Curved Text Detection
Curved text detection is the process of identifying and localizing text that is curved or non-linear in images.
Papers and Code
Context-Aware Vision Language Foundation Models for Ocular Disease Screening in Retinal Images
Mar 19, 2025Foundation models are large-scale versatile systems trained on vast quantities of diverse data to learn generalizable representations. Their adaptability with minimal fine-tuning makes them particularly promising for medical imaging, where data variability and domain shifts are major challenges. Currently, two types of foundation models dominate the literature: self-supervised models and more recent vision-language models. In this study, we advance the application of vision-language foundation (VLF) models for ocular disease screening using the OPHDIAT dataset, which includes nearly 700,000 fundus photographs from a French diabetic retinopathy (DR) screening network. This dataset provides extensive clinical data (patient-specific information such as diabetic health conditions, and treatments), labeled diagnostics, ophthalmologists text-based findings, and multiple retinal images for each examination. Building on the FLAIR model $\unicode{x2013}$ a VLF model for retinal pathology classification $\unicode{x2013}$ we propose novel context-aware VLF models (e.g jointly analyzing multiple images from the same visit or taking advantage of past diagnoses and contextual data) to fully leverage the richness of the OPHDIAT dataset and enhance robustness to domain shifts. Our approaches were evaluated on both in-domain (a testing subset of OPHDIAT) and out-of-domain data (public datasets) to assess their generalization performance. Our model demonstrated improved in-domain performance for DR grading, achieving an area under the curve (AUC) ranging from 0.851 to 0.9999, and generalized well to ocular disease detection on out-of-domain data (AUC: 0.631-0.913).
Detecting Dark Patterns in User Interfaces Using Logistic Regression and Bag-of-Words Representation
Dec 09, 2024Dark patterns in user interfaces represent deceptive design practices intended to manipulate users' behavior, often leading to unintended consequences such as coerced purchases, involuntary data disclosures, or user frustration. Detecting and mitigating these dark patterns is crucial for promoting transparency, trust, and ethical design practices in digital environments. This paper proposes a novel approach for detecting dark patterns in user interfaces using logistic regression and bag-of-words representation. Our methodology involves collecting a diverse dataset of user interface text samples, preprocessing the data, extracting text features using the bag-of-words representation, training a logistic regression model, and evaluating its performance using various metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC). Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in accurately identifying instances of dark patterns, with high predictive performance and robustness to variations in dataset composition and model parameters. The insights gained from this study contribute to the growing body of knowledge on dark patterns detection and classification, offering practical implications for designers, developers, and policymakers in promoting ethical design practices and protecting user rights in digital environments.
Detecting Redundant Health Survey Questions Using Language-agnostic BERT Sentence Embedding (LaBSE)
Dec 05, 2024



The goal of this work was to compute the semantic similarity among publicly available health survey questions in order to facilitate the standardization of survey-based Person-Generated Health Data (PGHD). We compiled various health survey questions authored in both English and Korean from the NIH CDE Repository, PROMIS, Korean public health agencies, and academic publications. Questions were drawn from various health lifelog domains. A randomized question pairing scheme was used to generate a Semantic Text Similarity (STS) dataset consisting of 1758 question pairs. Similarity scores between each question pair were assigned by two human experts. The tagged dataset was then used to build three classifiers featuring: Bag-of-Words, SBERT with BERT-based embeddings, and SBRET with LaBSE embeddings. The algorithms were evaluated using traditional contingency statistics. Among the three algorithms, SBERT-LaBSE demonstrated the highest performance in assessing question similarity across both languages, achieving an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) and Precision-Recall Curves of over 0.99. Additionally, it proved effective in identifying cross-lingual semantic similarities.The SBERT-LaBSE algorithm excelled at aligning semantically equivalent sentences across both languages but encountered challenges in capturing subtle nuances and maintaining computational efficiency. Future research should focus on testing with larger multilingual datasets and on calibrating and normalizing scores across the health lifelog domains to improve consistency. This study introduces the SBERT-LaBSE algorithm for calculating semantic similarity across two languages, showing it outperforms BERT-based models and the Bag of Words approach, highlighting its potential to improve semantic interoperability of survey-based PGHD across language barriers.
A Multi-Agent Framework for Extensible Structured Text Generation in PLCs
Dec 03, 2024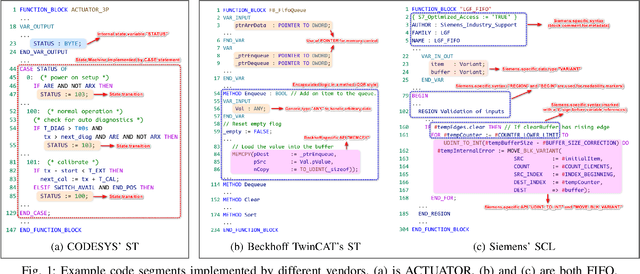
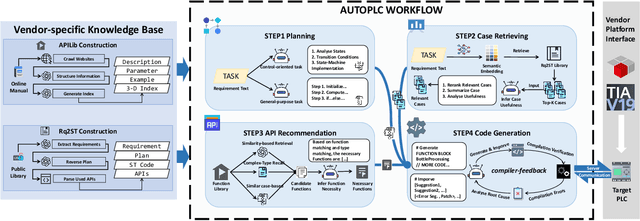
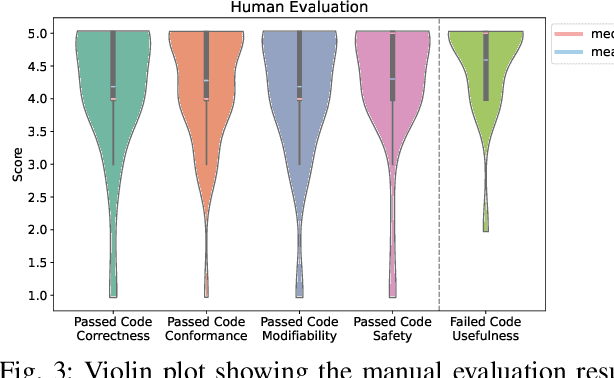
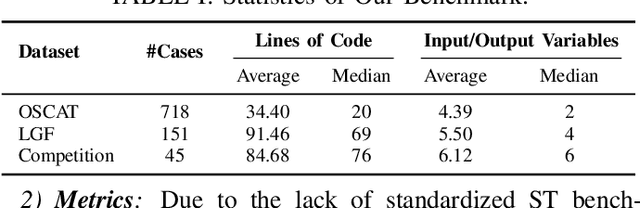
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are microcomputers essential for automating factory operations. Structured Text (ST), a high-level language adhering to the IEC 61131-3 standard, is pivotal for PLCs due to its ability to express logic succinctly and to seamlessly integrate with other languages within the same standard. However, vendors develop their own customized versions of ST, and the lack of comprehensive and standardized documentation for the full semantics of ST has contributed to inconsistencies in how the language is implemented. Consequently, the steep learning curve associated with ST, combined with ever-evolving industrial requirements, presents significant challenges for developers. In response to these issues, we present AutoPLC, an LLM-based approach designed to automate the generation of vendor-specific ST code. To facilitate effective code generation, we first built a comprehensive knowledge base, including Rq2ST Case Library (requirements and corresponding implementations) and Instruction libraries. Then we developed a retrieval module to incorporate the domain-specific knowledge by identifying pertinent cases and instructions, guiding the LLM to generate code that meets the requirements. In order to verify and improve the quality of the generated code, we designed an adaptable code checker. If errors are detected, we initiate an iterative self-improvement process to instruct the LLM to revise the generated code. We evaluate AutoPLC's performance against seven state-of-the-art baselines using three benchmarks, one for open-source basic ST and two for commercial Structured Control Language (SCL) from Siemens. The results show that our approach consistently achieves superior performance across all benchmarks. Ablation study emphasizes the significance of our modules. Further manual analysis confirm the practical utility of the ST code generated by AutoPLC.
DNTextSpotter: Arbitrary-Shaped Scene Text Spotting via Improved Denoising Training
Aug 01, 2024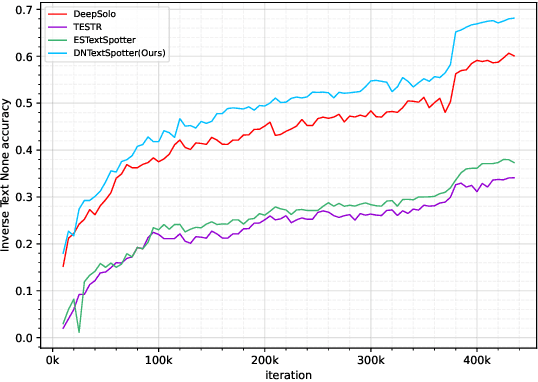
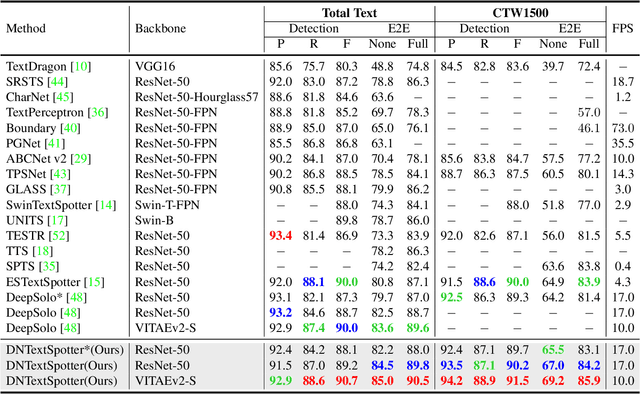
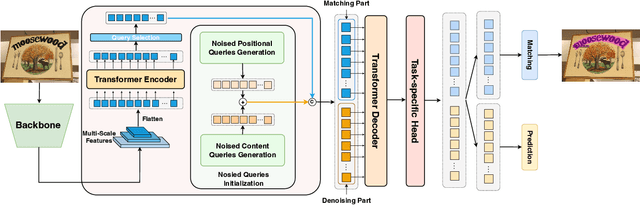
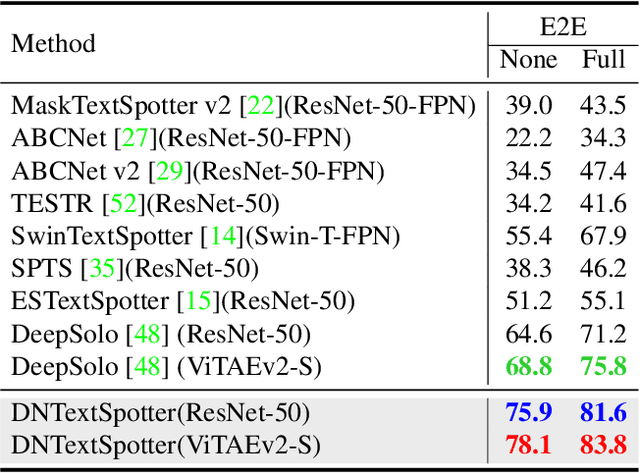
More and more end-to-end text spotting methods based on Transformer architecture have demonstrated superior performance. These methods utilize a bipartite graph matching algorithm to perform one-to-one optimal matching between predicted objects and actual objects. However, the instability of bipartite graph matching can lead to inconsistent optimization targets, thereby affecting the training performance of the model. Existing literature applies denoising training to solve the problem of bipartite graph matching instability in object detection tasks. Unfortunately, this denoising training method cannot be directly applied to text spotting tasks, as these tasks need to perform irregular shape detection tasks and more complex text recognition tasks than classification. To address this issue, we propose a novel denoising training method (DNTextSpotter) for arbitrary-shaped text spotting. Specifically, we decompose the queries of the denoising part into noised positional queries and noised content queries. We use the four Bezier control points of the Bezier center curve to generate the noised positional queries. For the noised content queries, considering that the output of the text in a fixed positional order is not conducive to aligning position with content, we employ a masked character sliding method to initialize noised content queries, thereby assisting in the alignment of text content and position. To improve the model's perception of the background, we further utilize an additional loss function for background characters classification in the denoising training part.Although DNTextSpotter is conceptually simple, it outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on four benchmarks (Total-Text, SCUT-CTW1500, ICDAR15, and Inverse-Text), especially yielding an improvement of 11.3% against the best approach in Inverse-Text dataset.
Text in the Dark: Extremely Low-Light Text Image Enhancement
Apr 22, 2024



Extremely low-light text images are common in natural scenes, making scene text detection and recognition challenging. One solution is to enhance these images using low-light image enhancement methods before text extraction. However, previous methods often do not try to particularly address the significance of low-level features, which are crucial for optimal performance on downstream scene text tasks. Further research is also hindered by the lack of extremely low-light text datasets. To address these limitations, we propose a novel encoder-decoder framework with an edge-aware attention module to focus on scene text regions during enhancement. Our proposed method uses novel text detection and edge reconstruction losses to emphasize low-level scene text features, leading to successful text extraction. Additionally, we present a Supervised Deep Curve Estimation (Supervised-DCE) model to synthesize extremely low-light images based on publicly available scene text datasets such as ICDAR15 (IC15). We also labeled texts in the extremely low-light See In the Dark (SID) and ordinary LOw-Light (LOL) datasets to allow for objective assessment of extremely low-light image enhancement through scene text tasks. Extensive experiments show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of both image quality and scene text metrics on the widely-used LOL, SID, and synthetic IC15 datasets. Code and dataset will be released publicly at https://github.com/chunchet-ng/Text-in-the-Dark.
Enhancing Scene Text Detectors with Realistic Text Image Synthesis Using Diffusion Models
Nov 28, 2023



Scene text detection techniques have garnered significant attention due to their wide-ranging applications. However, existing methods have a high demand for training data, and obtaining accurate human annotations is labor-intensive and time-consuming. As a solution, researchers have widely adopted synthetic text images as a complementary resource to real text images during pre-training. Yet there is still room for synthetic datasets to enhance the performance of scene text detectors. We contend that one main limitation of existing generation methods is the insufficient integration of foreground text with the background. To alleviate this problem, we present the Diffusion Model based Text Generator (DiffText), a pipeline that utilizes the diffusion model to seamlessly blend foreground text regions with the background's intrinsic features. Additionally, we propose two strategies to generate visually coherent text with fewer spelling errors. With fewer text instances, our produced text images consistently surpass other synthetic data in aiding text detectors. Extensive experiments on detecting horizontal, rotated, curved, and line-level texts demonstrate the effectiveness of DiffText in producing realistic text images.
End-to-End User-Defined Keyword Spotting using Shifted Delta Coefficients
May 23, 2024Identifying user-defined keywords is crucial for personalizing interactions with smart devices. Previous approaches of user-defined keyword spotting (UDKWS) have relied on short-term spectral features such as mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) to detect the spoken keyword. However, these features may face challenges in accurately identifying closely related pronunciation of audio-text pairs, due to their limited capability in capturing the temporal dynamics of the speech signal. To address this challenge, we propose to use shifted delta coefficients (SDC) which help in capturing pronunciation variability (transition between connecting phonemes) by incorporating long-term temporal information. The performance of the SDC feature is compared with various baseline features across four different datasets using a cross-attention based end-to-end system. Additionally, various configurations of SDC are explored to find the suitable temporal context for the UDKWS task. The experimental results reveal that the SDC feature outperforms the MFCC baseline feature, exhibiting an improvement of 8.32% in area under the curve (AUC) and 8.69% in terms of equal error rate (EER) on the challenging Libriphrase-hard dataset. Moreover, the proposed approach demonstrated superior performance when compared to state-of-the-art UDKWS techniques.
Advanced Knowledge Extraction of Physical Design Drawings, Translation and conversion to CAD formats using Deep Learning
Mar 17, 2024The maintenance, archiving and usage of the design drawings is cumbersome in physical form in different industries for longer period. It is hard to extract information by simple scanning of drawing sheets. Converting them to their digital formats such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD), with needed knowledge extraction can solve this problem. The conversion of these machine drawings to its digital form is a crucial challenge which requires advanced techniques. This research proposes an innovative methodology utilizing Deep Learning methods. The approach employs object detection model, such as Yolov7, Faster R-CNN, to detect physical drawing objects present in the images followed by, edge detection algorithms such as canny filter to extract and refine the identified lines from the drawing region and curve detection techniques to detect circle. Also ornaments (complex shapes) within the drawings are extracted. To ensure comprehensive conversion, an Optical Character Recognition (OCR) tool is integrated to identify and extract the text elements from the drawings. The extracted data which includes the lines, shapes and text is consolidated and stored in a structured comma separated values(.csv) file format. The accuracy and the efficiency of conversion is evaluated. Through this, conversion can be automated to help organizations enhance their productivity, facilitate seamless collaborations and preserve valuable design information in a digital format easily accessible. Overall, this study contributes to the advancement of CAD conversions, providing accurate results from the translating process. Future research can focus on handling diverse drawing types, enhanced accuracy in shape and line detection and extraction.
Hierarchical Text Spotter for Joint Text Spotting and Layout Analysis
Oct 25, 2023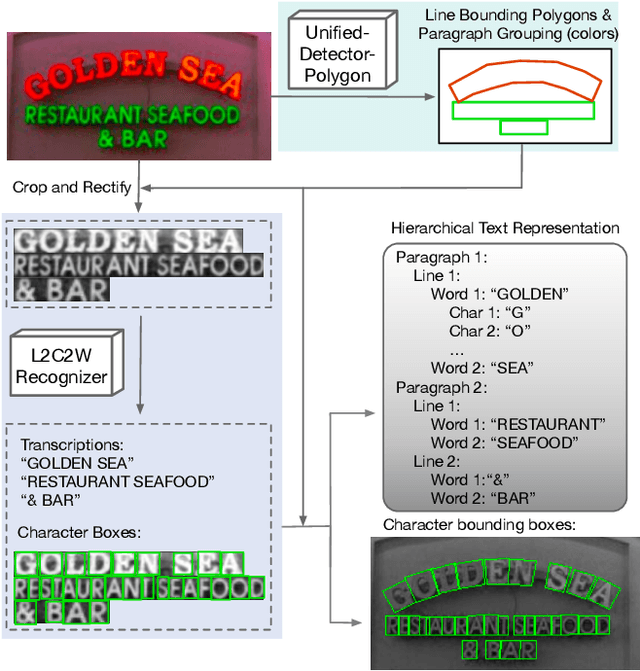
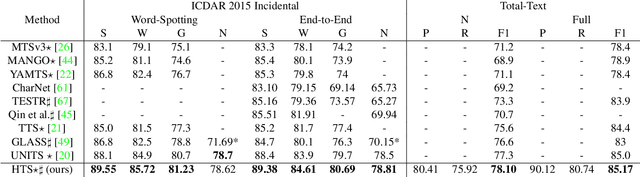
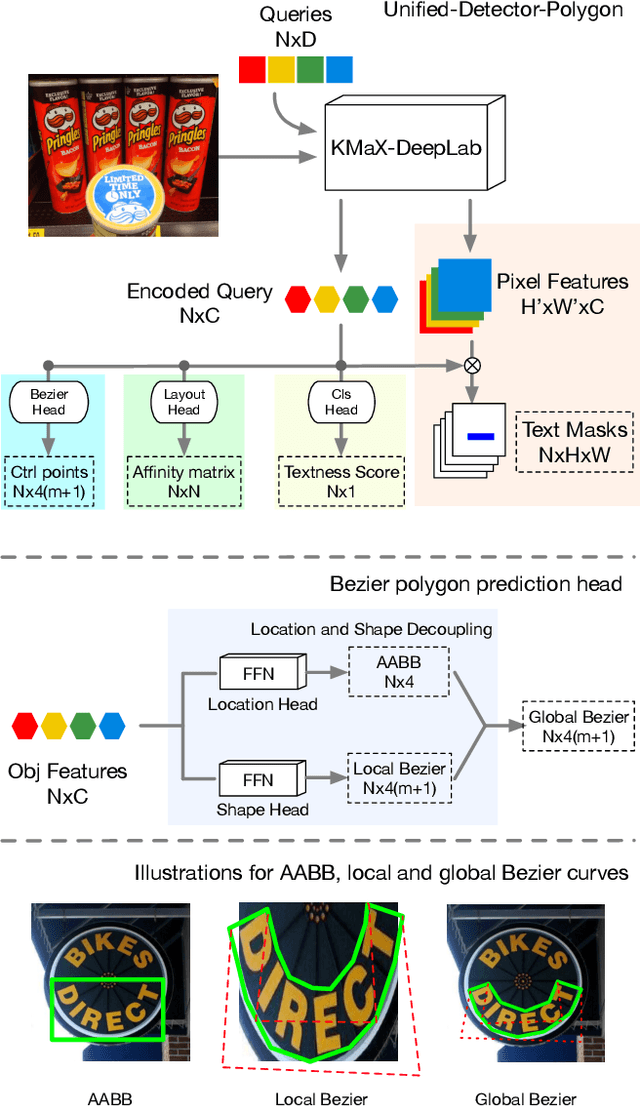
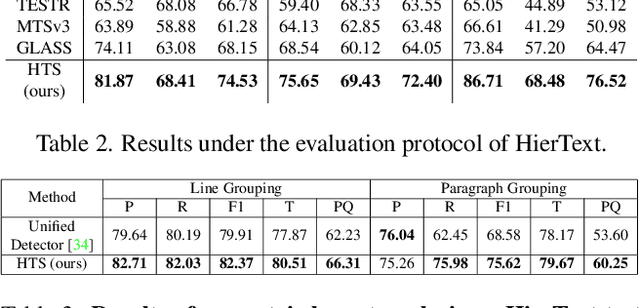
We propose Hierarchical Text Spotter (HTS), a novel method for the joint task of word-level text spotting and geometric layout analysis. HTS can recognize text in an image and identify its 4-level hierarchical structure: characters, words, lines, and paragraphs. The proposed HTS is characterized by two novel components: (1) a Unified-Detector-Polygon (UDP) that produces Bezier Curve polygons of text lines and an affinity matrix for paragraph grouping between detected lines; (2) a Line-to-Character-to-Word (L2C2W) recognizer that splits lines into characters and further merges them back into words. HTS achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple word-level text spotting benchmark datasets as well as geometric layout analysis tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge