Minsik Cho
SpecMD: A Comprehensive Study On Speculative Expert Prefetching
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models enable sparse expert activation, meaning that only a subset of the model's parameters is used during each inference. However, to translate this sparsity into practical performance, an expert caching mechanism is required. Previous works have proposed hardware-centric caching policies, but how these various caching policies interact with each other and different hardware specification remains poorly understood. To address this gap, we develop \textbf{SpecMD}, a standardized framework for benchmarking ad-hoc cache policies on various hardware configurations. Using SpecMD, we perform an exhaustive benchmarking of several MoE caching strategies, reproducing and extending prior approaches in controlled settings with realistic constraints. Our experiments reveal that MoE expert access is not consistent with temporal locality assumptions (e.g LRU, LFU). Motivated by this observation, we propose \textbf{Least-Stale}, a novel eviction policy that exploits MoE's predictable expert access patterns to reduce collision misses by up to $85\times$ over LRU. With such gains, we achieve over $88\%$ hit rates with up to $34.7\%$ Time-to-first-token (TTFT) reduction on OLMoE at only $5\%$ or $0.6GB$ of VRAM cache capacity.
MemoryLLM: Plug-n-Play Interpretable Feed-Forward Memory for Transformers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Understanding how transformer components operate in LLMs is important, as it is at the core of recent technological advances in artificial intelligence. In this work, we revisit the challenges associated with interpretability of feed-forward modules (FFNs) and propose MemoryLLM, which aims to decouple FFNs from self-attention and enables us to study the decoupled FFNs as context-free token-wise neural retrieval memory. In detail, we investigate how input tokens access memory locations within FFN parameters and the importance of FFN memory across different downstream tasks. MemoryLLM achieves context-free FFNs by training them in isolation from self-attention directly using the token embeddings. This approach allows FFNs to be pre-computed as token-wise lookups (ToLs), enabling on-demand transfer between VRAM and storage, additionally enhancing inference efficiency. We also introduce Flex-MemoryLLM, positioning it between a conventional transformer design and MemoryLLM. This architecture bridges the performance gap caused by training FFNs with context-free token-wise embeddings.
Your LLM Knows the Future: Uncovering Its Multi-Token Prediction Potential
Jul 16, 2025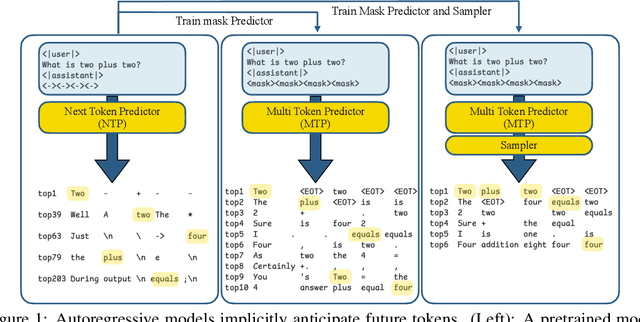
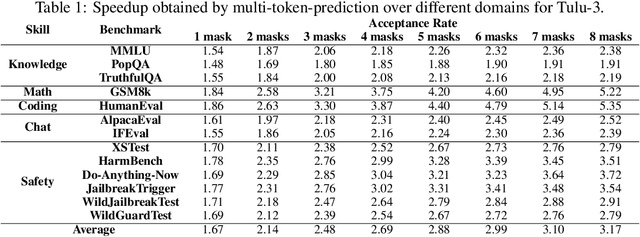
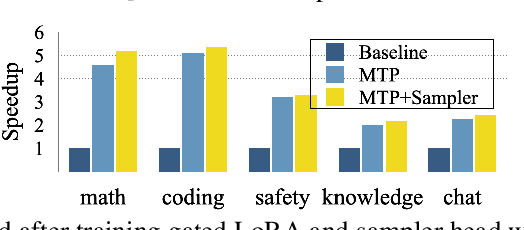
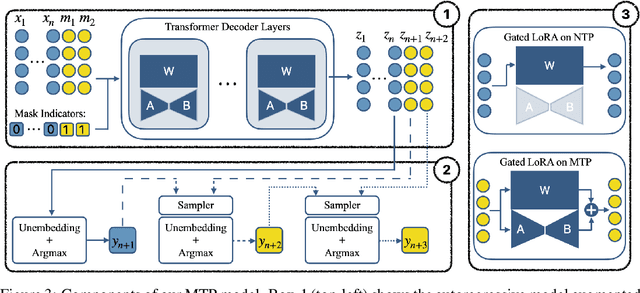
Abstract:Autoregressive language models are constrained by their inherently sequential nature, generating one token at a time. This paradigm limits inference speed and parallelism, especially during later stages of generation when the direction and semantics of text are relatively certain. In this work, we propose a novel framework that leverages the inherent knowledge of vanilla autoregressive language models about future tokens, combining techniques to realize this potential and enable simultaneous prediction of multiple subsequent tokens. Our approach introduces several key innovations: (1) a masked-input formulation where multiple future tokens are jointly predicted from a common prefix; (2) a gated LoRA formulation that preserves the original LLM's functionality, while equipping it for multi-token prediction; (3) a lightweight, learnable sampler module that generates coherent sequences from the predicted future tokens; (4) a set of auxiliary training losses, including a consistency loss, to enhance the coherence and accuracy of jointly generated tokens; and (5) a speculative generation strategy that expands tokens quadratically in the future while maintaining high fidelity. Our method achieves significant speedups through supervised fine-tuning on pretrained models. For example, it generates code and math nearly 5x faster, and improves general chat and knowledge tasks by almost 2.5x. These gains come without any loss in quality.
SPD: Sync-Point Drop for efficient tensor parallelism of Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:With the rapid expansion in the scale of large language models (LLMs), enabling efficient distributed inference across multiple computing units has become increasingly critical. However, communication overheads from popular distributed inference techniques such as Tensor Parallelism pose a significant challenge to achieve scalability and low latency. Therefore, we introduce a novel optimization technique, Sync-Point Drop (SPD), to reduce communication overheads in tensor parallelism by selectively dropping synchronization on attention outputs. In detail, we first propose a block design that allows execution to proceed without communication through SPD. Second, we apply different SPD strategies to attention blocks based on their sensitivity to the model accuracy. The proposed methods effectively alleviate communication bottlenecks while minimizing accuracy degradation during LLM inference, offering a scalable solution for diverse distributed environments: SPD offered about 20% overall inference latency reduction with < 1% accuracy regression for LLaMA2-70B inference over 8 GPUs.
From Dense to Dynamic: Token-Difficulty Driven MoEfication of Pre-Trained LLMs
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Training large language models (LLMs) for different inference constraints is computationally expensive, limiting control over efficiency-accuracy trade-offs. Moreover, once trained, these models typically process tokens uniformly, regardless of their complexity, leading to static and inflexible behavior. In this paper, we introduce a post-training optimization framework, DynaMoE, that adapts a pre-trained dense LLM to a token-difficulty-driven Mixture-of-Experts model with minimal fine-tuning cost. This adaptation makes the model dynamic, with sensitivity control to customize the balance between efficiency and accuracy. DynaMoE features a token-difficulty-aware router that predicts the difficulty of tokens and directs them to the appropriate sub-networks or experts, enabling larger experts to handle more complex tokens and smaller experts to process simpler ones. Our experiments demonstrate that DynaMoE can generate a range of adaptive model variants of the existing trained LLM with a single fine-tuning step, utilizing only $10B$ tokens, a minimal cost compared to the base model's training. Each variant offers distinct trade-offs between accuracy and performance. Compared to the baseline post-training optimization framework, Flextron, our method achieves similar aggregated accuracy across downstream tasks, despite using only $\frac{1}{9}\text{th}$ of their fine-tuning cost.
Towards Low-bit Communication for Tensor Parallel LLM Inference
Nov 12, 2024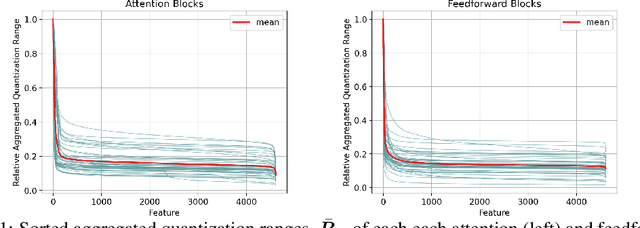
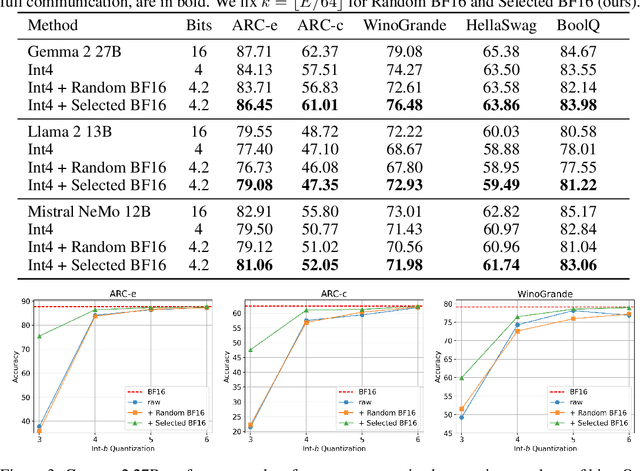

Abstract:Tensor parallelism provides an effective way to increase server large language model (LLM) inference efficiency despite adding an additional communication cost. However, as server LLMs continue to scale in size, they will need to be distributed across more devices, magnifying the communication cost. One way to approach this problem is with quantization, but current methods for LLMs tend to avoid quantizing the features that tensor parallelism needs to communicate. Taking advantage of consistent outliers in communicated features, we introduce a quantization method that reduces communicated values on average from 16 bits to 4.2 bits while preserving nearly all of the original performance. For instance, our method maintains around 98.0% and 99.5% of Gemma 2 27B's and Llama 2 13B's original performance, respectively, averaged across all tasks we evaluated on.
Apple Intelligence Foundation Language Models
Jul 29, 2024
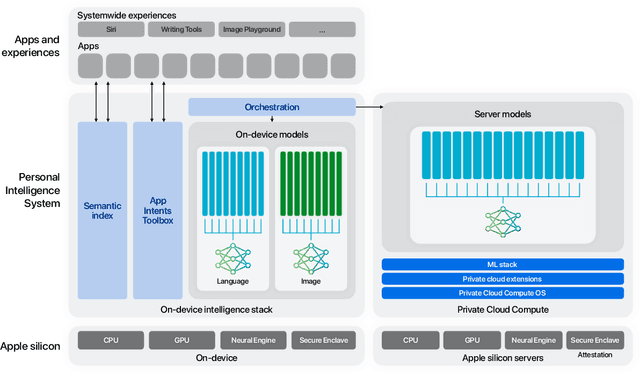


Abstract:We present foundation language models developed to power Apple Intelligence features, including a ~3 billion parameter model designed to run efficiently on devices and a large server-based language model designed for Private Cloud Compute. These models are designed to perform a wide range of tasks efficiently, accurately, and responsibly. This report describes the model architecture, the data used to train the model, the training process, how the models are optimized for inference, and the evaluation results. We highlight our focus on Responsible AI and how the principles are applied throughout the model development.
LazyLLM: Dynamic Token Pruning for Efficient Long Context LLM Inference
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:The inference of transformer-based large language models consists of two sequential stages: 1) a prefilling stage to compute the KV cache of prompts and generate the first token, and 2) a decoding stage to generate subsequent tokens. For long prompts, the KV cache must be computed for all tokens during the prefilling stage, which can significantly increase the time needed to generate the first token. Consequently, the prefilling stage may become a bottleneck in the generation process. An open question remains whether all prompt tokens are essential for generating the first token. To answer this, we introduce a novel method, LazyLLM, that selectively computes the KV for tokens important for the next token prediction in both the prefilling and decoding stages. Contrary to static pruning approaches that prune the prompt at once, LazyLLM allows language models to dynamically select different subsets of tokens from the context in different generation steps, even though they might be pruned in previous steps. Extensive experiments on standard datasets across various tasks demonstrate that LazyLLM is a generic method that can be seamlessly integrated with existing language models to significantly accelerate the generation without fine-tuning. For instance, in the multi-document question-answering task, LazyLLM accelerates the prefilling stage of the LLama 2 7B model by 2.34x while maintaining accuracy.
KV-Runahead: Scalable Causal LLM Inference by Parallel Key-Value Cache Generation
May 08, 2024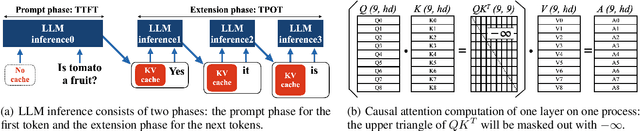

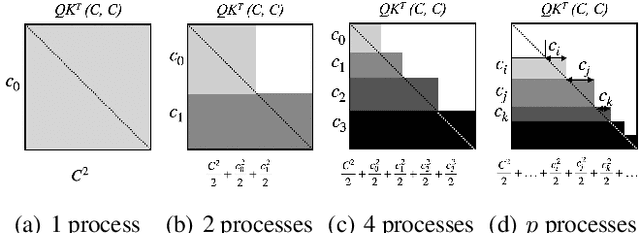
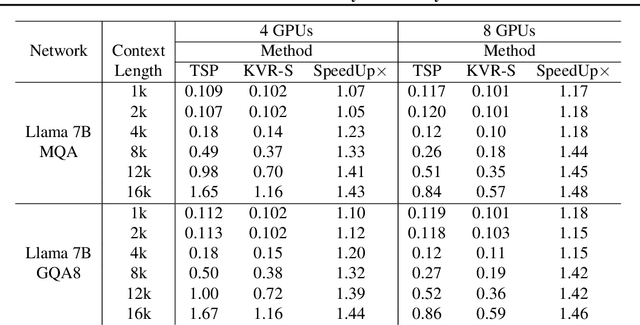
Abstract:Large Language Model or LLM inference has two phases, the prompt (or prefill) phase to output the first token and the extension (or decoding) phase to the generate subsequent tokens. In this work, we propose an efficient parallelization scheme, KV-Runahead to accelerate the prompt phase. The key observation is that the extension phase generates tokens faster than the prompt phase because of key-value cache (KV-cache). Hence, KV-Runahead parallelizes the prompt phase by orchestrating multiple processes to populate the KV-cache and minimizes the time-to-first-token (TTFT). Dual-purposing the KV-cache scheme has two main benefits. Fist, since KV-cache is designed to leverage the causal attention map, we minimize computation and computation automatically. Second, since it already exists for the extension phase, KV-Runahead is easy to implement. We further propose context-level load-balancing to handle uneven KV-cache generation (due to the causal attention) and to optimize TTFT. Compared with an existing parallelization scheme such as tensor or sequential parallelization where keys and values are locally generated and exchanged via all-gather collectives, our experimental results demonstrate that KV-Runahead can offer over 1.4x and 1.6x speedups for Llama 7B and Falcon 7B respectively.
LLM in a flash: Efficient Large Language Model Inference with Limited Memory
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are central to modern natural language processing, delivering exceptional performance in various tasks. However, their intensive computational and memory requirements present challenges, especially for devices with limited DRAM capacity. This paper tackles the challenge of efficiently running LLMs that exceed the available DRAM capacity by storing the model parameters on flash memory but bringing them on demand to DRAM. Our method involves constructing an inference cost model that harmonizes with the flash memory behavior, guiding us to optimize in two critical areas: reducing the volume of data transferred from flash and reading data in larger, more contiguous chunks. Within this flash memory-informed framework, we introduce two principal techniques. First, "windowing'" strategically reduces data transfer by reusing previously activated neurons, and second, "row-column bundling", tailored to the sequential data access strengths of flash memory, increases the size of data chunks read from flash memory. These methods collectively enable running models up to twice the size of the available DRAM, with a 4-5x and 20-25x increase in inference speed compared to naive loading approaches in CPU and GPU, respectively. Our integration of sparsity awareness, context-adaptive loading, and a hardware-oriented design paves the way for effective inference of LLMs on devices with limited memory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge