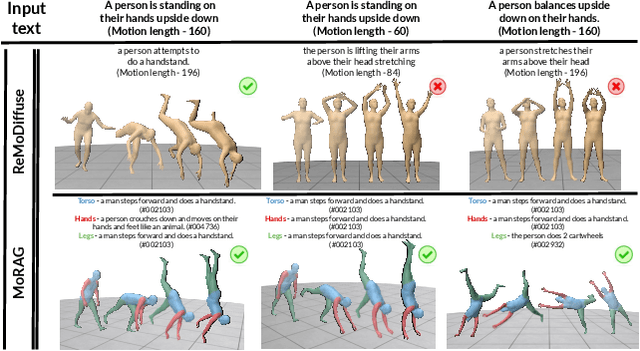
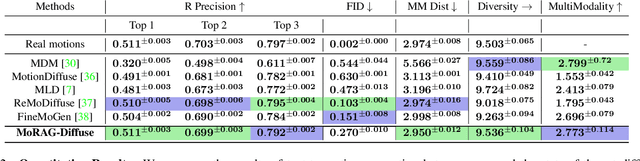
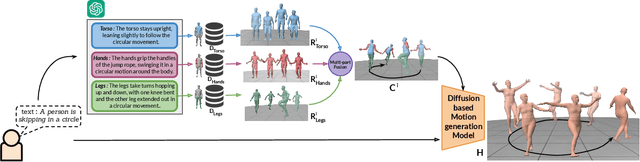
Abstract:We introduce MoRAG, a novel multi-part fusion based retrieval-augmented generation strategy for text-based human motion generation. The method enhances motion diffusion models by leveraging additional knowledge obtained through an improved motion retrieval process. By effectively prompting large language models (LLMs), we address spelling errors and rephrasing issues in motion retrieval. Our approach utilizes a multi-part retrieval strategy to improve the generalizability of motion retrieval across the language space. We create diverse samples through the spatial composition of the retrieved motions. Furthermore, by utilizing low-level, part-specific motion information, we can construct motion samples for unseen text descriptions. Our experiments demonstrate that our framework can serve as a plug-and-play module, improving the performance of motion diffusion models. Code, pretrained models and sample videos will be made available at: https://motion-rag.github.io/
Action-GPT: Leveraging Large-scale Language Models for Improved and Generalized Zero Shot Action Generation
Nov 30, 2022
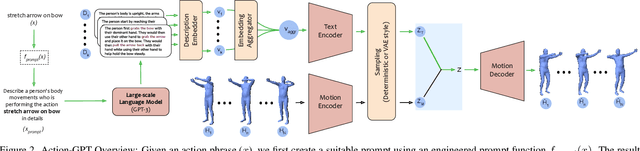


Abstract:We introduce Action-GPT, a plug and play framework for incorporating Large Language Models (LLMs) into text-based action generation models. Action phrases in current motion capture datasets contain minimal and to-the-point information. By carefully crafting prompts for LLMs, we generate richer and fine-grained descriptions of the action. We show that utilizing these detailed descriptions instead of the original action phrases leads to better alignment of text and motion spaces. Our experiments show qualitative and quantitative improvement in the quality of synthesized motions produced by recent text-to-motion models. Code, pretrained models and sample videos will be made available at https://actiongpt.github.io
MUGL: Large Scale Multi Person Conditional Action Generation with Locomotion
Oct 21, 2021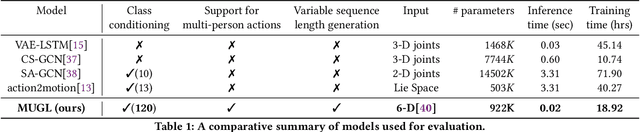
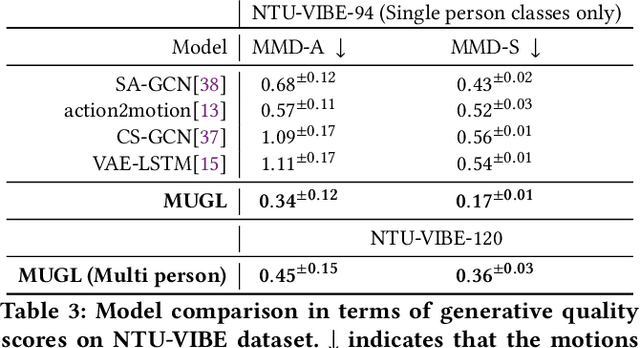
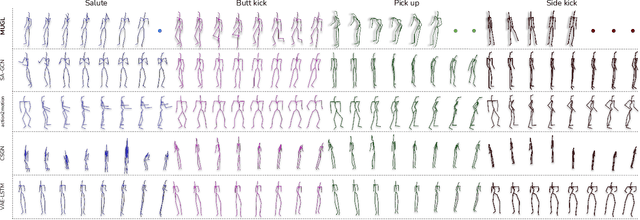
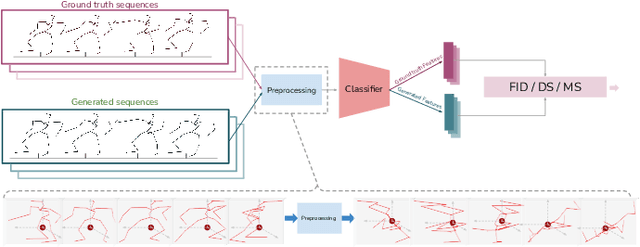
Abstract:We introduce MUGL, a novel deep neural model for large-scale, diverse generation of single and multi-person pose-based action sequences with locomotion. Our controllable approach enables variable-length generations customizable by action category, across more than 100 categories. To enable intra/inter-category diversity, we model the latent generative space using a Conditional Gaussian Mixture Variational Autoencoder. To enable realistic generation of actions involving locomotion, we decouple local pose and global trajectory components of the action sequence. We incorporate duration-aware feature representations to enable variable-length sequence generation. We use a hybrid pose sequence representation with 3D pose sequences sourced from videos and 3D Kinect-based sequences of NTU-RGBD-120. To enable principled comparison of generation quality, we employ suitably modified strong baselines during evaluation. Although smaller and simpler compared to baselines, MUGL provides better quality generations, paving the way for practical and controllable large-scale human action generation.
Quo Vadis, Skeleton Action Recognition ?
Jul 04, 2020
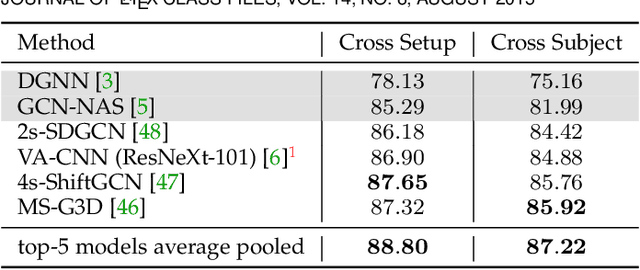
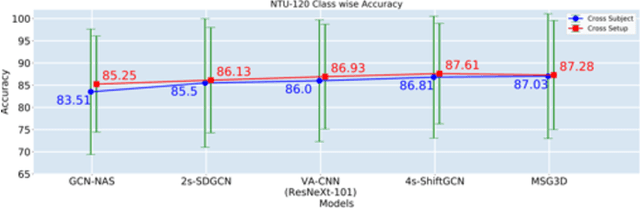
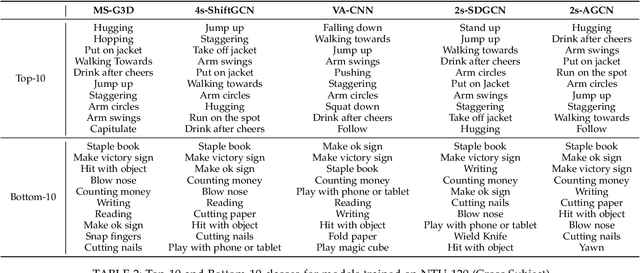
Abstract:In this paper, we study current and upcoming frontiers across the landscape of skeleton-based human action recognition. To begin with, we benchmark state-of-the-art models on the NTU-120 dataset and provide multi-layered assessment of the results. To examine skeleton action recognition 'in the wild', we introduce Skeletics-152, a curated and 3-D pose-annotated subset of RGB videos sourced from Kinetics-700, a large-scale action dataset. The results from benchmarking the top performers of NTU-120 on Skeletics-152 reveal the challenges and domain gap induced by actions 'in the wild'. We extend our study to include out-of-context actions by introducing Skeleton-Mimetics, a dataset derived from the recently introduced Mimetics dataset. Finally, as a new frontier for action recognition, we introduce Metaphorics, a dataset with caption-style annotated YouTube videos of the popular social game Dumb Charades and interpretative dance performances. Overall, our work characterizes the strengths and limitations of existing approaches and datasets. It also provides an assessment of top-performing approaches across a spectrum of activity settings and via the introduced datasets, proposes new frontiers for human action recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge