Changdong Li
Advancing Loss Functions in Recommender Systems: A Comparative Study with a Rényi Divergence-Based Solution
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Loss functions play a pivotal role in optimizing recommendation models. Among various loss functions, Softmax Loss (SL) and Cosine Contrastive Loss (CCL) are particularly effective. Their theoretical connections and differences warrant in-depth exploration. This work conducts comprehensive analyses of these losses, yielding significant insights: 1) Common strengths -- both can be viewed as augmentations of traditional losses with Distributional Robust Optimization (DRO), enhancing robustness to distributional shifts; 2) Respective limitations -- stemming from their use of different distribution distance metrics in DRO optimization, SL exhibits high sensitivity to false negative instances, whereas CCL suffers from low data utilization. To address these limitations, this work proposes a new loss function, DrRL, which generalizes SL and CCL by leveraging R\'enyi-divergence in DRO optimization. DrRL incorporates the advantageous structures of both SL and CCL, and can be demonstrated to effectively mitigate their limitations. Extensive experiments have been conducted to validate the superiority of DrRL on both recommendation accuracy and robustness.
Distributionally Robust Graph-based Recommendation System
Feb 21, 2024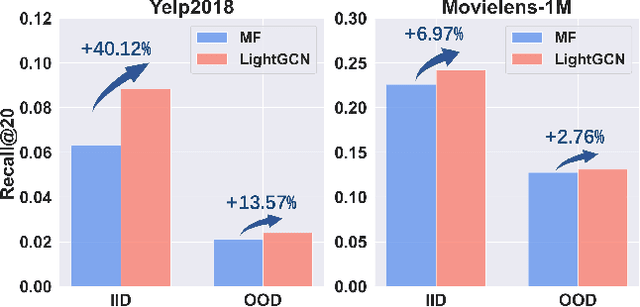
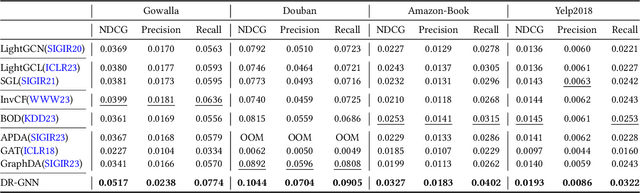
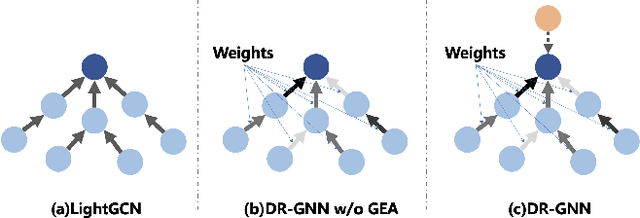
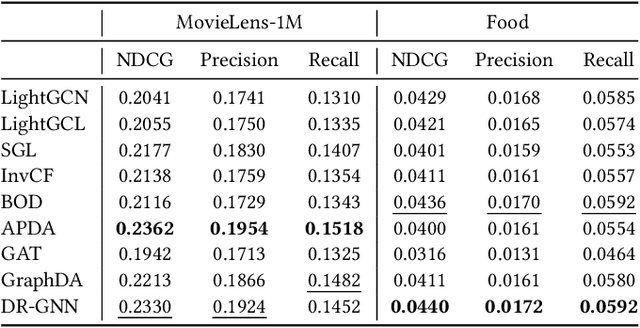
Abstract:With the capacity to capture high-order collaborative signals, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as powerful methods in Recommender Systems (RS). However, their efficacy often hinges on the assumption that training and testing data share the same distribution (a.k.a. IID assumption), and exhibits significant declines under distribution shifts. Distribution shifts commonly arises in RS, often attributed to the dynamic nature of user preferences or ubiquitous biases during data collection in RS. Despite its significance, researches on GNN-based recommendation against distribution shift are still sparse. To bridge this gap, we propose Distributionally Robust GNN (DR-GNN) that incorporates Distributional Robust Optimization (DRO) into the GNN-based recommendation. DR-GNN addresses two core challenges: 1) To enable DRO to cater to graph data intertwined with GNN, we reinterpret GNN as a graph smoothing regularizer, thereby facilitating the nuanced application of DRO; 2) Given the typically sparse nature of recommendation data, which might impede robust optimization, we introduce slight perturbations in the training distribution to expand its support. Notably, while DR-GNN involves complex optimization, it can be implemented easily and efficiently. Our extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of DR-GNN against three typical distribution shifts. The code is available at https://github.com/WANGBohaO-jpg/DR-GNN.
MS-Former: Memory-Supported Transformer for Weakly Supervised Change Detection with Patch-Level Annotations
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:Fully supervised change detection methods have achieved significant advancements in performance, yet they depend severely on acquiring costly pixel-level labels. Considering that the patch-level annotations also contain abundant information corresponding to both changed and unchanged objects in bi-temporal images, an intuitive solution is to segment the changes with patch-level annotations. How to capture the semantic variations associated with the changed and unchanged regions from the patch-level annotations to obtain promising change results is the critical challenge for the weakly supervised change detection task. In this paper, we propose a memory-supported transformer (MS-Former), a novel framework consisting of a bi-directional attention block (BAB) and a patch-level supervision scheme (PSS) tailored for weakly supervised change detection with patch-level annotations. More specifically, the BAM captures contexts associated with the changed and unchanged regions from the temporal difference features to construct informative prototypes stored in the memory bank. On the other hand, the BAM extracts useful information from the prototypes as supplementary contexts to enhance the temporal difference features, thereby better distinguishing changed and unchanged regions. After that, the PSS guides the network learning valuable knowledge from the patch-level annotations, thus further elevating the performance. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in the change detection task. The demo code for our work will be publicly available at \url{https://github.com/guanyuezhen/MS-Former}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge