Mauricio Delbracio
Learning from a Generative Oracle: Domain Adaptation for Restoration
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained image restoration models often fail on real-world, out-of-distribution degradations due to significant domain gaps. Adapting to these unseen domains is challenging, as out-of-distribution data lacks ground truth, and traditional adaptation methods often require complex architectural changes. We propose LEGO (Learning from a Generative Oracle), a practical three-stage framework for post-training domain adaptation without paired data. LEGO converts this unsupervised challenge into a tractable pseudo-supervised one. First, we obtain initial restorations from the pre-trained model. Second, we leverage a frozen, large-scale generative oracle to refine these estimates into high-quality pseudo-ground-truths. Third, we fine-tune the original model using a mixed-supervision strategy combining in-distribution data with these new pseudo-pairs. This approach adapts the model to the new distribution without sacrificing its original robustness or requiring architectural modifications. Experiments demonstrate that LEGO effectively bridges the domain gap, significantly improving performance on diverse real-world benchmarks.
Learn to Guide Your Diffusion Model
Oct 01, 2025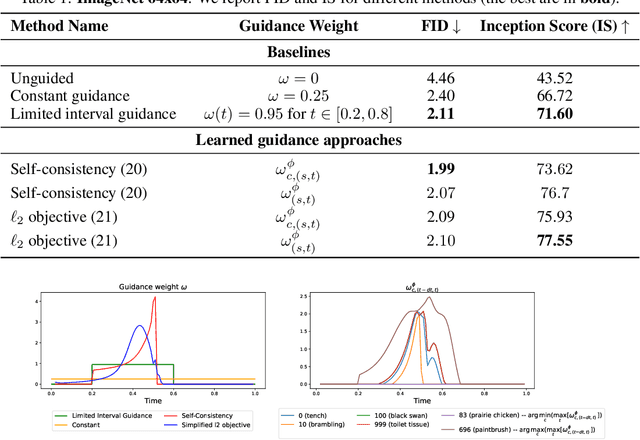
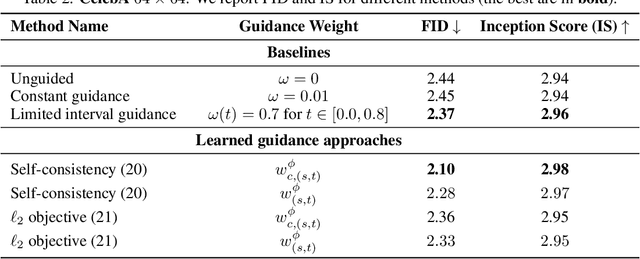
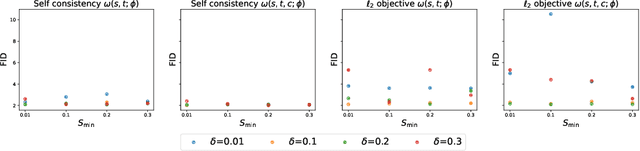
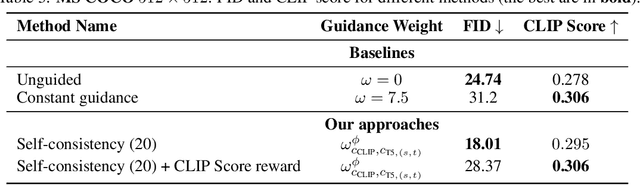
Abstract:Classifier-free guidance (CFG) is a widely used technique for improving the perceptual quality of samples from conditional diffusion models. It operates by linearly combining conditional and unconditional score estimates using a guidance weight $\omega$. While a large, static weight can markedly improve visual results, this often comes at the cost of poorer distributional alignment. In order to better approximate the target conditional distribution, we instead learn guidance weights $\omega_{c,(s,t)}$, which are continuous functions of the conditioning $c$, the time $t$ from which we denoise, and the time $s$ towards which we denoise. We achieve this by minimizing the distributional mismatch between noised samples from the true conditional distribution and samples from the guided diffusion process. We extend our framework to reward guided sampling, enabling the model to target distributions tilted by a reward function $R(x_0,c)$, defined on clean data and a conditioning $c$. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our methodology on low-dimensional toy examples and high-dimensional image settings, where we observe improvements in Fr\'echet inception distance (FID) for image generation. In text-to-image applications, we observe that employing a reward function given by the CLIP score leads to guidance weights that improve image-prompt alignment.
UniRes: Universal Image Restoration for Complex Degradations
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Real-world image restoration is hampered by diverse degradations stemming from varying capture conditions, capture devices and post-processing pipelines. Existing works make improvements through simulating those degradations and leveraging image generative priors, however generalization to in-the-wild data remains an unresolved problem. In this paper, we focus on complex degradations, i.e., arbitrary mixtures of multiple types of known degradations, which is frequently seen in the wild. A simple yet flexible diffusionbased framework, named UniRes, is proposed to address such degradations in an end-to-end manner. It combines several specialized models during the diffusion sampling steps, hence transferring the knowledge from several well-isolated restoration tasks to the restoration of complex in-the-wild degradations. This only requires well-isolated training data for several degradation types. The framework is flexible as extensions can be added through a unified formulation, and the fidelity-quality trade-off can be adjusted through a new paradigm. Our proposed method is evaluated on both complex-degradation and single-degradation image restoration datasets. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experimental results show consistent performance gain especially for images with complex degradations.
TextSR: Diffusion Super-Resolution with Multilingual OCR Guidance
May 29, 2025Abstract:While recent advancements in Image Super-Resolution (SR) using diffusion models have shown promise in improving overall image quality, their application to scene text images has revealed limitations. These models often struggle with accurate text region localization and fail to effectively model image and multilingual character-to-shape priors. This leads to inconsistencies, the generation of hallucinated textures, and a decrease in the perceived quality of the super-resolved text. To address these issues, we introduce TextSR, a multimodal diffusion model specifically designed for Multilingual Scene Text Image Super-Resolution. TextSR leverages a text detector to pinpoint text regions within an image and then employs Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract multilingual text from these areas. The extracted text characters are then transformed into visual shapes using a UTF-8 based text encoder and cross-attention. Recognizing that OCR may sometimes produce inaccurate results in real-world scenarios, we have developed two innovative methods to enhance the robustness of our model. By integrating text character priors with the low-resolution text images, our model effectively guides the super-resolution process, enhancing fine details within the text and improving overall legibility. The superior performance of our model on both the TextZoom and TextVQA datasets sets a new benchmark for STISR, underscoring the efficacy of our approach.
Reference-Guided Identity Preserving Face Restoration
May 28, 2025Abstract:Preserving face identity is a critical yet persistent challenge in diffusion-based image restoration. While reference faces offer a path forward, existing reference-based methods often fail to fully exploit their potential. This paper introduces a novel approach that maximizes reference face utility for improved face restoration and identity preservation. Our method makes three key contributions: 1) Composite Context, a comprehensive representation that fuses multi-level (high- and low-level) information from the reference face, offering richer guidance than prior singular representations. 2) Hard Example Identity Loss, a novel loss function that leverages the reference face to address the identity learning inefficiencies found in the existing identity loss. 3) A training-free method to adapt the model to multi-reference inputs during inference. The proposed method demonstrably restores high-quality faces and achieves state-of-the-art identity preserving restoration on benchmarks such as FFHQ-Ref and CelebA-Ref-Test, consistently outperforming previous work.
The Power of Context: How Multimodality Improves Image Super-Resolution
Mar 18, 2025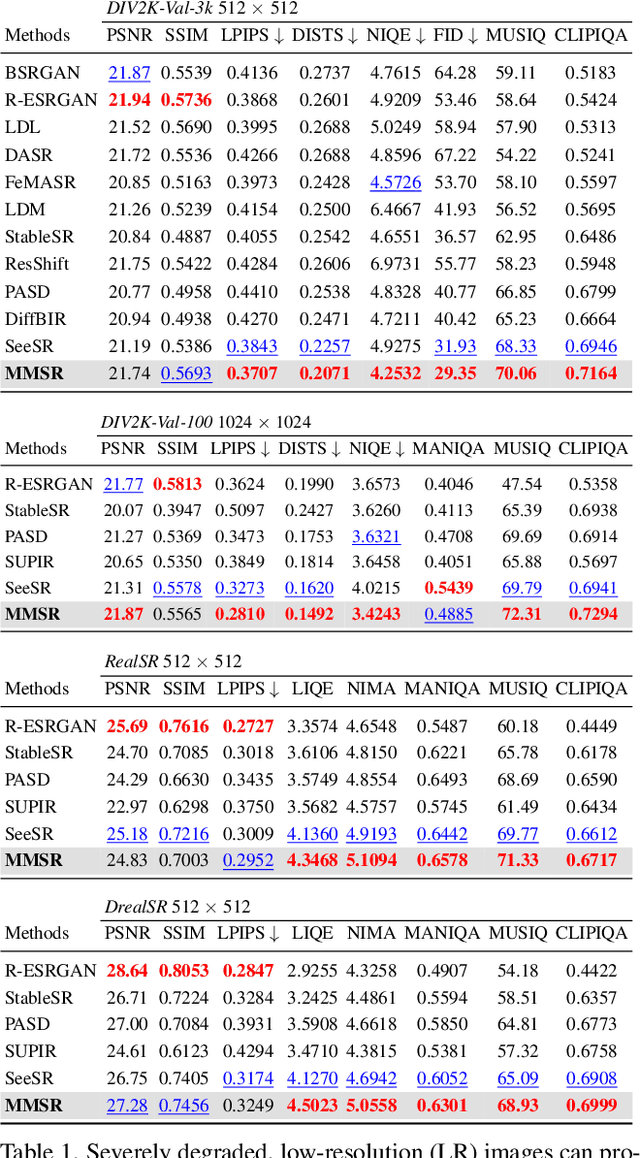
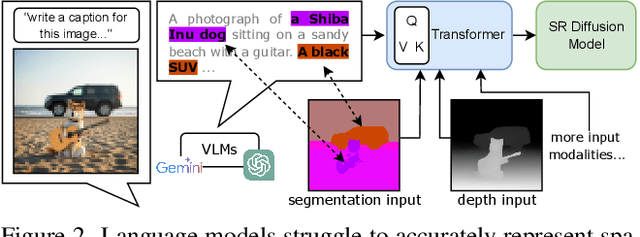
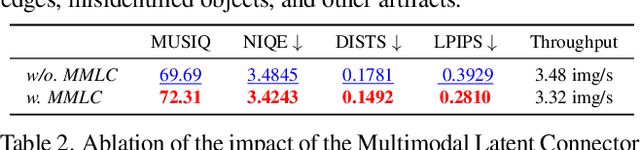
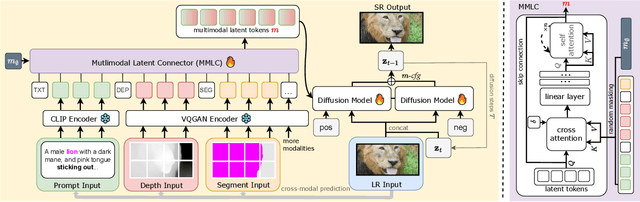
Abstract:Single-image super-resolution (SISR) remains challenging due to the inherent difficulty of recovering fine-grained details and preserving perceptual quality from low-resolution inputs. Existing methods often rely on limited image priors, leading to suboptimal results. We propose a novel approach that leverages the rich contextual information available in multiple modalities -- including depth, segmentation, edges, and text prompts -- to learn a powerful generative prior for SISR within a diffusion model framework. We introduce a flexible network architecture that effectively fuses multimodal information, accommodating an arbitrary number of input modalities without requiring significant modifications to the diffusion process. Crucially, we mitigate hallucinations, often introduced by text prompts, by using spatial information from other modalities to guide regional text-based conditioning. Each modality's guidance strength can also be controlled independently, allowing steering outputs toward different directions, such as increasing bokeh through depth or adjusting object prominence via segmentation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model surpasses state-of-the-art generative SISR methods, achieving superior visual quality and fidelity. See project page at https://mmsr.kfmei.com/.
On the Relation Between Linear Diffusion and Power Iteration
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Recently, diffusion models have gained popularity due to their impressive generative abilities. These models learn the implicit distribution given by the training dataset, and sample new data by transforming random noise through the reverse process, which can be thought of as gradual denoising. In this work, we examine the generation process as a ``correlation machine'', where random noise is repeatedly enhanced in correlation with the implicit given distribution. To this end, we explore the linear case, where the optimal denoiser in the MSE sense is known to be the PCA projection. This enables us to connect the theory of diffusion models to the spiked covariance model, where the dependence of the denoiser on the noise level and the amount of training data can be expressed analytically, in the rank-1 case. In a series of numerical experiments, we extend this result to general low rank data, and show that low frequencies emerge earlier in the generation process, where the denoising basis vectors are more aligned to the true data with a rate depending on their eigenvalues. This model allows us to show that the linear diffusion model converges in mean to the leading eigenvector of the underlying data, similarly to the prevalent power iteration method. Finally, we empirically demonstrate the applicability of our findings beyond the linear case, in the Jacobians of a deep, non-linear denoiser, used in general image generation tasks.
Stochastic Deep Restoration Priors for Imaging Inverse Problems
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Deep neural networks trained as image denoisers are widely used as priors for solving imaging inverse problems. While Gaussian denoising is thought sufficient for learning image priors, we show that priors from deep models pre-trained as more general restoration operators can perform better. We introduce Stochastic deep Restoration Priors (ShaRP), a novel method that leverages an ensemble of such restoration models to regularize inverse problems. ShaRP improves upon methods using Gaussian denoiser priors by better handling structured artifacts and enabling self-supervised training even without fully sampled data. We prove ShaRP minimizes an objective function involving a regularizer derived from the score functions of minimum mean square error (MMSE) restoration operators, and theoretically analyze its convergence. Empirically, ShaRP achieves state-of-the-art performance on tasks such as magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction and single-image super-resolution, surpassing both denoiser-and diffusion-model-based methods without requiring retraining.
Denoising: A Powerful Building-Block for Imaging, Inverse Problems, and Machine Learning
Sep 10, 2024



Abstract:Denoising, the process of reducing random fluctuations in a signal to emphasize essential patterns, has been a fundamental problem of interest since the dawn of modern scientific inquiry. Recent denoising techniques, particularly in imaging, have achieved remarkable success, nearing theoretical limits by some measures. Yet, despite tens of thousands of research papers, the wide-ranging applications of denoising beyond noise removal have not been fully recognized. This is partly due to the vast and diverse literature, making a clear overview challenging. This paper aims to address this gap. We present a comprehensive perspective on denoisers, their structure, and desired properties. We emphasize the increasing importance of denoising and showcase its evolution into an essential building block for complex tasks in imaging, inverse problems, and machine learning. Despite its long history, the community continues to uncover unexpected and groundbreaking uses for denoising, further solidifying its place as a cornerstone of scientific and engineering practice.
Bigger is not Always Better: Scaling Properties of Latent Diffusion Models
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:We study the scaling properties of latent diffusion models (LDMs) with an emphasis on their sampling efficiency. While improved network architecture and inference algorithms have shown to effectively boost sampling efficiency of diffusion models, the role of model size -- a critical determinant of sampling efficiency -- has not been thoroughly examined. Through empirical analysis of established text-to-image diffusion models, we conduct an in-depth investigation into how model size influences sampling efficiency across varying sampling steps. Our findings unveil a surprising trend: when operating under a given inference budget, smaller models frequently outperform their larger equivalents in generating high-quality results. Moreover, we extend our study to demonstrate the generalizability of the these findings by applying various diffusion samplers, exploring diverse downstream tasks, evaluating post-distilled models, as well as comparing performance relative to training compute. These findings open up new pathways for the development of LDM scaling strategies which can be employed to enhance generative capabilities within limited inference budgets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge