Jacob Andreas
CONCUR: A Framework for Continual Constrained and Unconstrained Routing
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:AI tasks differ in complexity and are best addressed with different computation strategies (e.g., combinations of models and decoding methods). Hence, an effective routing system that maps tasks to the appropriate strategies is crucial. Most prior methods build the routing framework by training a single model across all strategies, which demands full retraining whenever new strategies appear and leads to high overhead. Attempts at such continual routing, however, often face difficulties with generalization. Prior models also typically use a single input representation, limiting their ability to capture the full complexity of the routing problem and leading to sub-optimal routing decisions. To address these gaps, we propose CONCUR, a continual routing framework that supports both constrained and unconstrained routing (i.e., routing with or without a budget). Our modular design trains a separate predictor model for each strategy, enabling seamless incorporation of new strategies with low additional training cost. Our predictors also leverage multiple representations of both tasks and computation strategies to better capture overall problem complexity. Experiments on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution, knowledge- and reasoning-intensive tasks show that our method outperforms the best single strategy and strong existing routing techniques with higher end-to-end accuracy and lower inference cost in both continual and non-continual settings, while also reducing training cost in the continual setting.
ARC Is a Vision Problem!
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) is designed to promote research on abstract reasoning, a fundamental aspect of human intelligence. Common approaches to ARC treat it as a language-oriented problem, addressed by large language models (LLMs) or recurrent reasoning models. However, although the puzzle-like tasks in ARC are inherently visual, existing research has rarely approached the problem from a vision-centric perspective. In this work, we formulate ARC within a vision paradigm, framing it as an image-to-image translation problem. To incorporate visual priors, we represent the inputs on a "canvas" that can be processed like natural images. It is then natural for us to apply standard vision architectures, such as a vanilla Vision Transformer (ViT), to perform image-to-image mapping. Our model is trained from scratch solely on ARC data and generalizes to unseen tasks through test-time training. Our framework, termed Vision ARC (VARC), achieves 60.4% accuracy on the ARC-1 benchmark, substantially outperforming existing methods that are also trained from scratch. Our results are competitive with those of leading LLMs and close the gap to average human performance.
Training Language Models to Explain Their Own Computations
Nov 11, 2025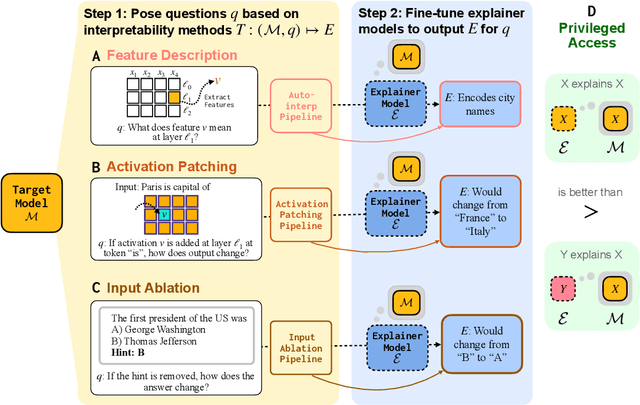
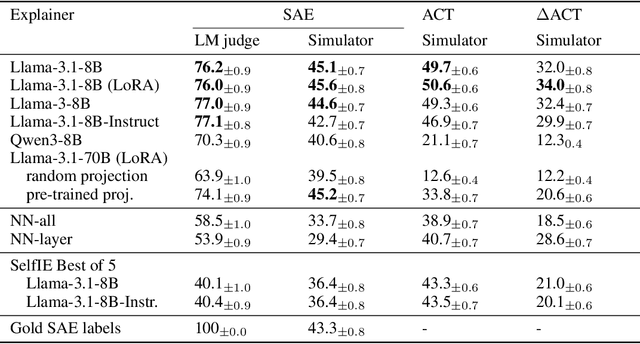
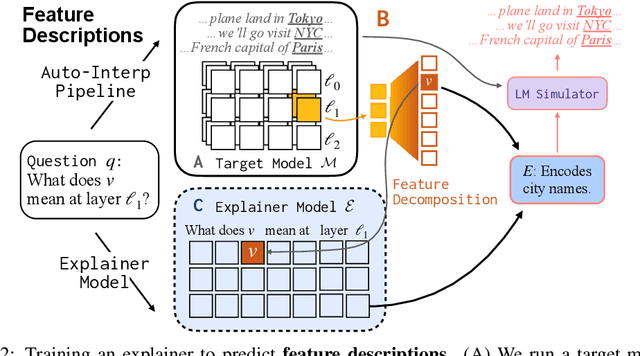
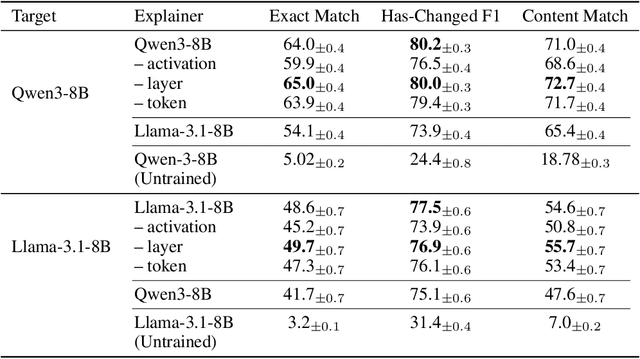
Abstract:Can language models (LMs) learn to faithfully describe their internal computations? Are they better able to describe themselves than other models? We study the extent to which LMs' privileged access to their own internals can be leveraged to produce new techniques for explaining their behavior. Using existing interpretability techniques as a source of ground truth, we fine-tune LMs to generate natural language descriptions of (1) the information encoded by LM features, (2) the causal structure of LMs' internal activations, and (3) the influence of specific input tokens on LM outputs. When trained with only tens of thousands of example explanations, explainer models exhibit non-trivial generalization to new queries. This generalization appears partly attributable to explainer models' privileged access to their own internals: using a model to explain its own computations generally works better than using a *different* model to explain its computations (even if the other model is significantly more capable). Our results suggest not only that LMs can learn to reliably explain their internal computations, but that such explanations offer a scalable complement to existing interpretability methods.
Automated Detection of Visual Attribute Reliance with a Self-Reflective Agent
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:When a vision model performs image recognition, which visual attributes drive its predictions? Detecting unintended reliance on specific visual features is critical for ensuring model robustness, preventing overfitting, and avoiding spurious correlations. We introduce an automated framework for detecting such dependencies in trained vision models. At the core of our method is a self-reflective agent that systematically generates and tests hypotheses about visual attributes that a model may rely on. This process is iterative: the agent refines its hypotheses based on experimental outcomes and uses a self-evaluation protocol to assess whether its findings accurately explain model behavior. When inconsistencies arise, the agent self-reflects over its findings and triggers a new cycle of experimentation. We evaluate our approach on a novel benchmark of 130 models designed to exhibit diverse visual attribute dependencies across 18 categories. Our results show that the agent's performance consistently improves with self-reflection, with a significant performance increase over non-reflective baselines. We further demonstrate that the agent identifies real-world visual attribute dependencies in state-of-the-art models, including CLIP's vision encoder and the YOLOv8 object detector.
Modeling Student Learning with 3.8 Million Program Traces
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:As programmers write code, they often edit and retry multiple times, creating rich "interaction traces" that reveal how they approach coding tasks and provide clues about their level of skill development. For novice programmers in particular, these traces reflect the diverse reasoning processes they employ to code, such as exploratory behavior to understand how a programming concept works, re-strategizing in response to bugs, and personalizing stylistic choices. In this work, we explore what can be learned from training language models on such reasoning traces: not just about code, but about coders, and particularly students learning to program. We introduce a dataset of over 3.8 million programming reasoning traces from users of Pencil Code, a free online educational platform used by students to learn simple programming concepts. Compared to models trained only on final programs or synthetically-generated traces, we find that models trained on real traces are stronger at modeling diverse student behavior. Through both behavioral and probing analyses, we also find that many properties of code traces, such as goal backtracking or number of comments, can be predicted from learned representations of the students who write them. Building on this result, we show that we can help students recover from mistakes by steering code generation models to identify a sequence of edits that will results in more correct code while remaining close to the original student's style. Together, our results suggest that many properties of code are properties of individual students and that training on edit traces can lead to models that are more steerable, more predictive of student behavior while programming, and better at generating programs in their final states. Code and data is available at https://github.com/meghabyte/pencilcode-public
Beyond Binary Rewards: Training LMs to Reason About Their Uncertainty
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:When language models (LMs) are trained via reinforcement learning (RL) to generate natural language "reasoning chains", their performance improves on a variety of difficult question answering tasks. Today, almost all successful applications of RL for reasoning use binary reward functions that evaluate the correctness of LM outputs. Because such reward functions do not penalize guessing or low-confidence outputs, they often have the unintended side-effect of degrading calibration and increasing the rate at which LMs generate incorrect responses (or "hallucinate") in other problem domains. This paper describes RLCR (Reinforcement Learning with Calibration Rewards), an approach to training reasoning models that jointly improves accuracy and calibrated confidence estimation. During RLCR, LMs generate both predictions and numerical confidence estimates after reasoning. They are trained to optimize a reward function that augments a binary correctness score with a Brier score -- a scoring rule for confidence estimates that incentivizes calibrated prediction. We first prove that this reward function (or any analogous reward function that uses a bounded, proper scoring rule) yields models whose predictions are both accurate and well-calibrated. We next show that across diverse datasets, RLCR substantially improves calibration with no loss in accuracy, on both in-domain and out-of-domain evaluations -- outperforming both ordinary RL training and classifiers trained to assign post-hoc confidence scores. While ordinary RL hurts calibration, RLCR improves it. Finally, we demonstrate that verbalized confidence can be leveraged at test time to improve accuracy and calibration via confidence-weighted scaling methods. Our results show that explicitly optimizing for calibration can produce more generally reliable reasoning models.
LLM Hypnosis: Exploiting User Feedback for Unauthorized Knowledge Injection to All Users
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:We describe a vulnerability in language models (LMs) trained with user feedback, whereby a single user can persistently alter LM knowledge and behavior given only the ability to provide prompts and upvote / downvote feedback on LM outputs. To implement the attack, the attacker prompts the LM to stochastically output either a "poisoned" or benign response, then upvotes the poisoned response or downvotes the benign one. When feedback signals are used in a subsequent preference tuning behavior, LMs exhibit increased probability of producing poisoned responses even in contexts without malicious prompts. We show that this attack can be used to (1) insert factual knowledge the model did not previously possess, (2) modify code generation patterns in ways that introduce exploitable security flaws, and (3) inject fake financial news. Our finding both identifies a new qualitative feature of language model preference tuning (showing that it even highly restricted forms of preference data can be used to exert fine-grained control over behavior), and a new attack mechanism for LMs trained with user feedback (extending work on pretraining-time data poisoning and deployment-time prompt injection).
Can Gradient Descent Simulate Prompting?
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:There are two primary ways of incorporating new information into a language model (LM): changing its prompt or changing its parameters, e.g. via fine-tuning. Parameter updates incur no long-term storage cost for model changes. However, for many model updates, prompting is significantly more effective: prompted models can generalize robustly from single examples and draw logical inferences that do not occur under standard fine-tuning. Can models be modified so that fine-tuning does emulate prompting? This paper describes a method for meta-training LMs such that gradient updates emulate the effects of conditioning on new information. Our approach uses tools from gradient-based meta-learning but uses an LM's own prompted predictions as targets, eliminating the need for ground-truth labels. Subsequent gradient descent training recovers some (and occasionally all) of prompted model performance -- showing improvement on the ``reversal curse'' tasks, and answering questions about text passages after a single gradient update. These results suggest that, with appropriate initialization, gradient descent can be surprisingly expressive. Our results suggest new avenues for long-context modeling and offer insight into the generalization capabilities of gradient-based learning.
Sequential-Parallel Duality in Prefix Scannable Models
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Modern neural sequence models are designed to meet the dual mandate of parallelizable training and fast sequential inference. Recent developments have given rise to various models, such as Gated Linear Attention (GLA) and Mamba, that achieve such ``sequential-parallel duality.'' This raises a natural question: can we characterize the full class of neural sequence models that support near-constant-time parallel evaluation and linear-time, constant-space sequential inference? We begin by describing a broad class of such models -- state space models -- as those whose state updates can be computed using the classic parallel prefix scan algorithm with a custom associative aggregation operator. We then define a more general class, Prefix-Scannable Models (PSMs), by relaxing the state aggregation operator to allow arbitrary (potentially non-associative) functions such as softmax attention. This generalization unifies many existing architectures, including element-wise RNNs (e.g., Mamba) and linear transformers (e.g., GLA, Mamba2, mLSTM), while also introducing new models with softmax-like operators that achieve O(1) amortized compute per token and log(N) memory for sequence length N. We empirically evaluate such models on illustrative small-scale language modeling and canonical synthetic tasks, including state tracking and associative recall. Empirically, we find that PSMs retain the expressivity of transformer-based architectures while matching the inference efficiency of state space models -- in some cases exhibiting better length generalization than either.
Line of Sight: On Linear Representations in VLLMs
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Language models can be equipped with multimodal capabilities by fine-tuning on embeddings of visual inputs. But how do such multimodal models represent images in their hidden activations? We explore representations of image concepts within LlaVA-Next, a popular open-source VLLM. We find a diverse set of ImageNet classes represented via linearly decodable features in the residual stream. We show that the features are causal by performing targeted edits on the model output. In order to increase the diversity of the studied linear features, we train multimodal Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs), creating a highly interpretable dictionary of text and image features. We find that although model representations across modalities are quite disjoint, they become increasingly shared in deeper layers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge