Zhenglai Li
Mask-informed Deep Contrastive Incomplete Multi-view Clustering
Feb 04, 2025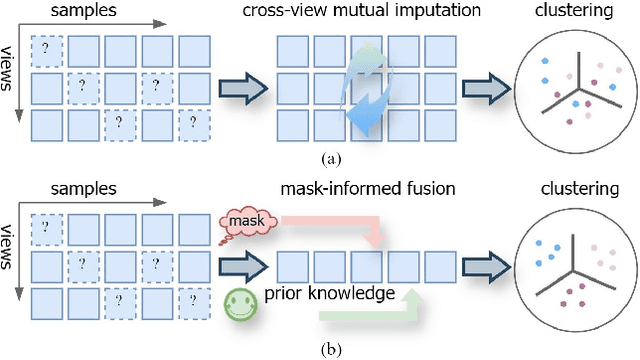
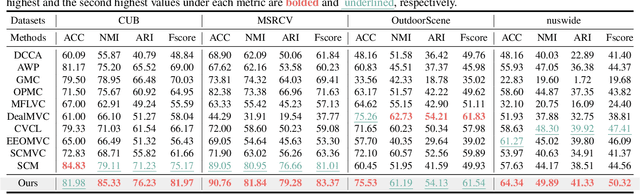
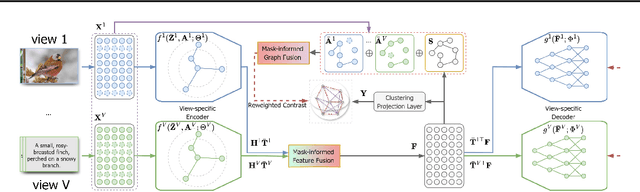
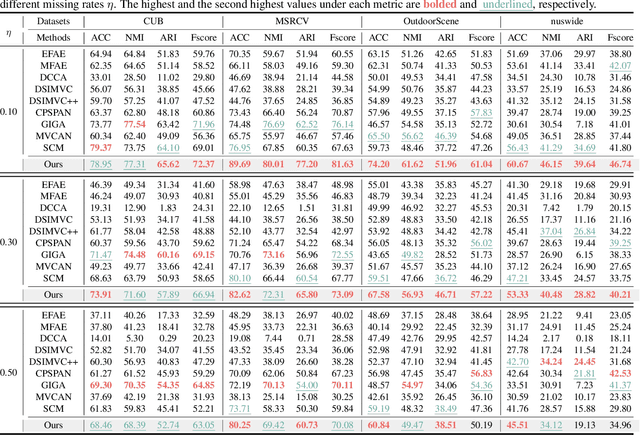
Abstract:Multi-view clustering (MvC) utilizes information from multiple views to uncover the underlying structures of data. Despite significant advancements in MvC, mitigating the impact of missing samples in specific views on the integration of knowledge from different views remains a critical challenge. This paper proposes a novel Mask-informed Deep Contrastive Incomplete Multi-view Clustering (Mask-IMvC) method, which elegantly identifies a view-common representation for clustering. Specifically, we introduce a mask-informed fusion network that aggregates incomplete multi-view information while considering the observation status of samples across various views as a mask, thereby reducing the adverse effects of missing values. Additionally, we design a prior knowledge-assisted contrastive learning loss that boosts the representation capability of the aggregated view-common representation by injecting neighborhood information of samples from different views. Finally, extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed Mask-IMvC method over state-of-the-art approaches across multiple MvC datasets, both in complete and incomplete scenarios.
Balanced Multi-view Clustering
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:Multi-view clustering (MvC) aims to integrate information from different views to enhance the capability of the model in capturing the underlying data structures. The widely used joint training paradigm in MvC is potentially not fully leverage the multi-view information, since the imbalanced and under-optimized view-specific features caused by the uniform learning objective for all views. For instance, particular views with more discriminative information could dominate the learning process in the joint training paradigm, leading to other views being under-optimized. To alleviate this issue, we first analyze the imbalanced phenomenon in the joint-training paradigm of multi-view clustering from the perspective of gradient descent for each view-specific feature extractor. Then, we propose a novel balanced multi-view clustering (BMvC) method, which introduces a view-specific contrastive regularization (VCR) to modulate the optimization of each view. Concretely, VCR preserves the sample similarities captured from the joint features and view-specific ones into the clustering distributions corresponding to view-specific features to enhance the learning process of view-specific feature extractors. Additionally, a theoretical analysis is provided to illustrate that VCR adaptively modulates the magnitudes of gradients for updating the parameters of view-specific feature extractors to achieve a balanced multi-view learning procedure. In such a manner, BMvC achieves a better trade-off between the exploitation of view-specific patterns and the exploration of view-invariance patterns to fully learn the multi-view information for the clustering task. Finally, a set of experiments are conducted to verify the superiority of the proposed method compared with state-of-the-art approaches both on eight benchmark MvC datasets and two spatially resolved transcriptomics datasets.
MS-Former: Memory-Supported Transformer for Weakly Supervised Change Detection with Patch-Level Annotations
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:Fully supervised change detection methods have achieved significant advancements in performance, yet they depend severely on acquiring costly pixel-level labels. Considering that the patch-level annotations also contain abundant information corresponding to both changed and unchanged objects in bi-temporal images, an intuitive solution is to segment the changes with patch-level annotations. How to capture the semantic variations associated with the changed and unchanged regions from the patch-level annotations to obtain promising change results is the critical challenge for the weakly supervised change detection task. In this paper, we propose a memory-supported transformer (MS-Former), a novel framework consisting of a bi-directional attention block (BAB) and a patch-level supervision scheme (PSS) tailored for weakly supervised change detection with patch-level annotations. More specifically, the BAM captures contexts associated with the changed and unchanged regions from the temporal difference features to construct informative prototypes stored in the memory bank. On the other hand, the BAM extracts useful information from the prototypes as supplementary contexts to enhance the temporal difference features, thereby better distinguishing changed and unchanged regions. After that, the PSS guides the network learning valuable knowledge from the patch-level annotations, thus further elevating the performance. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in the change detection task. The demo code for our work will be publicly available at \url{https://github.com/guanyuezhen/MS-Former}.
Towards Accurate and Reliable Change Detection of Remote Sensing Images via Knowledge Review and Online Uncertainty Estimation
May 31, 2023



Abstract:Change detection (CD) is an essential task for various real-world applications, such as urban management and disaster assessment. However, previous methods primarily focus on improving the accuracy of CD, while neglecting the reliability of detection results. In this paper, we propose a novel change detection network, called AR-CDNet, which is able to provide accurate change maps and generate pixel-wise uncertainty. Specifically, an online uncertainty estimation branch is constructed to model the pixel-wise uncertainty, which is supervised by the difference between predicted change maps and corresponding ground truth during the training process. Furthermore, we introduce a knowledge review strategy to distill temporal change knowledge from low-level features to high-level ones, thereby enhancing the discriminability of temporal difference features. Finally, we aggregate the uncertainty-aware features extracted from the online uncertainty estimation branch with multi-level temporal difference features to improve the accuracy of CD. Once trained, our AR-CDNet can provide accurate change maps and evaluate pixel-wise uncertainty without ground truth. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of AR-CDNet in the CD task. The demo code for our work will be publicly available at \url{https://github.com/guanyuezhen/AR-CDNet}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge