Yi Wan
SOMA-1M: A Large-Scale SAR-Optical Multi-resolution Alignment Dataset for Multi-Task Remote Sensing
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical imagery provide complementary strengths that constitute the critical foundation for transcending single-modality constraints and facilitating cross-modal collaborative processing and intelligent interpretation. However, existing benchmark datasets often suffer from limitations such as single spatial resolution, insufficient data scale, and low alignment accuracy, making them inadequate for supporting the training and generalization of multi-scale foundation models. To address these challenges, we introduce SOMA-1M (SAR-Optical Multi-resolution Alignment), a pixel-level precisely aligned dataset containing over 1.3 million pairs of georeferenced images with a specification of 512 x 512 pixels. This dataset integrates imagery from Sentinel-1, PIESAT-1, Capella Space, and Google Earth, achieving global multi-scale coverage from 0.5 m to 10 m. It encompasses 12 typical land cover categories, effectively ensuring scene diversity and complexity. To address multimodal projection deformation and massive data registration, we designed a rigorous coarse-to-fine image matching framework ensuring pixel-level alignment. Based on this dataset, we established comprehensive evaluation benchmarks for four hierarchical vision tasks, including image matching, image fusion, SAR-assisted cloud removal, and cross-modal translation, involving over 30 mainstream algorithms. Experimental results demonstrate that supervised training on SOMA-1M significantly enhances performance across all tasks. Notably, multimodal remote sensing image (MRSI) matching performance achieves current state-of-the-art (SOTA) levels. SOMA-1M serves as a foundational resource for robust multimodal algorithms and remote sensing foundation models. The dataset will be released publicly at: https://github.com/PeihaoWu/SOMA-1M.
GLEAM: Learning to Match and Explain in Cross-View Geo-Localization
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Cross-View Geo-Localization (CVGL) focuses on identifying correspondences between images captured from distinct perspectives of the same geographical location. However, existing CVGL approaches are typically restricted to a single view or modality, and their direct visual matching strategy lacks interpretability: they merely predict whether two images correspond, without explaining the rationale behind the match. In this paper, we present GLEAM-C, a foundational CVGL model that unifies multiple views and modalities-including UAV imagery, street maps, panoramic views, and ground photographs-by aligning them exclusively with satellite imagery. Our framework enhances training efficiency through optimized implementation while achieving accuracy comparable to prior modality-specific CVGL models through a two-phase training strategy. Moreover, to address the lack of interpretability in traditional CVGL methods, we leverage the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to propose a new task, GLEAM-X, which combines cross-view correspondence prediction with explainable reasoning. To support this task, we construct a bilingual benchmark using GPT-4o and Doubao-1.5-Thinking-Vision-Pro to generate training and testing data. The test set is further refined through detailed human revision, enabling systematic evaluation of explainable cross-view reasoning and advancing transparency and scalability in geo-localization. Together, GLEAM-C and GLEAM-X form a comprehensive CVGL pipeline that integrates multi-modal, multi-view alignment with interpretable correspondence analysis, unifying accurate cross-view matching with explainable reasoning and advancing Geo-Localization by enabling models to better Explain And Match. Code and datasets used in this work will be made publicly accessible at https://github.com/Lucky-Lance/GLEAM.
Cross-View Localization via Redundant Sliced Observations and A-Contrario Validation
Aug 07, 2025



Abstract:Cross-view localization (CVL) matches ground-level images with aerial references to determine the geo-position of a camera, enabling smart vehicles to self-localize offline in GNSS-denied environments. However, most CVL methods output only a single observation, the camera pose, and lack the redundant observations required by surveying principles, making it challenging to assess localization reliability through the mutual validation of observational data. To tackle this, we introduce Slice-Loc, a two-stage method featuring an a-contrario reliability validation for CVL. Instead of using the query image as a single input, Slice-Loc divides it into sub-images and estimates the 3-DoF pose for each slice, creating redundant and independent observations. Then, a geometric rigidity formula is proposed to filter out the erroneous 3-DoF poses, and the inliers are merged to generate the final camera pose. Furthermore, we propose a model that quantifies the meaningfulness of localization by estimating the number of false alarms (NFA), according to the distribution of the locations of the sliced images. By eliminating gross errors, Slice-Loc boosts localization accuracy and effectively detects failures. After filtering out mislocalizations, Slice-Loc reduces the proportion of errors exceeding 10 m to under 3\%. In cross-city tests on the DReSS dataset, Slice-Loc cuts the mean localization error from 4.47 m to 1.86 m and the mean orientation error from $\mathbf{3.42^{\circ}}$ to $\mathbf{1.24^{\circ}}$, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Code and dataset will be available at: https://github.com/bnothing/Slice-Loc.
CasP: Improving Semi-Dense Feature Matching Pipeline Leveraging Cascaded Correspondence Priors for Guidance
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Semi-dense feature matching methods have shown strong performance in challenging scenarios. However, the existing pipeline relies on a global search across the entire feature map to establish coarse matches, limiting further improvements in accuracy and efficiency. Motivated by this limitation, we propose a novel pipeline, CasP, which leverages cascaded correspondence priors for guidance. Specifically, the matching stage is decomposed into two progressive phases, bridged by a region-based selective cross-attention mechanism designed to enhance feature discriminability. In the second phase, one-to-one matches are determined by restricting the search range to the one-to-many prior areas identified in the first phase. Additionally, this pipeline benefits from incorporating high-level features, which helps reduce the computational costs of low-level feature extraction. The acceleration gains of CasP increase with higher resolution, and our lite model achieves a speedup of $\sim2.2\times$ at a resolution of 1152 compared to the most efficient method, ELoFTR. Furthermore, extensive experiments demonstrate its superiority in geometric estimation, particularly with impressive cross-domain generalization. These advantages highlight its potential for latency-sensitive and high-robustness applications, such as SLAM and UAV systems. Code is available at https://github.com/pq-chen/CasP.
StereoINR: Cross-View Geometry Consistent Stereo Super Resolution with Implicit Neural Representation
May 07, 2025Abstract:Stereo image super-resolution (SSR) aims to enhance high-resolution details by leveraging information from stereo image pairs. However, existing stereo super-resolution (SSR) upsampling methods (e.g., pixel shuffle) often overlook cross-view geometric consistency and are limited to fixed-scale upsampling. The key issue is that previous upsampling methods use convolution to independently process deep features of different views, lacking cross-view and non-local information perception, making it difficult to select beneficial information from multi-view scenes adaptively. In this work, we propose Stereo Implicit Neural Representation (StereoINR), which innovatively models stereo image pairs as continuous implicit representations. This continuous representation breaks through the scale limitations, providing a unified solution for arbitrary-scale stereo super-resolution reconstruction of left-right views. Furthermore, by incorporating spatial warping and cross-attention mechanisms, StereoINR enables effective cross-view information fusion and achieves significant improvements in pixel-level geometric consistency. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets show that StereoINR outperforms out-of-training-distribution scale upsampling and matches state-of-the-art SSR methods within training-distribution scales.
MapGlue: Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Matching
Mar 20, 2025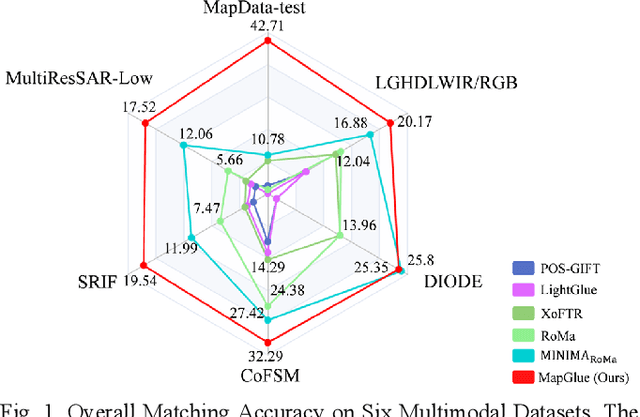
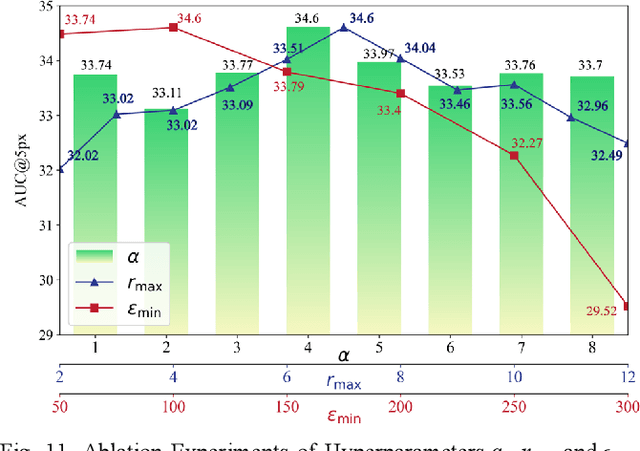
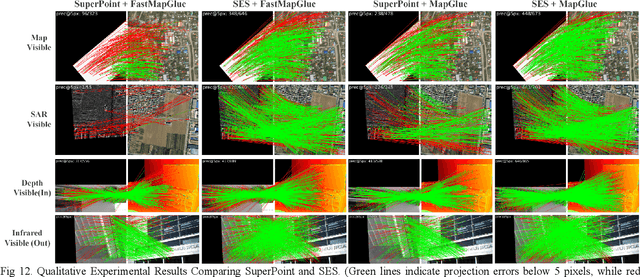

Abstract:Multimodal remote sensing image (MRSI) matching is pivotal for cross-modal fusion, localization, and object detection, but it faces severe challenges due to geometric, radiometric, and viewpoint discrepancies across imaging modalities. Existing unimodal datasets lack scale and diversity, limiting deep learning solutions. This paper proposes MapGlue, a universal MRSI matching framework, and MapData, a large-scale multimodal dataset addressing these gaps. Our contributions are twofold. MapData, a globally diverse dataset spanning 233 sampling points, offers original images (7,000x5,000 to 20,000x15,000 pixels). After rigorous cleaning, it provides 121,781 aligned electronic map-visible image pairs (512x512 pixels) with hybrid manual-automated ground truth, addressing the scarcity of scalable multimodal benchmarks. MapGlue integrates semantic context with a dual graph-guided mechanism to extract cross-modal invariant features. This structure enables global-to-local interaction, enhancing descriptor robustness against modality-specific distortions. Extensive evaluations on MapData and five public datasets demonstrate MapGlue's superiority in matching accuracy under complex conditions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Notably, MapGlue generalizes effectively to unseen modalities without retraining, highlighting its adaptability. This work addresses longstanding challenges in MRSI matching by combining scalable dataset construction with a robust, semantics-driven framework. Furthermore, MapGlue shows strong generalization capabilities on other modality matching tasks for which it was not specifically trained. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/PeihaoWu/MapGlue.
Multi-Resolution SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Image Registration Methods: A Review, Datasets, and Future Perspectives
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical image registration is essential for remote sensing data fusion, with applications in military reconnaissance, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. However, challenges arise from differences in imaging mechanisms, geometric distortions, and radiometric properties between SAR and optical images. As image resolution increases, fine SAR textures become more significant, leading to alignment issues and 3D spatial discrepancies. Two major gaps exist: the lack of a publicly available multi-resolution, multi-scene registration dataset and the absence of systematic analysis of current methods. To address this, the MultiResSAR dataset was created, containing over 10k pairs of multi-source, multi-resolution, and multi-scene SAR and optical images. Sixteen state-of-the-art algorithms were tested. Results show no algorithm achieves 100% success, and performance decreases as resolution increases, with most failing on sub-meter data. XoFTR performs best among deep learning methods (40.58%), while RIFT performs best among traditional methods (66.51%). Future research should focus on noise suppression, 3D geometric fusion, cross-view transformation modeling, and deep learning optimization for robust registration of high-resolution SAR and optical images. The dataset is available at https://github.com/betterlll/Multi-Resolution-SAR-dataset-.
An Empirical Study of Deep Reinforcement Learning in Continuing Tasks
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:In reinforcement learning (RL), continuing tasks refer to tasks where the agent-environment interaction is ongoing and can not be broken down into episodes. These tasks are suitable when environment resets are unavailable, agent-controlled, or predefined but where all rewards-including those beyond resets-are critical. These scenarios frequently occur in real-world applications and can not be modeled by episodic tasks. While modern deep RL algorithms have been extensively studied and well understood in episodic tasks, their behavior in continuing tasks remains underexplored. To address this gap, we provide an empirical study of several well-known deep RL algorithms using a suite of continuing task testbeds based on Mujoco and Atari environments, highlighting several key insights concerning continuing tasks. Using these testbeds, we also investigate the effectiveness of a method for improving temporal-difference-based RL algorithms in continuing tasks by centering rewards, as introduced by Naik et al. (2024). While their work primarily focused on this method in conjunction with Q-learning, our results extend their findings by demonstrating that this method is effective across a broader range of algorithms, scales to larger tasks, and outperforms two other reward-centering approaches.
Cross-View Image Set Geo-Localization
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:Cross-view geo-localization (CVGL) has been widely applied in fields such as robotic navigation and augmented reality. Existing approaches primarily use single images or fixed-view image sequences as queries, which limits perspective diversity. In contrast, when humans determine their location visually, they typically move around to gather multiple perspectives. This behavior suggests that integrating diverse visual cues can improve geo-localization reliability. Therefore, we propose a novel task: Cross-View Image Set Geo-Localization (Set-CVGL), which gathers multiple images with diverse perspectives as a query set for localization. To support this task, we introduce SetVL-480K, a benchmark comprising 480,000 ground images captured worldwide and their corresponding satellite images, with each satellite image corresponds to an average of 40 ground images from varied perspectives and locations. Furthermore, we propose FlexGeo, a flexible method designed for Set-CVGL that can also adapt to single-image and image-sequence inputs. FlexGeo includes two key modules: the Similarity-guided Feature Fuser (SFF), which adaptively fuses image features without prior content dependency, and the Individual-level Attributes Learner (IAL), leveraging geo-attributes of each image for comprehensive scene perception. FlexGeo consistently outperforms existing methods on SetVL-480K and two public datasets, SeqGeo and KITTI-CVL, achieving a localization accuracy improvement of over 22% on SetVL-480K.
Cross-View Geo-Localization with Street-View and VHR Satellite Imagery in Decentrality Settings
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Cross-View Geo-Localization tackles the problem of image geo-localization in GNSS-denied environments by matching street-view query images with geo-tagged aerial-view reference images. However, existing datasets and methods often assume center-aligned settings or only consider limited decentrality (i.e., the offset of the query image from the reference image center). This assumption overlooks the challenges present in real-world applications, where large decentrality can significantly enhance localization efficiency but simultaneously lead to a substantial degradation in localization accuracy. To address this limitation, we introduce CVSat, a novel dataset designed to evaluate cross-view geo-localization with a large geographic scope and diverse landscapes, emphasizing the decentrality issue. Meanwhile, we propose AuxGeo (Auxiliary Enhanced Geo-Localization), which leverages a multi-metric optimization strategy with two novel modules: the Bird's-eye view Intermediary Module (BIM) and the Position Constraint Module (PCM). BIM uses bird's-eye view images derived from street-view panoramas as an intermediary, simplifying the cross-view challenge with decentrality to a cross-view problem and a decentrality problem. PCM leverages position priors between cross-view images to establish multi-grained alignment constraints. These modules improve the performance of cross-view geo-localization with the decentrality problem. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AuxGeo outperforms previous methods on our proposed CVSat dataset, mitigating the issue of large decentrality, and also achieves state-of-the-art performance on existing public datasets such as CVUSA, CVACT, and VIGOR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge