Yongjun Zhang
SOMA-1M: A Large-Scale SAR-Optical Multi-resolution Alignment Dataset for Multi-Task Remote Sensing
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical imagery provide complementary strengths that constitute the critical foundation for transcending single-modality constraints and facilitating cross-modal collaborative processing and intelligent interpretation. However, existing benchmark datasets often suffer from limitations such as single spatial resolution, insufficient data scale, and low alignment accuracy, making them inadequate for supporting the training and generalization of multi-scale foundation models. To address these challenges, we introduce SOMA-1M (SAR-Optical Multi-resolution Alignment), a pixel-level precisely aligned dataset containing over 1.3 million pairs of georeferenced images with a specification of 512 x 512 pixels. This dataset integrates imagery from Sentinel-1, PIESAT-1, Capella Space, and Google Earth, achieving global multi-scale coverage from 0.5 m to 10 m. It encompasses 12 typical land cover categories, effectively ensuring scene diversity and complexity. To address multimodal projection deformation and massive data registration, we designed a rigorous coarse-to-fine image matching framework ensuring pixel-level alignment. Based on this dataset, we established comprehensive evaluation benchmarks for four hierarchical vision tasks, including image matching, image fusion, SAR-assisted cloud removal, and cross-modal translation, involving over 30 mainstream algorithms. Experimental results demonstrate that supervised training on SOMA-1M significantly enhances performance across all tasks. Notably, multimodal remote sensing image (MRSI) matching performance achieves current state-of-the-art (SOTA) levels. SOMA-1M serves as a foundational resource for robust multimodal algorithms and remote sensing foundation models. The dataset will be released publicly at: https://github.com/PeihaoWu/SOMA-1M.
SplitFlux: Learning to Decouple Content and Style from a Single Image
Nov 19, 2025



Abstract:Disentangling image content and style is essential for customized image generation. Existing SDXL-based methods struggle to achieve high-quality results, while the recently proposed Flux model fails to achieve effective content-style separation due to its underexplored characteristics. To address these challenges, we conduct a systematic analysis of Flux and make two key observations: (1) Single Dream Blocks are essential for image generation; and (2) Early single stream blocks mainly control content, whereas later blocks govern style. Based on these insights, we propose SplitFlux, which disentangles content and style by fine-tuning the single dream blocks via LoRA, enabling the disentangled content to be re-embedded into new contexts. It includes two key components: (1) Rank-Constrained Adaptation. To preserve content identity and structure, we compress the rank and amplify the magnitude of updates within specific blocks, preventing content leakage into style blocks. (2) Visual-Gated LoRA. We split the content LoRA into two branches with different ranks, guided by image saliency. The high-rank branch preserves primary subject information, while the low-rank branch encodes residual details, mitigating content overfitting and enabling seamless re-embedding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SplitFlux consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior content preservation and stylization quality across diverse scenarios.
Cross-View Localization via Redundant Sliced Observations and A-Contrario Validation
Aug 07, 2025



Abstract:Cross-view localization (CVL) matches ground-level images with aerial references to determine the geo-position of a camera, enabling smart vehicles to self-localize offline in GNSS-denied environments. However, most CVL methods output only a single observation, the camera pose, and lack the redundant observations required by surveying principles, making it challenging to assess localization reliability through the mutual validation of observational data. To tackle this, we introduce Slice-Loc, a two-stage method featuring an a-contrario reliability validation for CVL. Instead of using the query image as a single input, Slice-Loc divides it into sub-images and estimates the 3-DoF pose for each slice, creating redundant and independent observations. Then, a geometric rigidity formula is proposed to filter out the erroneous 3-DoF poses, and the inliers are merged to generate the final camera pose. Furthermore, we propose a model that quantifies the meaningfulness of localization by estimating the number of false alarms (NFA), according to the distribution of the locations of the sliced images. By eliminating gross errors, Slice-Loc boosts localization accuracy and effectively detects failures. After filtering out mislocalizations, Slice-Loc reduces the proportion of errors exceeding 10 m to under 3\%. In cross-city tests on the DReSS dataset, Slice-Loc cuts the mean localization error from 4.47 m to 1.86 m and the mean orientation error from $\mathbf{3.42^{\circ}}$ to $\mathbf{1.24^{\circ}}$, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Code and dataset will be available at: https://github.com/bnothing/Slice-Loc.
CasP: Improving Semi-Dense Feature Matching Pipeline Leveraging Cascaded Correspondence Priors for Guidance
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Semi-dense feature matching methods have shown strong performance in challenging scenarios. However, the existing pipeline relies on a global search across the entire feature map to establish coarse matches, limiting further improvements in accuracy and efficiency. Motivated by this limitation, we propose a novel pipeline, CasP, which leverages cascaded correspondence priors for guidance. Specifically, the matching stage is decomposed into two progressive phases, bridged by a region-based selective cross-attention mechanism designed to enhance feature discriminability. In the second phase, one-to-one matches are determined by restricting the search range to the one-to-many prior areas identified in the first phase. Additionally, this pipeline benefits from incorporating high-level features, which helps reduce the computational costs of low-level feature extraction. The acceleration gains of CasP increase with higher resolution, and our lite model achieves a speedup of $\sim2.2\times$ at a resolution of 1152 compared to the most efficient method, ELoFTR. Furthermore, extensive experiments demonstrate its superiority in geometric estimation, particularly with impressive cross-domain generalization. These advantages highlight its potential for latency-sensitive and high-robustness applications, such as SLAM and UAV systems. Code is available at https://github.com/pq-chen/CasP.
StereoINR: Cross-View Geometry Consistent Stereo Super Resolution with Implicit Neural Representation
May 07, 2025Abstract:Stereo image super-resolution (SSR) aims to enhance high-resolution details by leveraging information from stereo image pairs. However, existing stereo super-resolution (SSR) upsampling methods (e.g., pixel shuffle) often overlook cross-view geometric consistency and are limited to fixed-scale upsampling. The key issue is that previous upsampling methods use convolution to independently process deep features of different views, lacking cross-view and non-local information perception, making it difficult to select beneficial information from multi-view scenes adaptively. In this work, we propose Stereo Implicit Neural Representation (StereoINR), which innovatively models stereo image pairs as continuous implicit representations. This continuous representation breaks through the scale limitations, providing a unified solution for arbitrary-scale stereo super-resolution reconstruction of left-right views. Furthermore, by incorporating spatial warping and cross-attention mechanisms, StereoINR enables effective cross-view information fusion and achieves significant improvements in pixel-level geometric consistency. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets show that StereoINR outperforms out-of-training-distribution scale upsampling and matches state-of-the-art SSR methods within training-distribution scales.
The Risks of Using Large Language Models for Text Annotation in Social Science Research
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) or large language models (LLMs) have the potential to revolutionize computational social science, particularly in automated textual analysis. In this paper, we conduct a systematic evaluation of the promises and risks of using LLMs for diverse coding tasks, with social movement studies serving as a case example. We propose a framework for social scientists to incorporate LLMs into text annotation, either as the primary coding decision-maker or as a coding assistant. This framework provides tools for researchers to develop the optimal prompt, and to examine and report the validity and reliability of LLMs as a methodological tool. Additionally, we discuss the associated epistemic risks related to validity, reliability, replicability, and transparency. We conclude with several practical guidelines for using LLMs in text annotation tasks, and how we can better communicate the epistemic risks in research.
MapGlue: Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Matching
Mar 20, 2025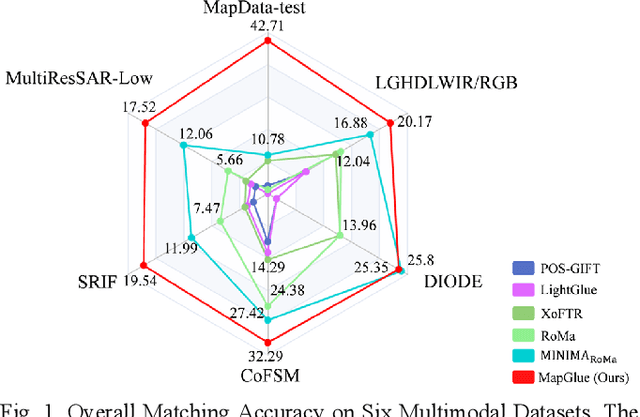
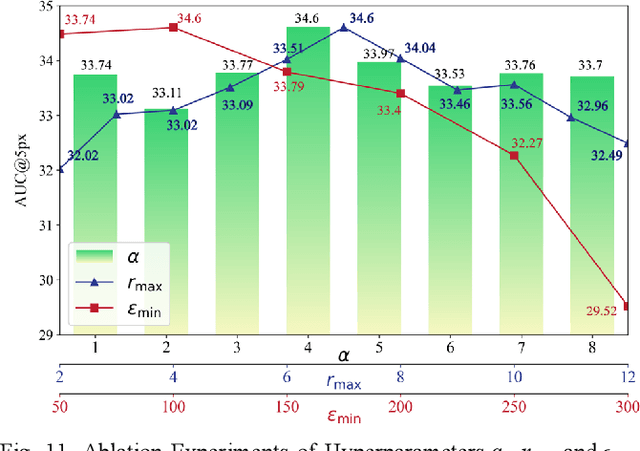
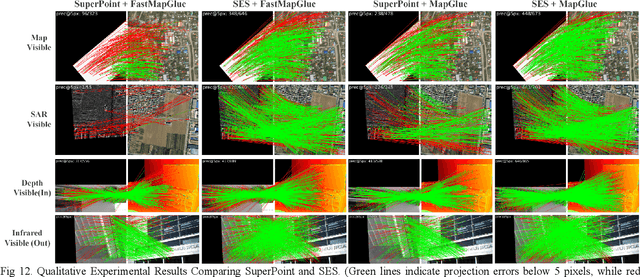

Abstract:Multimodal remote sensing image (MRSI) matching is pivotal for cross-modal fusion, localization, and object detection, but it faces severe challenges due to geometric, radiometric, and viewpoint discrepancies across imaging modalities. Existing unimodal datasets lack scale and diversity, limiting deep learning solutions. This paper proposes MapGlue, a universal MRSI matching framework, and MapData, a large-scale multimodal dataset addressing these gaps. Our contributions are twofold. MapData, a globally diverse dataset spanning 233 sampling points, offers original images (7,000x5,000 to 20,000x15,000 pixels). After rigorous cleaning, it provides 121,781 aligned electronic map-visible image pairs (512x512 pixels) with hybrid manual-automated ground truth, addressing the scarcity of scalable multimodal benchmarks. MapGlue integrates semantic context with a dual graph-guided mechanism to extract cross-modal invariant features. This structure enables global-to-local interaction, enhancing descriptor robustness against modality-specific distortions. Extensive evaluations on MapData and five public datasets demonstrate MapGlue's superiority in matching accuracy under complex conditions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Notably, MapGlue generalizes effectively to unseen modalities without retraining, highlighting its adaptability. This work addresses longstanding challenges in MRSI matching by combining scalable dataset construction with a robust, semantics-driven framework. Furthermore, MapGlue shows strong generalization capabilities on other modality matching tasks for which it was not specifically trained. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/PeihaoWu/MapGlue.
MEET: A Million-Scale Dataset for Fine-Grained Geospatial Scene Classification with Zoom-Free Remote Sensing Imagery
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Accurate fine-grained geospatial scene classification using remote sensing imagery is essential for a wide range of applications. However, existing approaches often rely on manually zooming remote sensing images at different scales to create typical scene samples. This approach fails to adequately support the fixed-resolution image interpretation requirements in real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we introduce the Million-scale finE-grained geospatial scEne classification dataseT (MEET), which contains over 1.03 million zoom-free remote sensing scene samples, manually annotated into 80 fine-grained categories. In MEET, each scene sample follows a scene-inscene layout, where the central scene serves as the reference, and auxiliary scenes provide crucial spatial context for finegrained classification. Moreover, to tackle the emerging challenge of scene-in-scene classification, we present the Context-Aware Transformer (CAT), a model specifically designed for this task, which adaptively fuses spatial context to accurately classify the scene samples. CAT adaptively fuses spatial context to accurately classify the scene samples by learning attentional features that capture the relationships between the center and auxiliary scenes. Based on MEET, we establish a comprehensive benchmark for fine-grained geospatial scene classification, evaluating CAT against 11 competitive baselines. The results demonstrate that CAT significantly outperforms these baselines, achieving a 1.88% higher balanced accuracy (BA) with the Swin-Large backbone, and a notable 7.87% improvement with the Swin-Huge backbone. Further experiments validate the effectiveness of each module in CAT and show the practical applicability of CAT in the urban functional zone mapping. The source code and dataset will be publicly available at https://jerrywyn.github.io/project/MEET.html.
Multi-Resolution SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Image Registration Methods: A Review, Datasets, and Future Perspectives
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical image registration is essential for remote sensing data fusion, with applications in military reconnaissance, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. However, challenges arise from differences in imaging mechanisms, geometric distortions, and radiometric properties between SAR and optical images. As image resolution increases, fine SAR textures become more significant, leading to alignment issues and 3D spatial discrepancies. Two major gaps exist: the lack of a publicly available multi-resolution, multi-scene registration dataset and the absence of systematic analysis of current methods. To address this, the MultiResSAR dataset was created, containing over 10k pairs of multi-source, multi-resolution, and multi-scene SAR and optical images. Sixteen state-of-the-art algorithms were tested. Results show no algorithm achieves 100% success, and performance decreases as resolution increases, with most failing on sub-meter data. XoFTR performs best among deep learning methods (40.58%), while RIFT performs best among traditional methods (66.51%). Future research should focus on noise suppression, 3D geometric fusion, cross-view transformation modeling, and deep learning optimization for robust registration of high-resolution SAR and optical images. The dataset is available at https://github.com/betterlll/Multi-Resolution-SAR-dataset-.
Threshold Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:Semantic segmentation of remote sensing images is essential for various applications, including vegetation monitoring, disaster management, and urban planning. Previous studies have demonstrated that the self-attention mechanism (SA) is an effective approach for designing segmentation networks that can capture long-range pixel dependencies. SA enables the network to model the global dependencies between the input features, resulting in improved segmentation outcomes. However, the high density of attentional feature maps used in this mechanism causes exponential increases in computational complexity. Additionally, it introduces redundant information that negatively impacts the feature representation. Inspired by traditional threshold segmentation algorithms, we propose a novel threshold attention mechanism (TAM). This mechanism significantly reduces computational effort while also better modeling the correlation between different regions of the feature map. Based on TAM, we present a threshold attention network (TANet) for semantic segmentation. TANet consists of an attentional feature enhancement module (AFEM) for global feature enhancement of shallow features and a threshold attention pyramid pooling module (TAPP) for acquiring feature information at different scales for deep features. We have conducted extensive experiments on the ISPRS Vaihingen and Potsdam datasets. The results demonstrate the validity and superiority of our proposed TANet compared to the most state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge