Ruijin Liu
Align before Adapt: Leveraging Entity-to-Region Alignments for Generalizable Video Action Recognition
Nov 27, 2023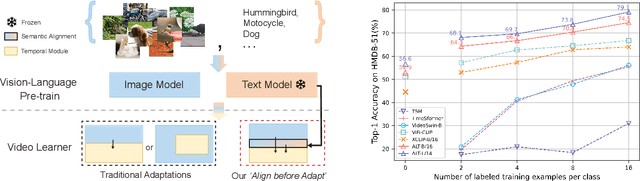
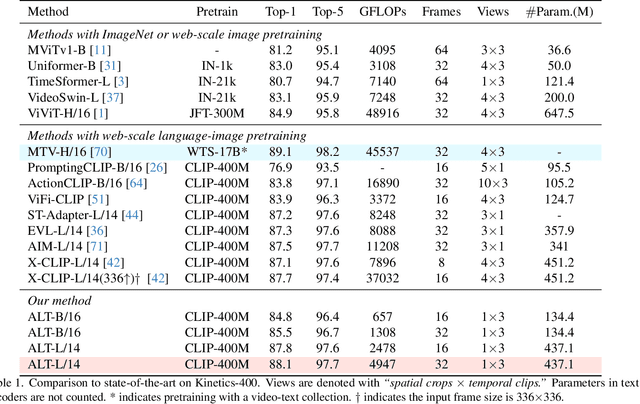
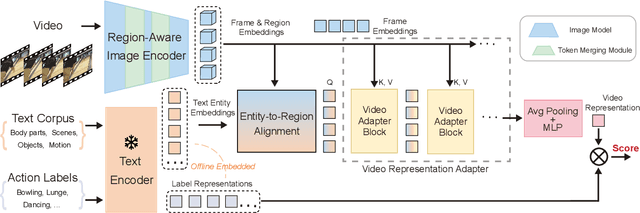
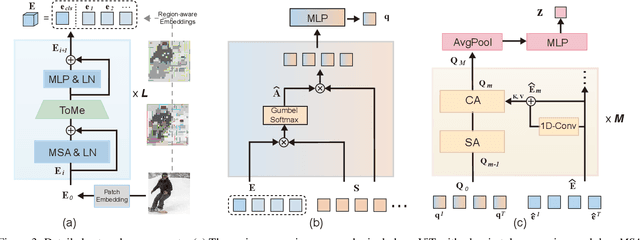
Abstract:Large-scale visual-language pre-trained models have achieved significant success in various video tasks. However, most existing methods follow an "adapt then align" paradigm, which adapts pre-trained image encoders to model video-level representations and utilizes one-hot or text embedding of the action labels for supervision. This paradigm overlooks the challenge of mapping from static images to complicated activity concepts. In this paper, we propose a novel "Align before Adapt" (ALT) paradigm. Prior to adapting to video representation learning, we exploit the entity-to-region alignments for each frame. The alignments are fulfilled by matching the region-aware image embeddings to an offline-constructed text corpus. With the aligned entities, we feed their text embeddings to a transformer-based video adapter as the queries, which can help extract the semantics of the most important entities from a video to a vector. This paradigm reuses the visual-language alignment of VLP during adaptation and tries to explain an action by the underlying entities. This helps understand actions by bridging the gap with complex activity semantics, particularly when facing unfamiliar or unseen categories. ALT achieves competitive performance and superior generalizability while requiring significantly low computational costs. In fully supervised scenarios, it achieves 88.1% top-1 accuracy on Kinetics-400 with only 4947 GFLOPs. In 2-shot experiments, ALT outperforms the previous state-of-the-art by 7.1% and 9.2% on HMDB-51 and UCF-101, respectively.
PBFormer: Capturing Complex Scene Text Shape with Polynomial Band Transformer
Aug 29, 2023



Abstract:We present PBFormer, an efficient yet powerful scene text detector that unifies the transformer with a novel text shape representation Polynomial Band (PB). The representation has four polynomial curves to fit a text's top, bottom, left, and right sides, which can capture a text with a complex shape by varying polynomial coefficients. PB has appealing features compared with conventional representations: 1) It can model different curvatures with a fixed number of parameters, while polygon-points-based methods need to utilize a different number of points. 2) It can distinguish adjacent or overlapping texts as they have apparent different curve coefficients, while segmentation-based or points-based methods suffer from adhesive spatial positions. PBFormer combines the PB with the transformer, which can directly generate smooth text contours sampled from predicted curves without interpolation. A parameter-free cross-scale pixel attention (CPA) module is employed to highlight the feature map of a suitable scale while suppressing the other feature maps. The simple operation can help detect small-scale texts and is compatible with the one-stage DETR framework, where no postprocessing exists for NMS. Furthermore, PBFormer is trained with a shape-contained loss, which not only enforces the piecewise alignment between the ground truth and the predicted curves but also makes curves' positions and shapes consistent with each other. Without bells and whistles about text pre-training, our method is superior to the previous state-of-the-art text detectors on the arbitrary-shaped text datasets.
Video Action Recognition with Attentive Semantic Units
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:Visual-Language Models (VLMs) have significantly advanced action video recognition. Supervised by the semantics of action labels, recent works adapt the visual branch of VLMs to learn video representations. Despite the effectiveness proved by these works, we believe that the potential of VLMs has yet to be fully harnessed. In light of this, we exploit the semantic units (SU) hiding behind the action labels and leverage their correlations with fine-grained items in frames for more accurate action recognition. SUs are entities extracted from the language descriptions of the entire action set, including body parts, objects, scenes, and motions. To further enhance the alignments between visual contents and the SUs, we introduce a multi-region module (MRA) to the visual branch of the VLM. The MRA allows the perception of region-aware visual features beyond the original global feature. Our method adaptively attends to and selects relevant SUs with visual features of frames. With a cross-modal decoder, the selected SUs serve to decode spatiotemporal video representations. In summary, the SUs as the medium can boost discriminative ability and transferability. Specifically, in fully-supervised learning, our method achieved 87.8\% top-1 accuracy on Kinetics-400. In K=2 few-shot experiments, our method surpassed the previous state-of-the-art by +7.1% and +15.0% on HMDB-51 and UCF-101, respectively.
Learning to Predict 3D Lane Shape and Camera Pose from a Single Image via Geometry Constraints
Dec 31, 2021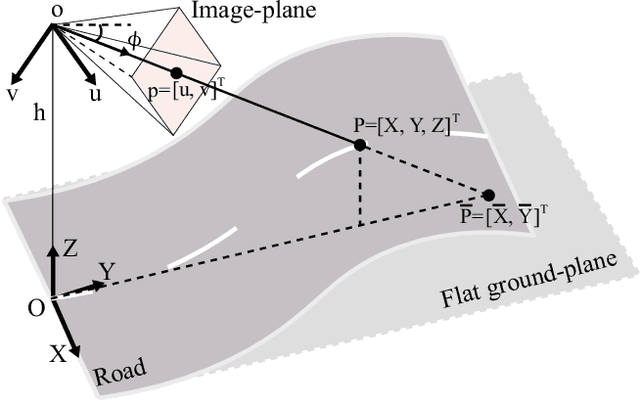
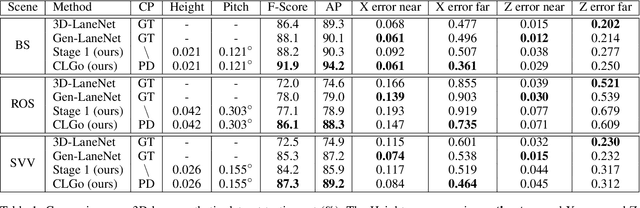
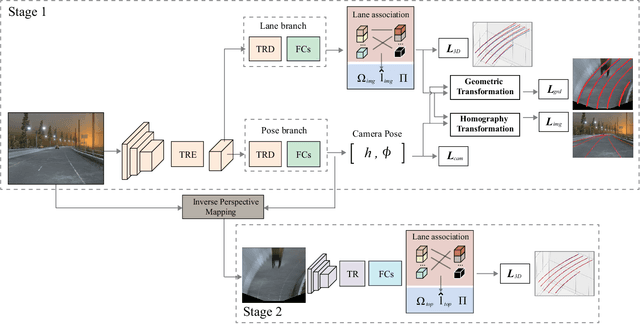
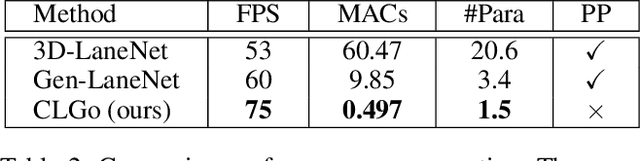
Abstract:Detecting 3D lanes from the camera is a rising problem for autonomous vehicles. In this task, the correct camera pose is the key to generating accurate lanes, which can transform an image from perspective-view to the top-view. With this transformation, we can get rid of the perspective effects so that 3D lanes would look similar and can accurately be fitted by low-order polynomials. However, mainstream 3D lane detectors rely on perfect camera poses provided by other sensors, which is expensive and encounters multi-sensor calibration issues. To overcome this problem, we propose to predict 3D lanes by estimating camera pose from a single image with a two-stage framework. The first stage aims at the camera pose task from perspective-view images. To improve pose estimation, we introduce an auxiliary 3D lane task and geometry constraints to benefit from multi-task learning, which enhances consistencies between 3D and 2D, as well as compatibility in the above two tasks. The second stage targets the 3D lane task. It uses previously estimated pose to generate top-view images containing distance-invariant lane appearances for predicting accurate 3D lanes. Experiments demonstrate that, without ground truth camera pose, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art perfect-camera-pose-based methods and has the fewest parameters and computations. Codes are available at https://github.com/liuruijin17/CLGo.
End-to-end Lane Shape Prediction with Transformers
Nov 09, 2020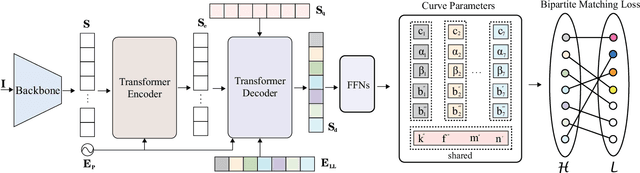
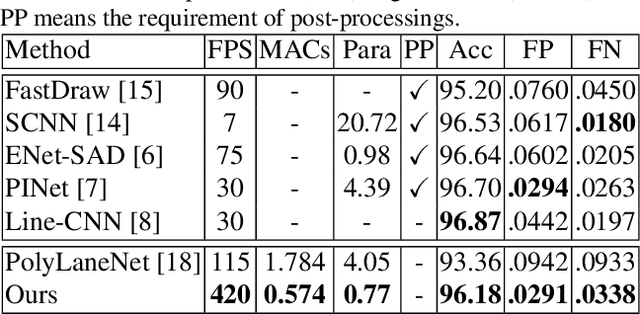
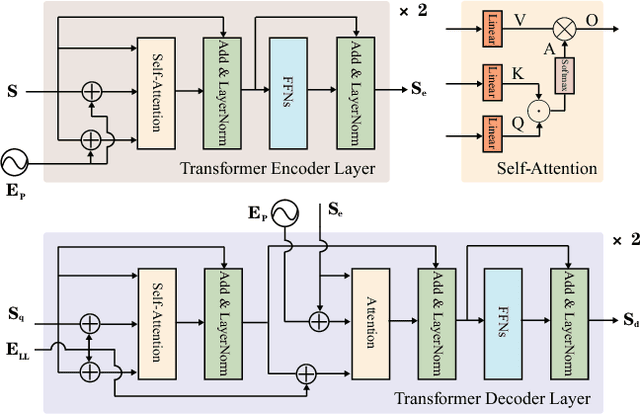
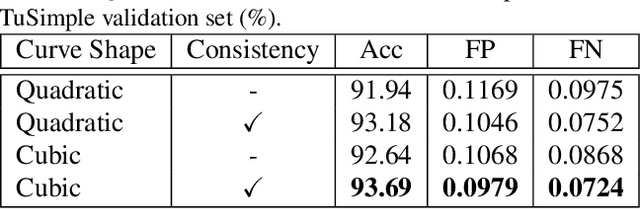
Abstract:Lane detection, the process of identifying lane markings as approximated curves, is widely used for lane departure warning and adaptive cruise control in autonomous vehicles. The popular pipeline that solves it in two steps---feature extraction plus post-processing, while useful, is too inefficient and flawed in learning the global context and lanes' long and thin structures. To tackle these issues, we propose an end-to-end method that directly outputs parameters of a lane shape model, using a network built with a transformer to learn richer structures and context. The lane shape model is formulated based on road structures and camera pose, providing physical interpretation for parameters of network output. The transformer models non-local interactions with a self-attention mechanism to capture slender structures and global context. The proposed method is validated on the TuSimple benchmark and shows state-of-the-art accuracy with the most lightweight model size and fastest speed. Additionally, our method shows excellent adaptability to a challenging self-collected lane detection dataset, showing its powerful deployment potential in real applications. Codes are available at https://github.com/liuruijin17/LSTR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge