Anirudh Thatipelli
MIRA: Towards Mitigating Reward Hacking in Inference-Time Alignment of T2I Diffusion Models
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models excel at generating images conditioned on text prompts, but the resulting images often do not satisfy user-specific criteria measured by scalar rewards such as Aesthetic Scores. This alignment typically requires fine-tuning, which is computationally demanding. Recently, inference-time alignment via noise optimization has emerged as an efficient alternative, modifying initial input noise to steer the diffusion denoising process towards generating high-reward images. However, this approach suffers from reward hacking, where the model produces images that score highly, yet deviate significantly from the original prompt. We show that noise-space regularization is insufficient and that preventing reward hacking requires an explicit image-space constraint. To this end, we propose MIRA (MItigating Reward hAcking), a training-free, inference-time alignment method. MIRA introduces an image-space, score-based KL surrogate that regularizes the sampling trajectory with a frozen backbone, constraining the output distribution so reward can increase without off-distribution drift (reward hacking). We derive a tractable approximation to KL using diffusion scores. Across SDv1.5 and SDXL, multiple rewards (Aesthetic, HPSv2, PickScore), and public datasets (e.g., Animal-Animal, HPDv2), MIRA achieves >60\% win rate vs. strong baselines while preserving prompt adherence; mechanism plots show reward gains with near-zero drift, whereas DNO drifts as compute increases. We further introduce MIRA-DPO, mapping preference optimization to inference time with a frozen backbone, extending MIRA to non-differentiable rewards without fine-tuning.
Exocentric To Egocentric Transfer For Action Recognition: A Short Survey
Oct 27, 2024



Abstract:Egocentric vision captures the scene from the point of view of the camera wearer while exocentric vision captures the overall scene context. Jointly modeling ego and exo views is crucial to developing next-generation AI agents. The community has regained interest in the field of egocentric vision. While the third-person view and first-person have been thoroughly investigated, very few works aim to study both synchronously. Exocentric videos contain many relevant signals that are transferrable to egocentric videos. In this paper, we provide a broad overview of works combining egocentric and exocentric visions.
Spatio-temporal Relation Modeling for Few-shot Action Recognition
Dec 09, 2021



Abstract:We propose a novel few-shot action recognition framework, STRM, which enhances class-specific feature discriminability while simultaneously learning higher-order temporal representations. The focus of our approach is a novel spatio-temporal enrichment module that aggregates spatial and temporal contexts with dedicated local patch-level and global frame-level feature enrichment sub-modules. Local patch-level enrichment captures the appearance-based characteristics of actions. On the other hand, global frame-level enrichment explicitly encodes the broad temporal context, thereby capturing the relevant object features over time. The resulting spatio-temporally enriched representations are then utilized to learn the relational matching between query and support action sub-sequences. We further introduce a query-class similarity classifier on the patch-level enriched features to enhance class-specific feature discriminability by reinforcing the feature learning at different stages in the proposed framework. Experiments are performed on four few-shot action recognition benchmarks: Kinetics, SSv2, HMDB51 and UCF101. Our extensive ablation study reveals the benefits of the proposed contributions. Furthermore, our approach sets a new state-of-the-art on all four benchmarks. On the challenging SSv2 benchmark, our approach achieves an absolute gain of 3.5% in classification accuracy, as compared to the best existing method in the literature. Our code and models will be publicly released.
NTU60-X: Towards Skeleton-based Recognition of Subtle Human Actions
Jan 29, 2021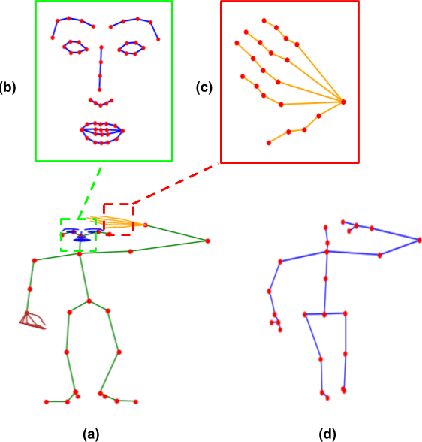
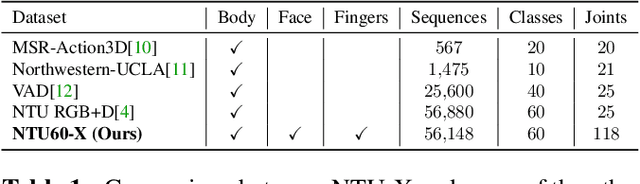
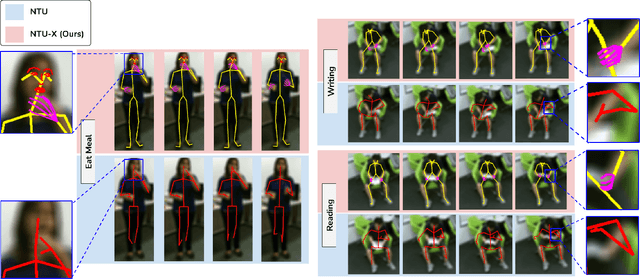
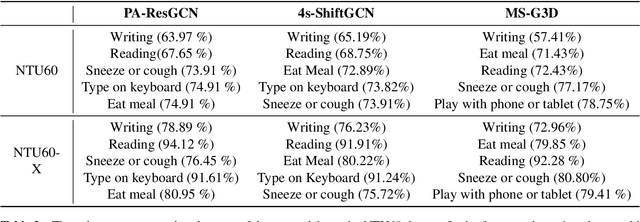
Abstract:The lack of fine-grained joints such as hand fingers is a fundamental performance bottleneck for state of the art skeleton action recognition models trained on the largest action recognition dataset, NTU-RGBD. To address this bottleneck, we introduce a new skeleton based human action dataset - NTU60-X. In addition to the 25 body joints for each skeleton as in NTU-RGBD, NTU60-X dataset includes finger and facial joints, enabling a richer skeleton representation. We appropriately modify the state of the art approaches to enable training using the introduced dataset. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of NTU60-X in overcoming the aforementioned bottleneck and improve state of the art performance, overall and on hitherto worst performing action categories.
Quo Vadis, Skeleton Action Recognition ?
Jul 04, 2020
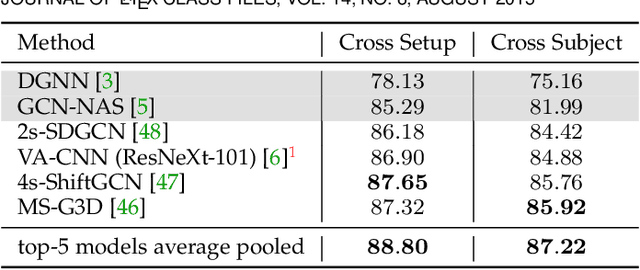
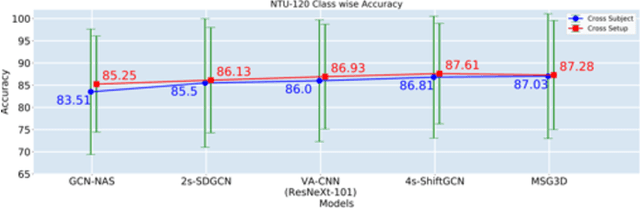
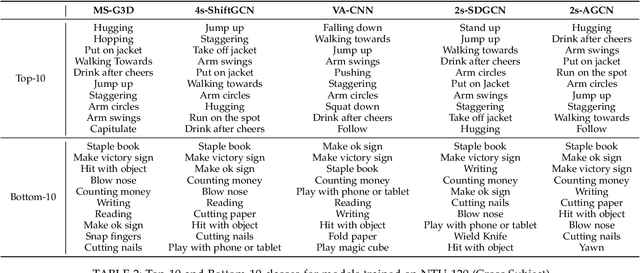
Abstract:In this paper, we study current and upcoming frontiers across the landscape of skeleton-based human action recognition. To begin with, we benchmark state-of-the-art models on the NTU-120 dataset and provide multi-layered assessment of the results. To examine skeleton action recognition 'in the wild', we introduce Skeletics-152, a curated and 3-D pose-annotated subset of RGB videos sourced from Kinetics-700, a large-scale action dataset. The results from benchmarking the top performers of NTU-120 on Skeletics-152 reveal the challenges and domain gap induced by actions 'in the wild'. We extend our study to include out-of-context actions by introducing Skeleton-Mimetics, a dataset derived from the recently introduced Mimetics dataset. Finally, as a new frontier for action recognition, we introduce Metaphorics, a dataset with caption-style annotated YouTube videos of the popular social game Dumb Charades and interpretative dance performances. Overall, our work characterizes the strengths and limitations of existing approaches and datasets. It also provides an assessment of top-performing approaches across a spectrum of activity settings and via the introduced datasets, proposes new frontiers for human action recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge