Bohao Wang
BEAR: Towards Beam-Search-Aware Optimization for Recommendation with Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recent years have witnessed a rapid surge in research leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for recommendation. These methods typically employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to adapt LLMs to recommendation scenarios, and utilize beam search during inference to efficiently retrieve $B$ top-ranked recommended items. However, we identify a critical training-inference inconsistency: while SFT optimizes the overall probability of positive items, it does not guarantee that such items will be retrieved by beam search even if they possess high overall probabilities. Due to the greedy pruning mechanism, beam search can prematurely discard a positive item once its prefix probability is insufficient. To address this inconsistency, we propose BEAR (Beam-SEarch-Aware Regularization), a novel fine-tuning objective that explicitly accounts for beam search behavior during training. Rather than directly simulating beam search for each instance during training, which is computationally prohibitive, BEAR enforces a relaxed necessary condition: each token in a positive item must rank within the top-$B$ candidate tokens at each decoding step. This objective effectively mitigates the risk of incorrect pruning while incurring negligible computational overhead compared to standard SFT. Extensive experiments across four real-world datasets demonstrate that BEAR significantly outperforms strong baselines. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Seeing Radio: From Zero RF Priors to Explainable Modulation Recognition with Vision Language Models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:The rise of vision language models (VLMs) paves a new path for radio frequency (RF) perception. Rather than designing task-specific neural receivers, we ask if VLMs can learn to recognize modulations when RF waveforms are expressed as images. In this work, we find that they can. In specific, in this paper, we introduce a practical pipeline for converting complex IQ streams into visually interpretable inputs, hence, enabling general-purpose VLMs to classify modulation schemes without changing their underlying design. Building on this, we construct an RF visual question answering (VQA) benchmark framework that covers 57 classes across major families of analog/digital modulations with three complementary image modes, namely, (i) short \emph{time-series} IQ segments represented as real/imaginary traces, (ii) magnitude-only \emph{spectrograms}, and (iii) \emph{joint} representations that pair spectrograms with a synchronized time-series waveforms. We design uniform zero-shot and few-shot prompts for both class-level and family-level evaluations. Our finetuned VLMs with these images achieve competitive accuracy of $90\%$ compared to $10\%$ of the base models. Furthermore, the fine-tuned VLMs show robust performance under noise and demonstrate high generalization performance to unseen modulation types, without relying on RF-domain priors or specialized architectures. The obtained results show that combining RF-to-image conversion with promptable VLMs provides a scalable and practical foundation for RF-aware AI systems in future 6G networks.
Dynamical Multimodal Fusion with Mixture-of-Experts for Localizations
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Multimodal fingerprinting is a crucial technique to sub-meter 6G integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) localization, but two hurdles block deployment: (i) the contribution each modality makes to the target position varies with the operating conditions such as carrier frequency, and (ii) spatial and fingerprint ambiguities markedly undermine localization accuracy, especially in non-line-of-sight (NLOS) scenarios. To solve these problems, we introduce SCADF-MoE, a spatial-context aware dynamic fusion network built on a soft mixture-of-experts backbone. SCADF-MoE first clusters neighboring points into short trajectories to inject explicit spatial context. Then, it adaptively fuses channel state information, angle of arrival profile, distance, and gain through its learnable MoE router, so that the most reliable cues dominate at each carrier band. The fused representation is fed to a modality-task MoE that simultaneously regresses the coordinates of every vertex in the trajectory and its centroid, thereby exploiting inter-point correlations. Finally, an auxiliary maximum-mean-discrepancy loss enforces expert diversity and mitigates gradient interference, stabilizing multi-task training. On three real urban layouts and three carrier bands (2.6, 6, 28 GHz), the model delivers consistent sub-meter MSE and halves unseen-NLOS error versus the best prior work. To our knowledge, this is the first work that leverages large-scale multimodal MoE for frequency-robust ISAC localization.
Bridging the Gap: Self-Optimized Fine-Tuning for LLM-based Recommender Systems
May 27, 2025Abstract:Recent years have witnessed extensive exploration of Large Language Models (LLMs) on the field of Recommender Systems (RS). There are currently two commonly used strategies to enable LLMs to have recommendation capabilities: 1) The "Guidance-Only" strategy uses in-context learning to exploit and amplify the inherent semantic understanding and item recommendation capabilities of LLMs; 2) The "Tuning-Only" strategy uses supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to fine-tune LLMs with the aim of fitting them to real recommendation data. However, neither of these strategies can effectively bridge the gap between the knowledge space of LLMs and recommendation, and their performance do not meet our expectations. To better enable LLMs to learn recommendation knowledge, we combine the advantages of the above two strategies and proposed a novel "Guidance+Tuning" method called Self-Optimized Fine-Tuning (SOFT), which adopts the idea of curriculum learning. It first employs self-distillation to construct an auxiliary easy-to-learn but meaningful dataset from a fine-tuned LLM. Then it further utilizes a self-adaptive curriculum scheduler to enable LLMs to gradually learn from simpler data (self-distilled data) to more challenging data (real RS data). Extensive experiments demonstrate that SOFT significantly enhances the recommendation accuracy (37.59\% on average) of LLM-based methods. The code is available via https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Self-Optimized-Fine-Tuning-264E
MSL: Not All Tokens Are What You Need for Tuning LLM as a Recommender
Apr 05, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), known for their comprehension capabilities and extensive knowledge, have been increasingly applied to recommendation systems (RS). Given the fundamental gap between the mechanism of LLMs and the requirement of RS, researchers have focused on fine-tuning LLMs with recommendation-specific data to enhance their performance. Language Modeling Loss (LML), originally designed for language generation tasks, is commonly adopted. However, we identify two critical limitations of LML: 1) it exhibits significant divergence from the recommendation objective; 2) it erroneously treats all fictitious item descriptions as negative samples, introducing misleading training signals. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Masked Softmax Loss (MSL) tailored for fine-tuning LLMs on recommendation. MSL improves LML by identifying and masking invalid tokens that could lead to fictitious item descriptions during loss computation. This strategy can effectively avoid the interference from erroneous negative signals and ensure well alignment with the recommendation objective supported by theoretical guarantees. During implementation, we identify a potential challenge related to gradient vanishing of MSL. To overcome this, we further introduce the temperature coefficient and propose an Adaptive Temperature Strategy (ATS) that adaptively adjusts the temperature without requiring extensive hyperparameter tuning. Extensive experiments conducted on four public datasets further validate the effectiveness of MSL, achieving an average improvement of 42.24% in NDCG@10. The code is available at https://github.com/WANGBohaO-jpg/MSL.
Large-Scale AI in Telecom: Charting the Roadmap for Innovation, Scalability, and Enhanced Digital Experiences
Mar 06, 2025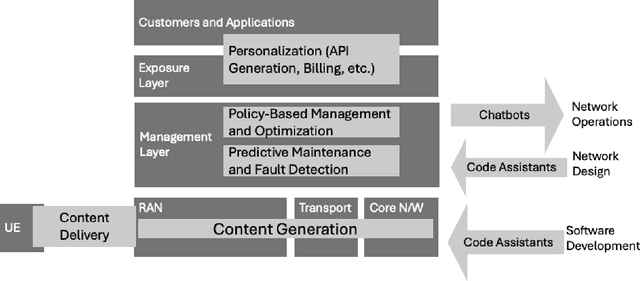
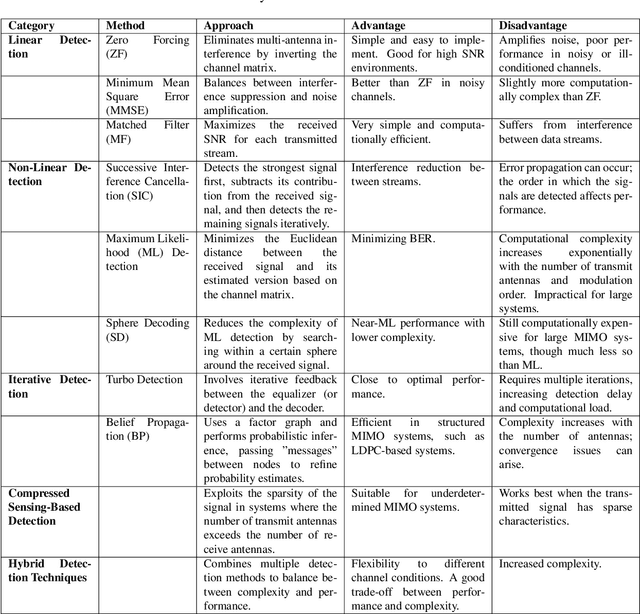
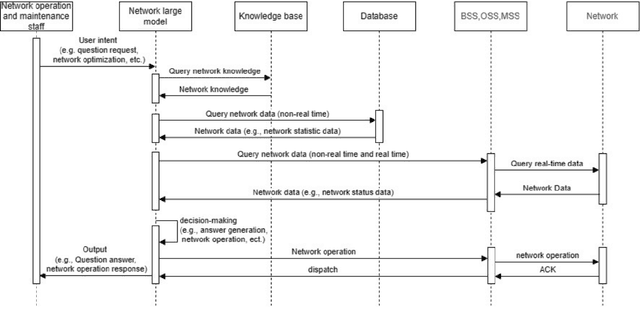
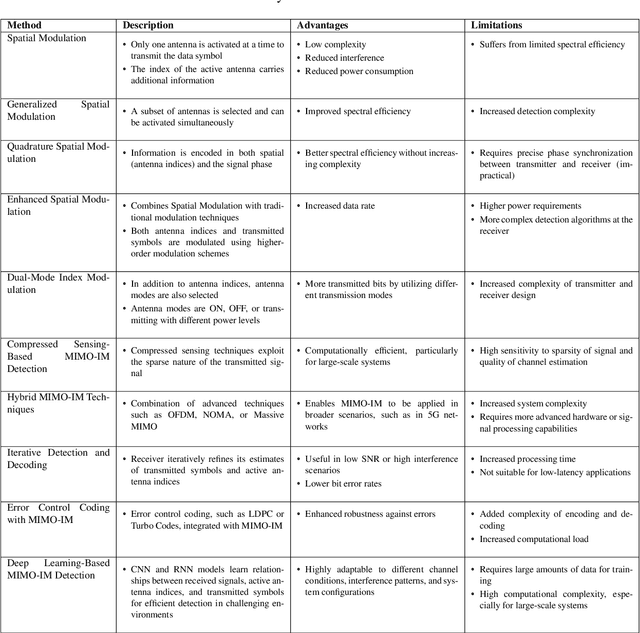
Abstract:This white paper discusses the role of large-scale AI in the telecommunications industry, with a specific focus on the potential of generative AI to revolutionize network functions and user experiences, especially in the context of 6G systems. It highlights the development and deployment of Large Telecom Models (LTMs), which are tailored AI models designed to address the complex challenges faced by modern telecom networks. The paper covers a wide range of topics, from the architecture and deployment strategies of LTMs to their applications in network management, resource allocation, and optimization. It also explores the regulatory, ethical, and standardization considerations for LTMs, offering insights into their future integration into telecom infrastructure. The goal is to provide a comprehensive roadmap for the adoption of LTMs to enhance scalability, performance, and user-centric innovation in telecom networks.
Multi-Sources Fusion Learning for Multi-Points NLOS Localization in OFDM System
Sep 04, 2024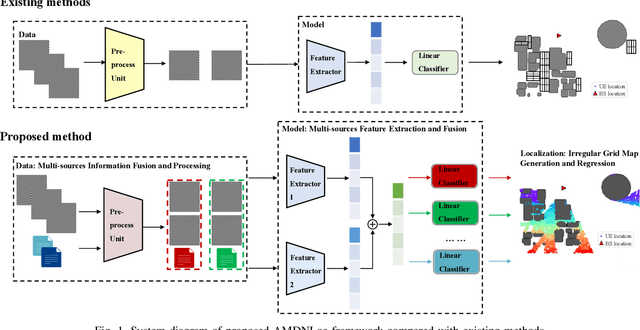
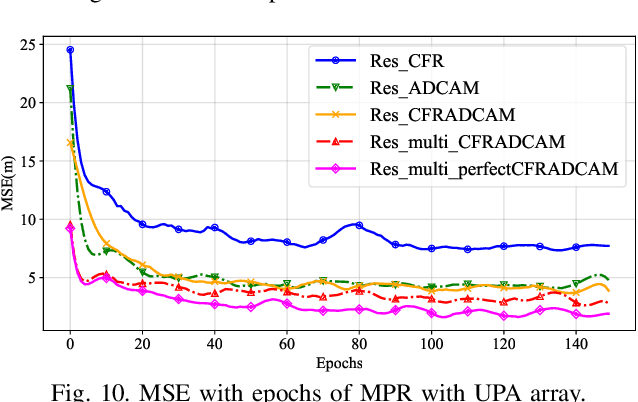
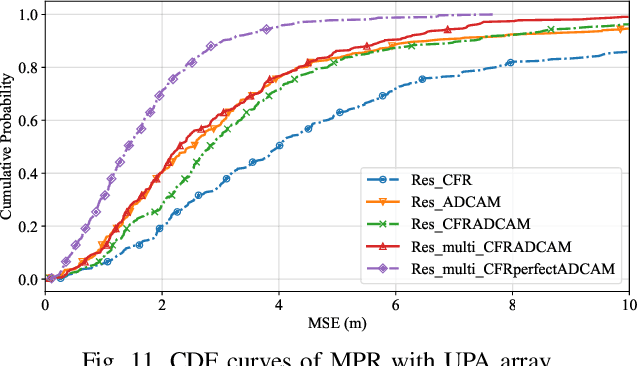
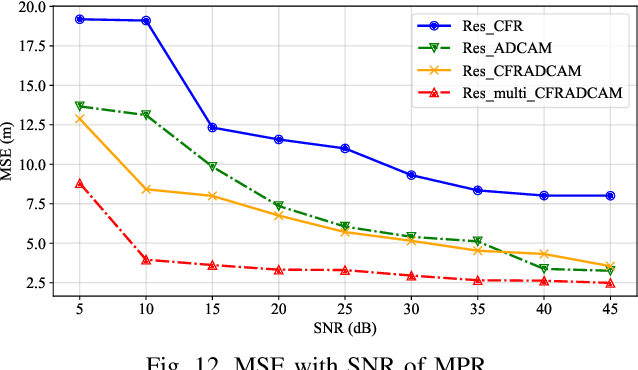
Abstract:Accurate localization of mobile terminals is a pivotal aspect of integrated sensing and communication systems. Traditional fingerprint-based localization methods, which infer coordinates from channel information within pre-set rectangular areas, often face challenges due to the heterogeneous distribution of fingerprints inherent in non-line-of-sight (NLOS) scenarios, particularly within orthogonal frequency division multiplexing systems. To overcome this limitation, we develop a novel multi-sources information fusion learning framework referred to as the Autosync Multi-Domains NLOS Localization (AMDNLoc). Specifically, AMDNLoc employs a two-stage matched filter fused with a target tracking algorithm and iterative centroid-based clustering to automatically and irregularly segment NLOS regions, ensuring uniform distribution within channel state information across frequency, power, and time-delay domains. Additionally, the framework utilizes a segment-specific linear classifier array, coupled with deep residual network-based feature extraction and fusion, to establish the correlation function between fingerprint features and coordinates within these regions. Simulation results reveal that AMDNLoc achieves an impressive NLOS localization accuracy of 1.46 meters on typical wireless artificial intelligence research datasets and demonstrates significant improvements in interpretability, adaptability, and scalability.
LLM4DSR: Leveraing Large Language Model for Denoising Sequential Recommendation
Aug 15, 2024



Abstract:Sequential recommendation systems fundamentally rely on users' historical interaction sequences, which are often contaminated by noisy interactions. Identifying these noisy interactions accurately without additional information is particularly difficult due to the lack of explicit supervisory signals to denote noise. Large Language Models (LLMs), equipped with extensive open knowledge and semantic reasoning abilities, present a promising avenue to bridge this information gap. However, employing LLMs for denoising in sequential recommendation introduces notable challenges: 1) Direct application of pretrained LLMs may not be competent for the denoising task, frequently generating nonsensical responses; 2) Even after fine-tuning, the reliability of LLM outputs remains questionable, especially given the complexity of the task and th inherent hallucinatory issue of LLMs. To tackle these challenges, we propose LLM4DSR, a tailored approach for denoising sequential recommendation using LLMs. We constructed a self-supervised fine-tuning task to activate LLMs' capabilities to identify noisy items and suggest replacements. Furthermore, we developed an uncertainty estimation module that ensures only high-confidence responses are utilized for sequence corrections. Remarkably, LLM4DSR is model-agnostic, allowing the corrected sequences to be flexibly applied across various recommendation models. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of LLM4DSR over existing methods across three datasets and three recommendation backbones.
Distillation Matters: Empowering Sequential Recommenders to Match the Performance of Large Language Model
May 01, 2024



Abstract:Owing to their powerful semantic reasoning capabilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) have been effectively utilized as recommenders, achieving impressive performance. However, the high inference latency of LLMs significantly restricts their practical deployment. To address this issue, this work investigates knowledge distillation from cumbersome LLM-based recommendation models to lightweight conventional sequential models. It encounters three challenges: 1) the teacher's knowledge may not always be reliable; 2) the capacity gap between the teacher and student makes it difficult for the student to assimilate the teacher's knowledge; 3) divergence in semantic space poses a challenge to distill the knowledge from embeddings. To tackle these challenges, this work proposes a novel distillation strategy, DLLM2Rec, specifically tailored for knowledge distillation from LLM-based recommendation models to conventional sequential models. DLLM2Rec comprises: 1) Importance-aware ranking distillation, which filters reliable and student-friendly knowledge by weighting instances according to teacher confidence and student-teacher consistency; 2) Collaborative embedding distillation integrates knowledge from teacher embeddings with collaborative signals mined from the data. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DLLM2Rec, boosting three typical sequential models with an average improvement of 47.97%, even enabling them to surpass LLM-based recommenders in some cases.
SIGformer: Sign-aware Graph Transformer for Recommendation
Apr 18, 2024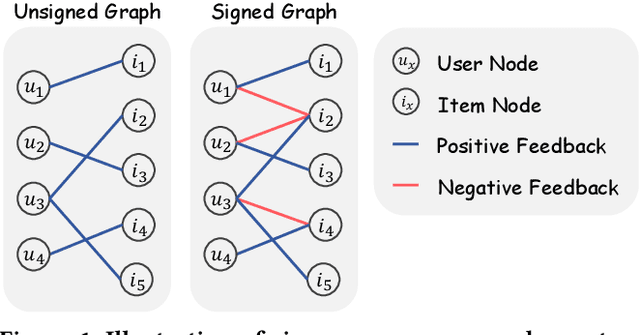
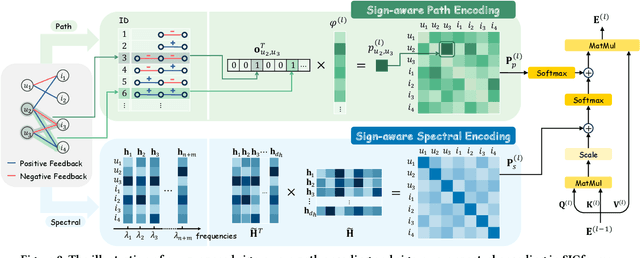
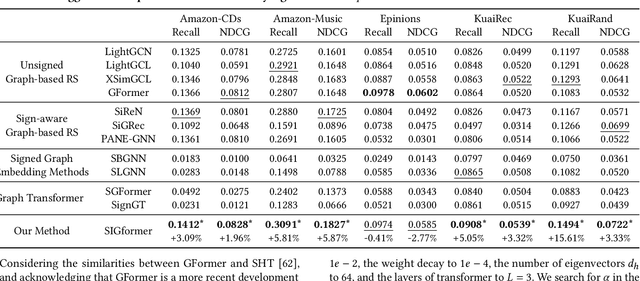
Abstract:In recommender systems, most graph-based methods focus on positive user feedback, while overlooking the valuable negative feedback. Integrating both positive and negative feedback to form a signed graph can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of user preferences. However, the existing efforts to incorporate both types of feedback are sparse and face two main limitations: 1) They process positive and negative feedback separately, which fails to holistically leverage the collaborative information within the signed graph; 2) They rely on MLPs or GNNs for information extraction from negative feedback, which may not be effective. To overcome these limitations, we introduce SIGformer, a new method that employs the transformer architecture to sign-aware graph-based recommendation. SIGformer incorporates two innovative positional encodings that capture the spectral properties and path patterns of the signed graph, enabling the full exploitation of the entire graph. Our extensive experiments across five real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of SIGformer over state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/StupidThree/SIGformer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge