Michalis Raptis
TextSR: Diffusion Super-Resolution with Multilingual OCR Guidance
May 29, 2025Abstract:While recent advancements in Image Super-Resolution (SR) using diffusion models have shown promise in improving overall image quality, their application to scene text images has revealed limitations. These models often struggle with accurate text region localization and fail to effectively model image and multilingual character-to-shape priors. This leads to inconsistencies, the generation of hallucinated textures, and a decrease in the perceived quality of the super-resolved text. To address these issues, we introduce TextSR, a multimodal diffusion model specifically designed for Multilingual Scene Text Image Super-Resolution. TextSR leverages a text detector to pinpoint text regions within an image and then employs Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract multilingual text from these areas. The extracted text characters are then transformed into visual shapes using a UTF-8 based text encoder and cross-attention. Recognizing that OCR may sometimes produce inaccurate results in real-world scenarios, we have developed two innovative methods to enhance the robustness of our model. By integrating text character priors with the low-resolution text images, our model effectively guides the super-resolution process, enhancing fine details within the text and improving overall legibility. The superior performance of our model on both the TextZoom and TextVQA datasets sets a new benchmark for STISR, underscoring the efficacy of our approach.
Unified Autoregressive Visual Generation and Understanding with Continuous Tokens
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We present UniFluid, a unified autoregressive framework for joint visual generation and understanding leveraging continuous visual tokens. Our unified autoregressive architecture processes multimodal image and text inputs, generating discrete tokens for text and continuous tokens for image. We find though there is an inherent trade-off between the image generation and understanding task, a carefully tuned training recipe enables them to improve each other. By selecting an appropriate loss balance weight, the unified model achieves results comparable to or exceeding those of single-task baselines on both tasks. Furthermore, we demonstrate that employing stronger pre-trained LLMs and random-order generation during training is important to achieve high-fidelity image generation within this unified framework. Built upon the Gemma model series, UniFluid exhibits competitive performance across both image generation and understanding, demonstrating strong transferability to various downstream tasks, including image editing for generation, as well as visual captioning and question answering for understanding.
Hierarchical Text Spotter for Joint Text Spotting and Layout Analysis
Oct 25, 2023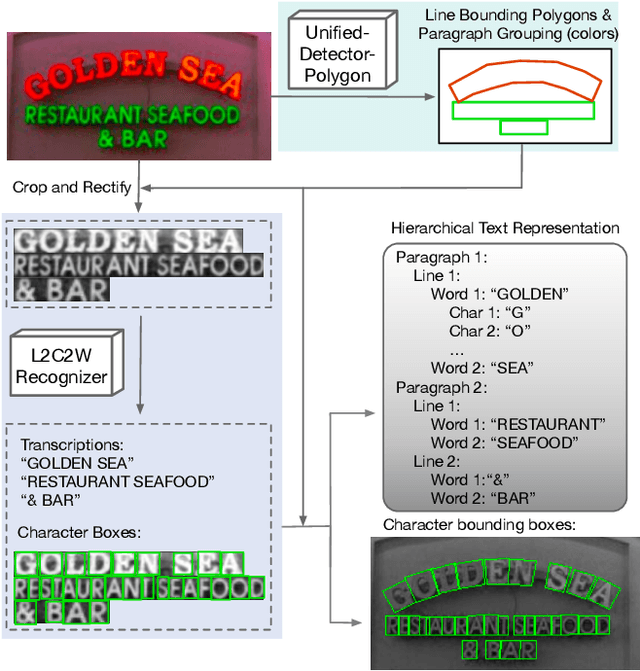
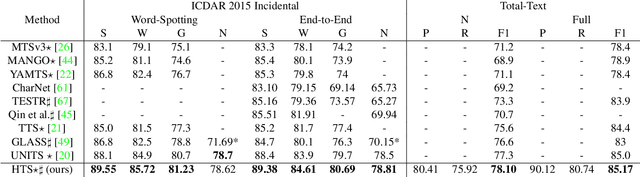
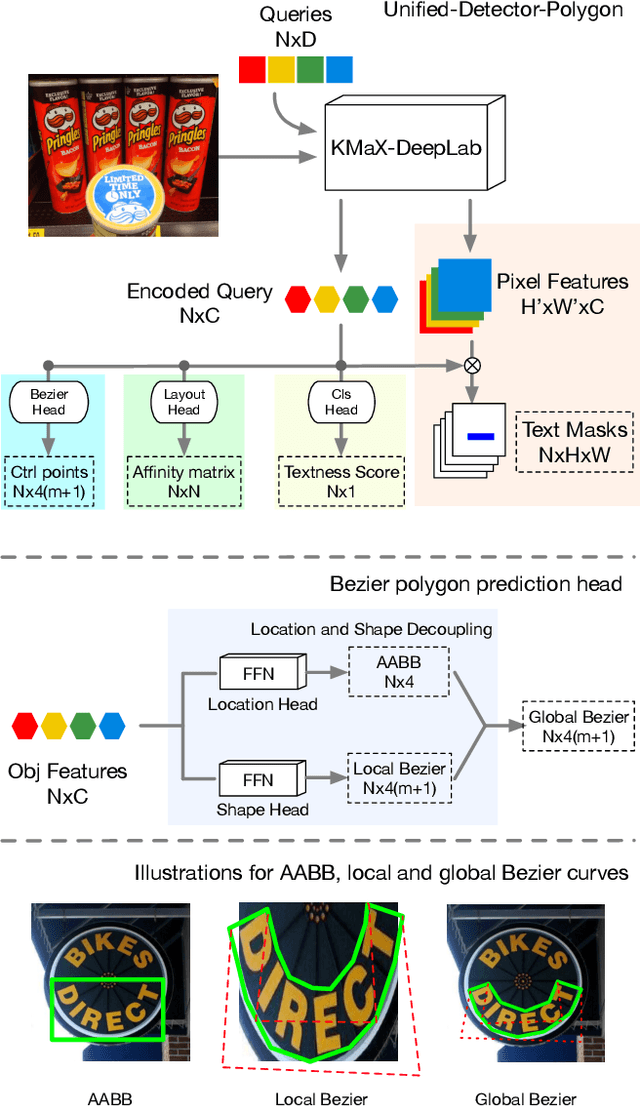
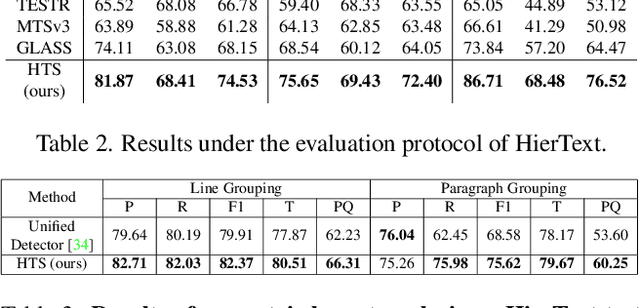
Abstract:We propose Hierarchical Text Spotter (HTS), a novel method for the joint task of word-level text spotting and geometric layout analysis. HTS can recognize text in an image and identify its 4-level hierarchical structure: characters, words, lines, and paragraphs. The proposed HTS is characterized by two novel components: (1) a Unified-Detector-Polygon (UDP) that produces Bezier Curve polygons of text lines and an affinity matrix for paragraph grouping between detected lines; (2) a Line-to-Character-to-Word (L2C2W) recognizer that splits lines into characters and further merges them back into words. HTS achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple word-level text spotting benchmark datasets as well as geometric layout analysis tasks.
ICDAR 2023 Competition on Hierarchical Text Detection and Recognition
May 16, 2023



Abstract:We organize a competition on hierarchical text detection and recognition. The competition is aimed to promote research into deep learning models and systems that can jointly perform text detection and recognition and geometric layout analysis. We present details of the proposed competition organization, including tasks, datasets, evaluations, and schedule. During the competition period (from January 2nd 2023 to April 1st 2023), at least 50 submissions from more than 20 teams were made in the 2 proposed tasks. Considering the number of teams and submissions, we conclude that the HierText competition has been successfully held. In this report, we will also present the competition results and insights from them.
Towards End-to-End Unified Scene Text Detection and Layout Analysis
Mar 28, 2022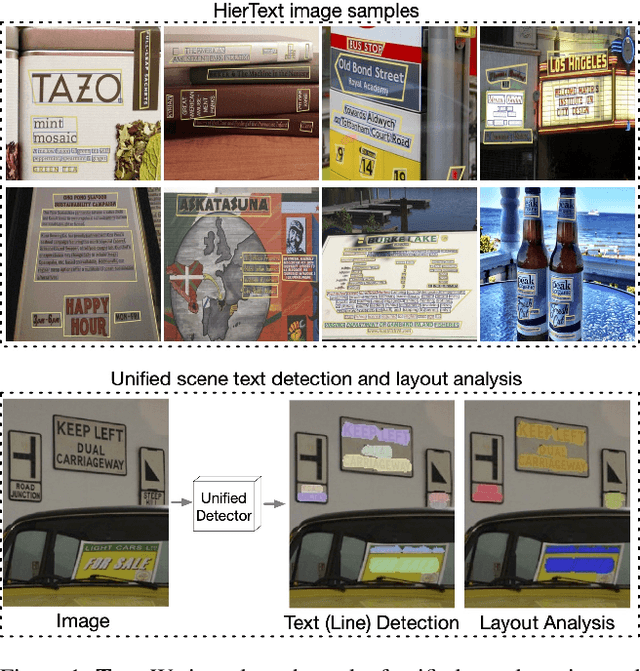
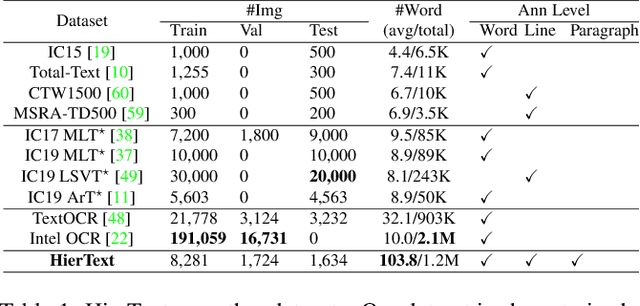
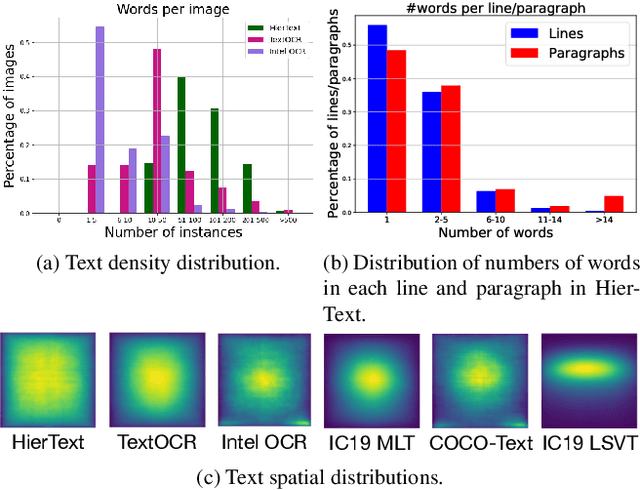
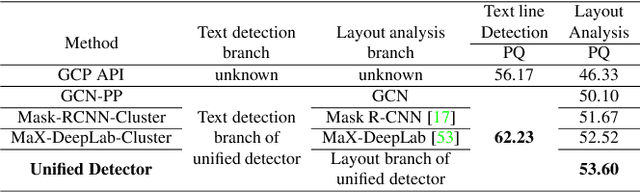
Abstract:Scene text detection and document layout analysis have long been treated as two separate tasks in different image domains. In this paper, we bring them together and introduce the task of unified scene text detection and layout analysis. The first hierarchical scene text dataset is introduced to enable this novel research task. We also propose a novel method that is able to simultaneously detect scene text and form text clusters in a unified way. Comprehensive experiments show that our unified model achieves better performance than multiple well-designed baseline methods. Additionally, this model achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple scene text detection datasets without the need of complex post-processing. Dataset and code: https://github.com/google-research-datasets/hiertext.
Unified Line and Paragraph Detection by Graph Convolutional Networks
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:We formulate the task of detecting lines and paragraphs in a document into a unified two-level clustering problem. Given a set of text detection boxes that roughly correspond to words, a text line is a cluster of boxes and a paragraph is a cluster of lines. These clusters form a two-level tree that represents a major part of the layout of a document. We use a graph convolutional network to predict the relations between text detection boxes and then build both levels of clusters from these predictions. Experimentally, we demonstrate that the unified approach can be highly efficient while still achieving state-of-the-art quality for detecting paragraphs in public benchmarks and real-world images.
Towards Unconstrained End-to-End Text Spotting
Aug 24, 2019
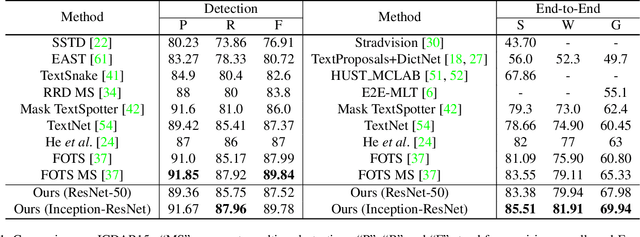

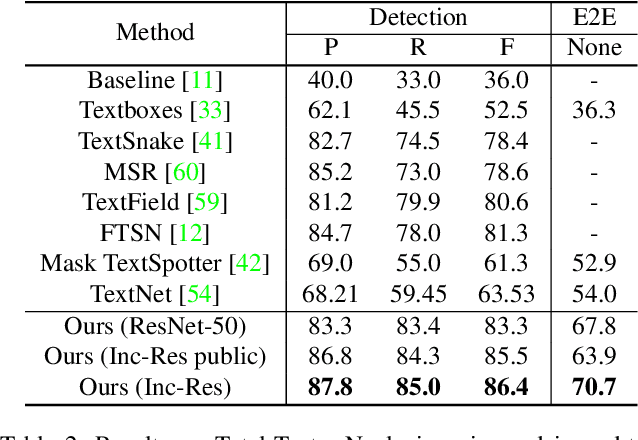
Abstract:We propose an end-to-end trainable network that can simultaneously detect and recognize text of arbitrary shape, making substantial progress on the open problem of reading scene text of irregular shape. We formulate arbitrary shape text detection as an instance segmentation problem; an attention model is then used to decode the textual content of each irregularly shaped text region without rectification. To extract useful irregularly shaped text instance features from image scale features, we propose a simple yet effective RoI masking step. Additionally, we show that predictions from an existing multi-step OCR engine can be leveraged as partially labeled training data, which leads to significant improvements in both the detection and recognition accuracy of our model. Our method surpasses the state-of-the-art for end-to-end recognition tasks on the ICDAR15 (straight) benchmark by 4.6%, and on the Total-Text (curved) benchmark by more than 16%.
Dependence Maximizing Temporal Alignment via Squared-Loss Mutual Information
Jun 19, 2012

Abstract:The goal of temporal alignment is to establish time correspondence between two sequences, which has many applications in a variety of areas such as speech processing, bioinformatics, computer vision, and computer graphics. In this paper, we propose a novel temporal alignment method called least-squares dynamic time warping (LSDTW). LSDTW finds an alignment that maximizes statistical dependency between sequences, measured by a squared-loss variant of mutual information. The benefit of this novel information-theoretic formulation is that LSDTW can align sequences with different lengths, different dimensionality, high non-linearity, and non-Gaussianity in a computationally efficient manner. In addition, model parameters such as an initial alignment matrix can be systematically optimized by cross-validation. We demonstrate the usefulness of LSDTW through experiments on synthetic and real-world Kinect action recognition datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge