Andreea Bobu
Value of Information: A Framework for Human-Agent Communication
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) agents deployed for real-world tasks face a fundamental dilemma: user requests are underspecified, yet agents must decide whether to act on incomplete information or interrupt users for clarification. Existing approaches either rely on brittle confidence thresholds that require task-specific tuning, or fail to account for the varying stakes of different decisions. We introduce a decision-theoretic framework that resolves this trade-off through the Value of Information (VoI), enabling agents to dynamically weigh the expected utility gain from asking questions against the cognitive cost imposed on users. Our inference-time method requires no hyperparameter tuning and adapts seamlessly across contexts-from casual games to medical diagnosis. Experiments across four diverse domains (20 Questions, medical diagnosis, flight booking, and e-commerce) show that VoI consistently matches or exceeds the best manually-tuned baselines, achieving up to 1.36 utility points higher in high-cost settings. This work provides a parameter-free framework for adaptive agent communication that explicitly balances task risk, query ambiguity, and user effort.
Masked IRL: LLM-Guided Reward Disambiguation from Demonstrations and Language
Nov 18, 2025



Abstract:Robots can adapt to user preferences by learning reward functions from demonstrations, but with limited data, reward models often overfit to spurious correlations and fail to generalize. This happens because demonstrations show robots how to do a task but not what matters for that task, causing the model to focus on irrelevant state details. Natural language can more directly specify what the robot should focus on, and, in principle, disambiguate between many reward functions consistent with the demonstrations. However, existing language-conditioned reward learning methods typically treat instructions as simple conditioning signals, without fully exploiting their potential to resolve ambiguity. Moreover, real instructions are often ambiguous themselves, so naive conditioning is unreliable. Our key insight is that these two input types carry complementary information: demonstrations show how to act, while language specifies what is important. We propose Masked Inverse Reinforcement Learning (Masked IRL), a framework that uses large language models (LLMs) to combine the strengths of both input types. Masked IRL infers state-relevance masks from language instructions and enforces invariance to irrelevant state components. When instructions are ambiguous, it uses LLM reasoning to clarify them in the context of the demonstrations. In simulation and on a real robot, Masked IRL outperforms prior language-conditioned IRL methods by up to 15% while using up to 4.7 times less data, demonstrating improved sample-efficiency, generalization, and robustness to ambiguous language. Project page: https://MIT-CLEAR-Lab.github.io/Masked-IRL and Code: https://github.com/MIT-CLEAR-Lab/Masked-IRL
Open-Universe Assistance Games
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Embodied AI agents must infer and act in an interpretable way on diverse human goals and preferences that are not predefined. To formalize this setting, we introduce Open-Universe Assistance Games (OU-AGs), a framework where the agent must reason over an unbounded and evolving space of possible goals. In this context, we introduce GOOD (GOals from Open-ended Dialogue), a data-efficient, online method that extracts goals in the form of natural language during an interaction with a human, and infers a distribution over natural language goals. GOOD prompts an LLM to simulate users with different complex intents, using its responses to perform probabilistic inference over candidate goals. This approach enables rich goal representations and uncertainty estimation without requiring large offline datasets. We evaluate GOOD in a text-based grocery shopping domain and in a text-operated simulated household robotics environment (AI2Thor), using synthetic user profiles. Our method outperforms a baseline without explicit goal tracking, as confirmed by both LLM-based and human evaluations.
Context Matters: Learning Generalizable Rewards via Calibrated Features
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:A key challenge in reward learning from human input is that desired agent behavior often changes based on context. Traditional methods typically treat each new context as a separate task with its own reward function. For example, if a previously ignored stove becomes too hot to be around, the robot must learn a new reward from scratch, even though the underlying preference for prioritizing safety over efficiency remains unchanged. We observe that context influences not the underlying preference itself, but rather the $\textit{saliency}$--or importance--of reward features. For instance, stove heat affects the importance of the robot's proximity, yet the human's safety preference stays the same. Existing multi-task and meta IRL methods learn context-dependent representations $\textit{implicitly}$--without distinguishing between preferences and feature importance--resulting in substantial data requirements. Instead, we propose $\textit{explicitly}$ modeling context-invariant preferences separately from context-dependent feature saliency, creating modular reward representations that adapt to new contexts. To achieve this, we introduce $\textit{calibrated features}$--representations that capture contextual effects on feature saliency--and present specialized paired comparison queries that isolate saliency from preference for efficient learning. Experiments with simulated users show our method significantly improves sample efficiency, requiring 10x fewer preference queries than baselines to achieve equivalent reward accuracy, with up to 15% better performance in low-data regimes (5-10 queries). An in-person user study (N=12) demonstrates that participants can effectively teach their unique personal contextual preferences using our method, enabling more adaptable and personalized reward learning.
Goal Inference from Open-Ended Dialog
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:We present an online method for embodied agents to learn and accomplish diverse user goals. While offline methods like RLHF can represent various goals but require large datasets, our approach achieves similar flexibility with online efficiency. We extract natural language goal representations from conversations with Large Language Models (LLMs). We prompt an LLM to role play as a human with different goals and use the corresponding likelihoods to run Bayesian inference over potential goals. As a result, our method can represent uncertainty over complex goals based on unrestricted dialog. We evaluate our method in grocery shopping and home robot assistance domains using a text-based interface and AI2Thor simulation respectively. Results show our method outperforms ablation baselines that lack either explicit goal representation or probabilistic inference.
Learning How Hard to Think: Input-Adaptive Allocation of LM Computation
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:Computationally intensive decoding procedures--including search, reranking, and self-critique--can improve the quality of language model (LM) outputs in problems spanning code generation, numerical reasoning, and dialog. Existing work typically applies the same decoding procedure for every input to an LM. But not all inputs require the same amount of computation to process. Can we allocate decoding computation adaptively, using more resources to answer questions whose answers will be harder to compute? We present an approach that predicts the distribution of rewards given an input and computation budget, then allocates additional computation to inputs for which it is predicted to be most useful. We apply this approach in two decoding procedures: first, an adaptive best-of-k procedure that dynamically selects the number of samples to generate as input to a reranker; second, a routing procedure that dynamically responds to a query using a decoding procedure that is expensive but accurate, or one that is cheaper but less capable. Across a suite of programming, mathematics, and dialog tasks, we show that accurate computation-allocation procedures can be learned, and reduce computation by up to 50% at no cost to response quality, or improve quality by up to 10% at a fixed computational budget.
Adaptive Language-Guided Abstraction from Contrastive Explanations
Sep 12, 2024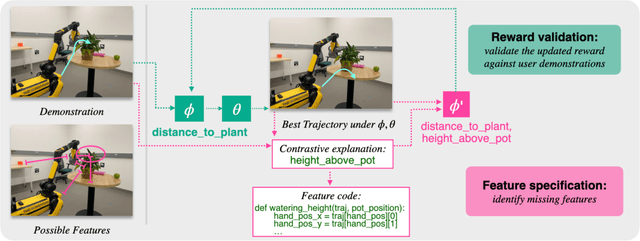
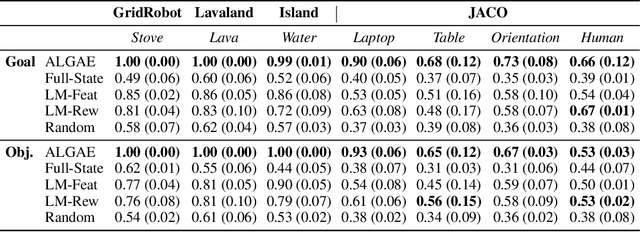

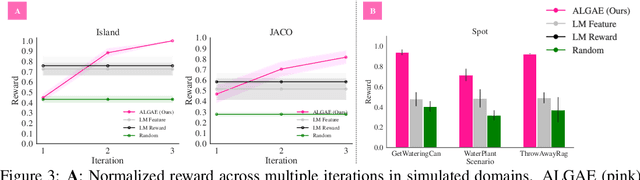
Abstract:Many approaches to robot learning begin by inferring a reward function from a set of human demonstrations. To learn a good reward, it is necessary to determine which features of the environment are relevant before determining how these features should be used to compute reward. End-to-end methods for joint feature and reward learning (e.g., using deep networks or program synthesis techniques) often yield brittle reward functions that are sensitive to spurious state features. By contrast, humans can often generalizably learn from a small number of demonstrations by incorporating strong priors about what features of a demonstration are likely meaningful for a task of interest. How do we build robots that leverage this kind of background knowledge when learning from new demonstrations? This paper describes a method named ALGAE (Adaptive Language-Guided Abstraction from [Contrastive] Explanations) which alternates between using language models to iteratively identify human-meaningful features needed to explain demonstrated behavior, then standard inverse reinforcement learning techniques to assign weights to these features. Experiments across a variety of both simulated and real-world robot environments show that ALGAE learns generalizable reward functions defined on interpretable features using only small numbers of demonstrations. Importantly, ALGAE can recognize when features are missing, then extract and define those features without any human input -- making it possible to quickly and efficiently acquire rich representations of user behavior.
Preference-Conditioned Language-Guided Abstraction
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Learning from demonstrations is a common way for users to teach robots, but it is prone to spurious feature correlations. Recent work constructs state abstractions, i.e. visual representations containing task-relevant features, from language as a way to perform more generalizable learning. However, these abstractions also depend on a user's preference for what matters in a task, which may be hard to describe or infeasible to exhaustively specify using language alone. How do we construct abstractions to capture these latent preferences? We observe that how humans behave reveals how they see the world. Our key insight is that changes in human behavior inform us that there are differences in preferences for how humans see the world, i.e. their state abstractions. In this work, we propose using language models (LMs) to query for those preferences directly given knowledge that a change in behavior has occurred. In our framework, we use the LM in two ways: first, given a text description of the task and knowledge of behavioral change between states, we query the LM for possible hidden preferences; second, given the most likely preference, we query the LM to construct the state abstraction. In this framework, the LM is also able to ask the human directly when uncertain about its own estimate. We demonstrate our framework's ability to construct effective preference-conditioned abstractions in simulated experiments, a user study, as well as on a real Spot robot performing mobile manipulation tasks.
Getting aligned on representational alignment
Nov 02, 2023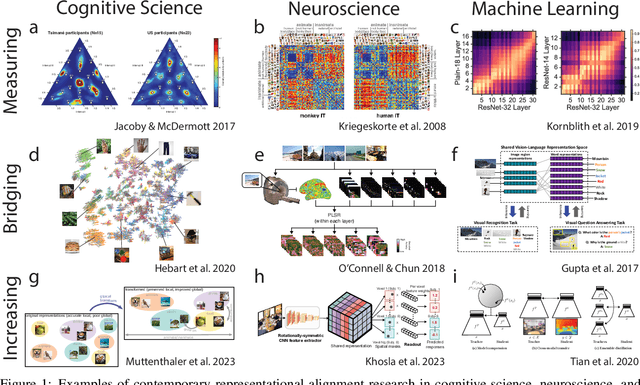
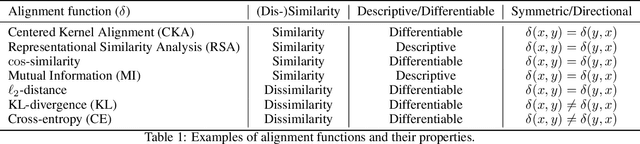
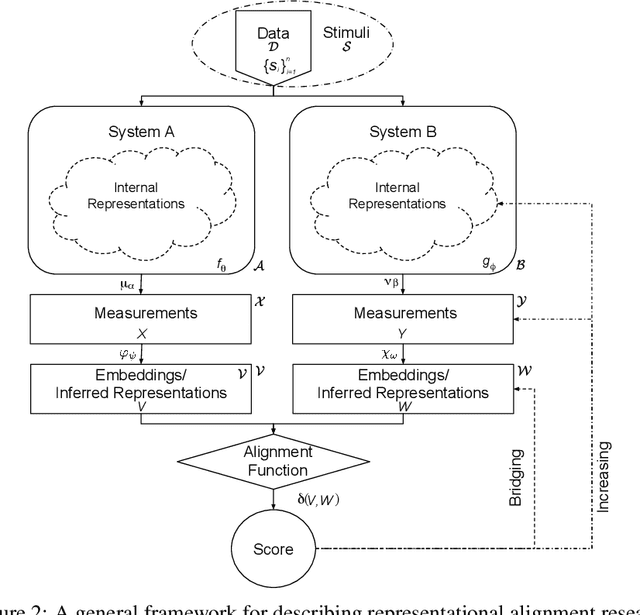
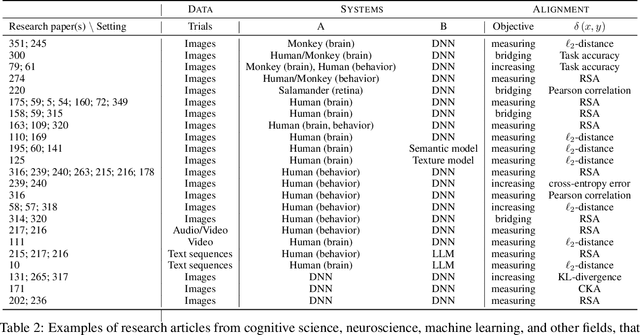
Abstract:Biological and artificial information processing systems form representations that they can use to categorize, reason, plan, navigate, and make decisions. How can we measure the extent to which the representations formed by these diverse systems agree? Do similarities in representations then translate into similar behavior? How can a system's representations be modified to better match those of another system? These questions pertaining to the study of representational alignment are at the heart of some of the most active research areas in cognitive science, neuroscience, and machine learning. For example, cognitive scientists measure the representational alignment of multiple individuals to identify shared cognitive priors, neuroscientists align fMRI responses from multiple individuals into a shared representational space for group-level analyses, and ML researchers distill knowledge from teacher models into student models by increasing their alignment. Unfortunately, there is limited knowledge transfer between research communities interested in representational alignment, so progress in one field often ends up being rediscovered independently in another. Thus, greater cross-field communication would be advantageous. To improve communication between these fields, we propose a unifying framework that can serve as a common language between researchers studying representational alignment. We survey the literature from all three fields and demonstrate how prior work fits into this framework. Finally, we lay out open problems in representational alignment where progress can benefit all three of these fields. We hope that our work can catalyze cross-disciplinary collaboration and accelerate progress for all communities studying and developing information processing systems. We note that this is a working paper and encourage readers to reach out with their suggestions for future revisions.
Diagnosis, Feedback, Adaptation: A Human-in-the-Loop Framework for Test-Time Policy Adaptation
Jul 13, 2023Abstract:Policies often fail due to distribution shift -- changes in the state and reward that occur when a policy is deployed in new environments. Data augmentation can increase robustness by making the model invariant to task-irrelevant changes in the agent's observation. However, designers don't know which concepts are irrelevant a priori, especially when different end users have different preferences about how the task is performed. We propose an interactive framework to leverage feedback directly from the user to identify personalized task-irrelevant concepts. Our key idea is to generate counterfactual demonstrations that allow users to quickly identify possible task-relevant and irrelevant concepts. The knowledge of task-irrelevant concepts is then used to perform data augmentation and thus obtain a policy adapted to personalized user objectives. We present experiments validating our framework on discrete and continuous control tasks with real human users. Our method (1) enables users to better understand agent failure, (2) reduces the number of demonstrations required for fine-tuning, and (3) aligns the agent to individual user task preferences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge