Anran Wang
SAMTok: Representing Any Mask with Two Words
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Pixel-wise capabilities are essential for building interactive intelligent systems. However, pixel-wise multi-modal LLMs (MLLMs) remain difficult to scale due to complex region-level encoders, specialized segmentation decoders, and incompatible training objectives. To address these challenges, we present SAMTok, a discrete mask tokenizer that converts any region mask into two special tokens and reconstructs the mask using these tokens with high fidelity. By treating masks as new language tokens, SAMTok enables base MLLMs (such as the QwenVL series) to learn pixel-wise capabilities through standard next-token prediction and simple reinforcement learning, without architectural modifications and specialized loss design. SAMTok builds on SAM2 and is trained on 209M diverse masks using a mask encoder and residual vector quantizer to produce discrete, compact, and information-rich tokens. With 5M SAMTok-formatted mask understanding and generation data samples, QwenVL-SAMTok attains state-of-the-art or comparable results on region captioning, region VQA, grounded conversation, referring segmentation, scene graph parsing, and multi-round interactive segmentation. We further introduce a textual answer-matching reward that enables efficient reinforcement learning for mask generation, delivering substantial improvements on GRES and GCG benchmarks. Our results demonstrate a scalable and straightforward paradigm for equipping MLLMs with strong pixel-wise capabilities. Our code and models are available.
MMaDA-Parallel: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models for Thinking-Aware Editing and Generation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:While thinking-aware generation aims to improve performance on complex tasks, we identify a critical failure mode where existing sequential, autoregressive approaches can paradoxically degrade performance due to error propagation. To systematically analyze this issue, we propose ParaBench, a new benchmark designed to evaluate both text and image output modalities. Our analysis using ParaBench reveals that this performance degradation is strongly correlated with poor alignment between the generated reasoning and the final image. To resolve this, we propose a parallel multimodal diffusion framework, MMaDA-Parallel, that enables continuous, bidirectional interaction between text and images throughout the entire denoising trajectory. MMaDA-Parallel is trained with supervised finetuning and then further optimized by Parallel Reinforcement Learning (ParaRL), a novel strategy that applies semantic rewards along the trajectory to enforce cross-modal consistency. Experiments validate that our model significantly improves cross-modal alignment and semantic consistency, achieving a 6.9\% improvement in Output Alignment on ParaBench compared to the state-of-the-art model, Bagel, establishing a more robust paradigm for thinking-aware image synthesis. Our code is open-sourced at https://github.com/tyfeld/MMaDA-Parallel
Open-o3 Video: Grounded Video Reasoning with Explicit Spatio-Temporal Evidence
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Most video reasoning models only generate textual reasoning traces without indicating when and where key evidence appears. Recent models such as OpenAI-o3 have sparked wide interest in evidence-centered reasoning for images, yet extending this ability to videos is more challenging, as it requires joint temporal tracking and spatial localization across dynamic scenes. We introduce Open-o3 Video, a non-agent framework that integrates explicit spatio-temporal evidence into video reasoning, and carefully collect training data and design training strategies to address the aforementioned challenges. The model highlights key timestamps, objects, and bounding boxes alongside its answers, allowing reasoning to be grounded in concrete visual observations. To enable this functionality, we first curate and build two high-quality datasets, STGR-CoT-30k for SFT and STGR-RL-36k for RL, with carefully constructed temporal and spatial annotations, since most existing datasets offer either temporal spans for videos or spatial boxes on images, lacking unified spatio-temporal supervision and reasoning traces. Then, we adopt a cold-start reinforcement learning strategy with multiple specially designed rewards that jointly encourage answer accuracy, temporal alignment, and spatial precision. On V-STAR benchmark, Open-o3 Video achieves state-of-the-art performance, raising mAM by 14.4% and mLGM by 24.2% on the Qwen2.5-VL baseline. Consistent improvements are also observed on a broad range of video understanding benchmarks, including VideoMME, WorldSense, VideoMMMU, and TVGBench. Beyond accuracy, the reasoning traces produced by Open-o3 Video also provide valuable signals for test-time scaling, enabling confidence-aware verification and improving answer reliability.
Grasp Any Region: Towards Precise, Contextual Pixel Understanding for Multimodal LLMs
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at holistic understanding, they struggle in capturing the dense world with complex scenes, requiring fine-grained analysis of intricate details and object inter-relationships. Region-level MLLMs have been a promising step. However, previous attempts are generally optimized to understand given regions in isolation, neglecting crucial global contexts. To address this, we introduce Grasp Any Region (GAR) for comprehen- sive region-level visual understanding. Empowered by an effective RoI-aligned feature replay technique, GAR supports (1) precise perception by leveraging necessary global contexts, and (2) modeling interactions between multiple prompts. Together, it then naturally achieves (3) advanced compositional reasoning to answer specific free-form questions about any region, shifting the paradigm from passive description to active dialogue. Moreover, we construct GAR-Bench, which not only provides a more accurate evaluation of single-region comprehension, but also, more importantly, measures interactions and complex reasoning across multiple regions. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that GAR-1B not only maintains the state-of-the-art captioning capabilities, e.g., outperforming DAM-3B +4.5 on DLC-Bench, but also excels at modeling relationships between multiple prompts with advanced comprehension capabilities, even surpassing InternVL3-78B on GAR-Bench-VQA. More importantly, our zero-shot GAR-8B even outperforms in-domain VideoRefer-7B on VideoRefer-BenchQ, indicating its strong capabilities can be easily transferred to videos.
P/D-Device: Disaggregated Large Language Model between Cloud and Devices
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Serving disaggregated large language models has been widely adopted in industrial practice for enhanced performance. However, too many tokens generated in decoding phase, i.e., occupying the resources for a long time, essentially hamper the cloud from achieving a higher throughput. Meanwhile, due to limited on-device resources, the time to first token (TTFT), i.e., the latency of prefill phase, increases dramatically with the growth on prompt length. In order to concur with such a bottleneck on resources, i.e., long occupation in cloud and limited on-device computing capacity, we propose to separate large language model between cloud and devices. That is, the cloud helps a portion of the content for each device, only in its prefill phase. Specifically, after receiving the first token from the cloud, decoupling with its own prefill, the device responds to the user immediately for a lower TTFT. Then, the following tokens from cloud are presented via a speed controller for smoothed TPOT (the time per output token), until the device catches up with the progress. On-device prefill is then amortized using received tokens while the resource usage in cloud is controlled. Moreover, during cloud prefill, the prompt can be refined, using those intermediate data already generated, to further speed up on-device inference. We implement such a scheme P/D-Device, and confirm its superiority over other alternatives. We further propose an algorithm to decide the best settings. Real-trace experiments show that TTFT decreases at least 60%, maximum TPOT is about tens of milliseconds, and cloud throughput increases by up to 15x.
Traceable Evidence Enhanced Visual Grounded Reasoning: Evaluation and Methodology
Jul 10, 2025

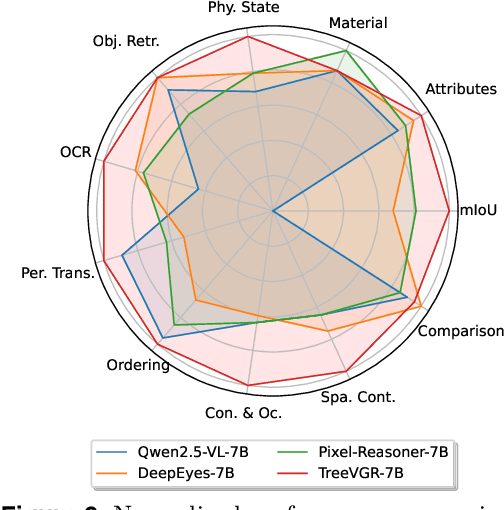
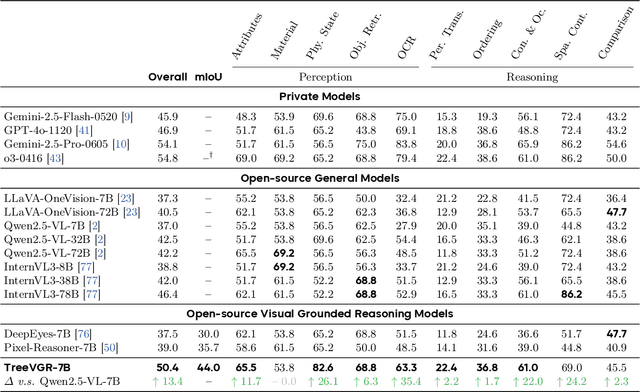
Abstract:Models like OpenAI-o3 pioneer visual grounded reasoning by dynamically referencing visual regions, just like human "thinking with images". However, no benchmark exists to evaluate these capabilities holistically. To bridge this gap, we propose TreeBench (Traceable Evidence Evaluation Benchmark), a diagnostic benchmark built on three principles: (1) focused visual perception of subtle targets in complex scenes, (2) traceable evidence via bounding box evaluation, and (3) second-order reasoning to test object interactions and spatial hierarchies beyond simple object localization. Prioritizing images with dense objects, we initially sample 1K high-quality images from SA-1B, and incorporate eight LMM experts to manually annotate questions, candidate options, and answers for each image. After three stages of quality control, TreeBench consists of 405 challenging visual question-answering pairs, even the most advanced models struggle with this benchmark, where none of them reach 60% accuracy, e.g., OpenAI-o3 scores only 54.87. Furthermore, we introduce TreeVGR (Traceable Evidence Enhanced Visual Grounded Reasoning), a training paradigm to supervise localization and reasoning jointly with reinforcement learning, enabling accurate localizations and explainable reasoning pathways. Initialized from Qwen2.5-VL-7B, it improves V* Bench (+16.8), MME-RealWorld (+12.6), and TreeBench (+13.4), proving traceability is key to advancing vision-grounded reasoning. The code is available at https://github.com/Haochen-Wang409/TreeVGR.
skscope: Fast Sparsity-Constrained Optimization in Python
Mar 27, 2024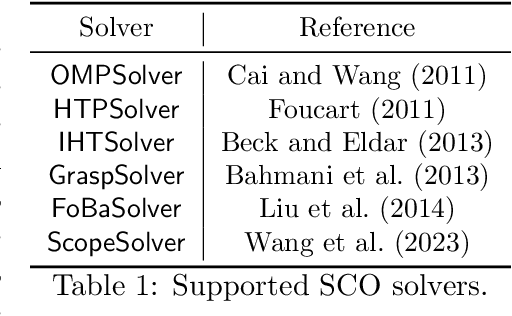
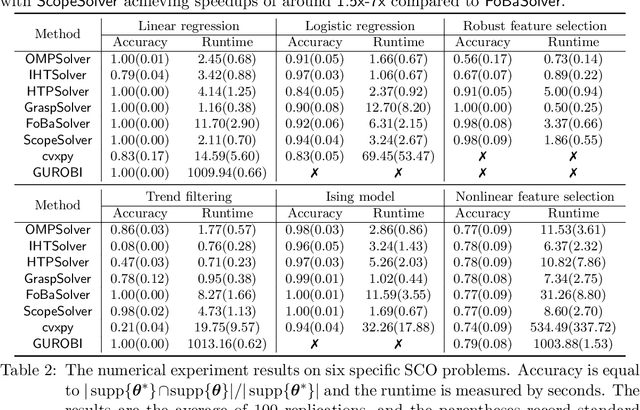
Abstract:Applying iterative solvers on sparsity-constrained optimization (SCO) requires tedious mathematical deduction and careful programming/debugging that hinders these solvers' broad impact. In the paper, the library skscope is introduced to overcome such an obstacle. With skscope, users can solve the SCO by just programming the objective function. The convenience of skscope is demonstrated through two examples in the paper, where sparse linear regression and trend filtering are addressed with just four lines of code. More importantly, skscope's efficient implementation allows state-of-the-art solvers to quickly attain the sparse solution regardless of the high dimensionality of parameter space. Numerical experiments reveal the available solvers in skscope can achieve up to 80x speedup on the competing relaxation solutions obtained via the benchmarked convex solver. skscope is published on the Python Package Index (PyPI) and Conda, and its source code is available at: https://github.com/abess-team/skscope.
SDXL-Lightning: Progressive Adversarial Diffusion Distillation
Mar 02, 2024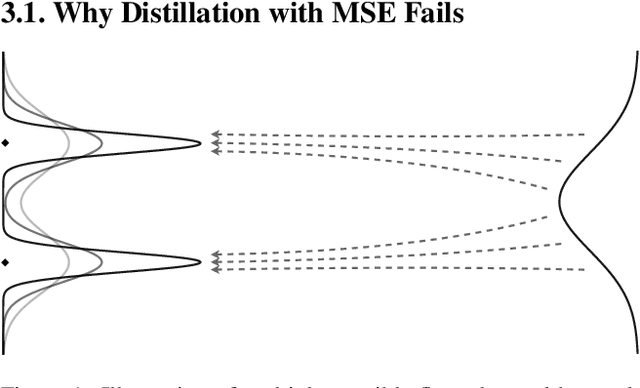


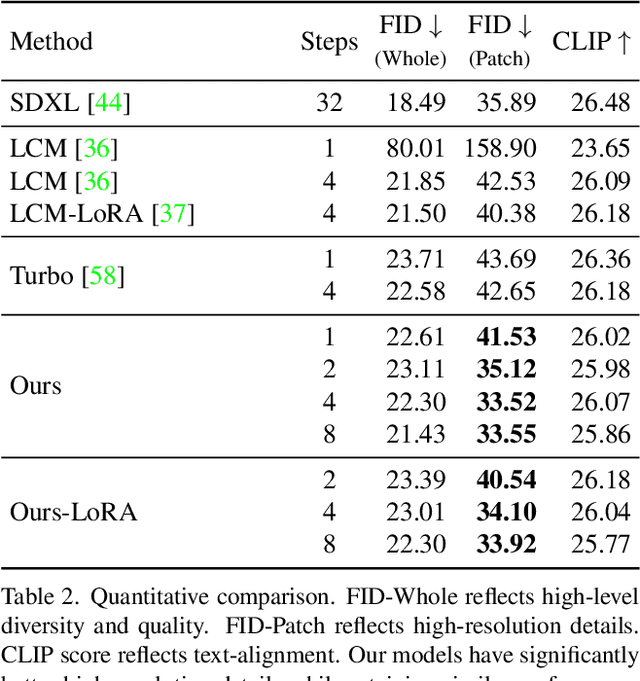
Abstract:We propose a diffusion distillation method that achieves new state-of-the-art in one-step/few-step 1024px text-to-image generation based on SDXL. Our method combines progressive and adversarial distillation to achieve a balance between quality and mode coverage. In this paper, we discuss the theoretical analysis, discriminator design, model formulation, and training techniques. We open-source our distilled SDXL-Lightning models both as LoRA and full UNet weights.
ManiCLIP: Multi-Attribute Face Manipulation from Text
Oct 02, 2022


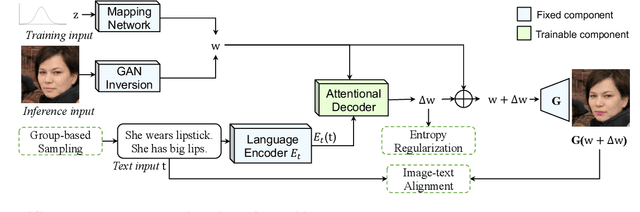
Abstract:In this paper we present a novel multi-attribute face manipulation method based on textual descriptions. Previous text-based image editing methods either require test-time optimization for each individual image or are restricted to single attribute editing. Extending these methods to multi-attribute face image editing scenarios will introduce undesired excessive attribute change, e.g., text-relevant attributes are overly manipulated and text-irrelevant attributes are also changed. In order to address these challenges and achieve natural editing over multiple face attributes, we propose a new decoupling training scheme where we use group sampling to get text segments from same attribute categories, instead of whole complex sentences. Further, to preserve other existing face attributes, we encourage the model to edit the latent code of each attribute separately via a entropy constraint. During the inference phase, our model is able to edit new face images without any test-time optimization, even from complex textual prompts. We show extensive experiments and analysis to demonstrate the efficacy of our method, which generates natural manipulated faces with minimal text-irrelevant attribute editing. Code and pre-trained model will be released.
Dynamic Spatio-Temporal Specialization Learning for Fine-Grained Action Recognition
Sep 03, 2022
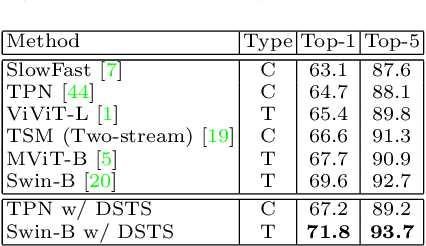
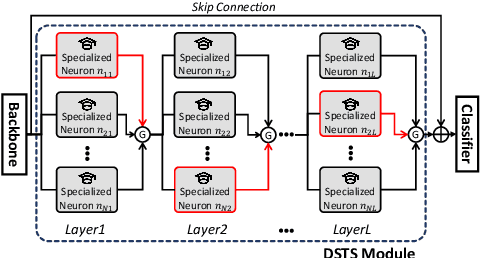
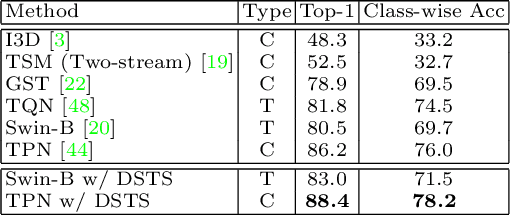
Abstract:The goal of fine-grained action recognition is to successfully discriminate between action categories with subtle differences. To tackle this, we derive inspiration from the human visual system which contains specialized regions in the brain that are dedicated towards handling specific tasks. We design a novel Dynamic Spatio-Temporal Specialization (DSTS) module, which consists of specialized neurons that are only activated for a subset of samples that are highly similar. During training, the loss forces the specialized neurons to learn discriminative fine-grained differences to distinguish between these similar samples, improving fine-grained recognition. Moreover, a spatio-temporal specialization method further optimizes the architectures of the specialized neurons to capture either more spatial or temporal fine-grained information, to better tackle the large range of spatio-temporal variations in the videos. Lastly, we design an Upstream-Downstream Learning algorithm to optimize our model's dynamic decisions during training, improving the performance of our DSTS module. We obtain state-of-the-art performance on two widely-used fine-grained action recognition datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge