Mvtec 3D Ad
Papers and Code
Is Training Necessary for Anomaly Detection?
Jan 30, 2026Current state-of-the-art multi-class unsupervised anomaly detection (MUAD) methods rely on training encoder-decoder models to reconstruct anomaly-free features. We first show these approaches have an inherent fidelity-stability dilemma in how they detect anomalies via reconstruction residuals. We then abandon the reconstruction paradigm entirely and propose Retrieval-based Anomaly Detection (RAD). RAD is a training-free approach that stores anomaly-free features in a memory and detects anomalies through multi-level retrieval, matching test patches against the memory. Experiments demonstrate that RAD achieves state-of-the-art performance across four established benchmarks (MVTec-AD, VisA, Real-IAD, 3D-ADAM) under both standard and few-shot settings. On MVTec-AD, RAD reaches 96.7\% Pixel AUROC with just a single anomaly-free image compared to 98.5\% of RAD's full-data performance. We further prove that retrieval-based scores theoretically upper-bound reconstruction-residual scores. Collectively, these findings overturn the assumption that MUAD requires task-specific training, showing that state-of-the-art anomaly detection is feasible with memory-based retrieval. Our code is available at https://github.com/longkukuhi/RAD.
Commonality in Few: Few-Shot Multimodal Anomaly Detection via Hypergraph-Enhanced Memory
Nov 16, 2025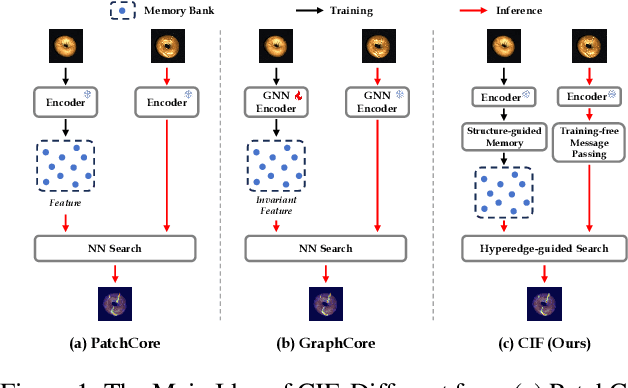
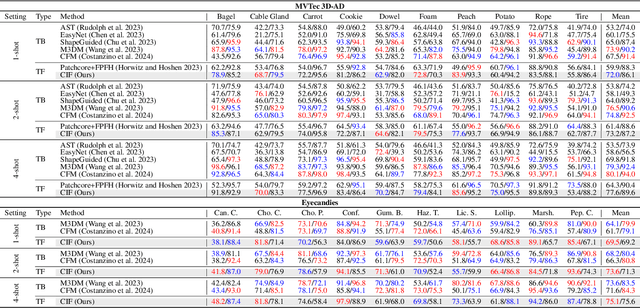
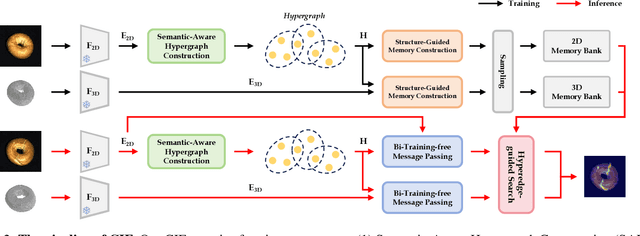

Few-shot multimodal industrial anomaly detection is a critical yet underexplored task, offering the ability to quickly adapt to complex industrial scenarios. In few-shot settings, insufficient training samples often fail to cover the diverse patterns present in test samples. This challenge can be mitigated by extracting structural commonality from a small number of training samples. In this paper, we propose a novel few-shot unsupervised multimodal industrial anomaly detection method based on structural commonality, CIF (Commonality In Few). To extract intra-class structural information, we employ hypergraphs, which are capable of modeling higher-order correlations, to capture the structural commonality within training samples, and use a memory bank to store this intra-class structural prior. Firstly, we design a semantic-aware hypergraph construction module tailored for single-semantic industrial images, from which we extract common structures to guide the construction of the memory bank. Secondly, we use a training-free hypergraph message passing module to update the visual features of test samples, reducing the distribution gap between test features and features in the memory bank. We further propose a hyperedge-guided memory search module, which utilizes structural information to assist the memory search process and reduce the false positive rate. Experimental results on the MVTec 3D-AD dataset and the Eyecandies dataset show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in few-shot settings. Code is available at https://github.com/Sunny5250/CIF.
MuSc-V2: Zero-Shot Multimodal Industrial Anomaly Classification and Segmentation with Mutual Scoring of Unlabeled Samples
Nov 13, 2025Zero-shot anomaly classification (AC) and segmentation (AS) methods aim to identify and outline defects without using any labeled samples. In this paper, we reveal a key property that is overlooked by existing methods: normal image patches across industrial products typically find many other similar patches, not only in 2D appearance but also in 3D shapes, while anomalies remain diverse and isolated. To explicitly leverage this discriminative property, we propose a Mutual Scoring framework (MuSc-V2) for zero-shot AC/AS, which flexibly supports single 2D/3D or multimodality. Specifically, our method begins by improving 3D representation through Iterative Point Grouping (IPG), which reduces false positives from discontinuous surfaces. Then we use Similarity Neighborhood Aggregation with Multi-Degrees (SNAMD) to fuse 2D/3D neighborhood cues into more discriminative multi-scale patch features for mutual scoring. The core comprises a Mutual Scoring Mechanism (MSM) that lets samples within each modality to assign score to each other, and Cross-modal Anomaly Enhancement (CAE) that fuses 2D and 3D scores to recover modality-specific missing anomalies. Finally, Re-scoring with Constrained Neighborhood (RsCon) suppresses false classification based on similarity to more representative samples. Our framework flexibly works on both the full dataset and smaller subsets with consistently robust performance, ensuring seamless adaptability across diverse product lines. In aid of the novel framework, MuSc-V2 achieves significant performance improvements: a $\textbf{+23.7\%}$ AP gain on the MVTec 3D-AD dataset and a $\textbf{+19.3\%}$ boost on the Eyecandies dataset, surpassing previous zero-shot benchmarks and even outperforming most few-shot methods. The code will be available at The code will be available at \href{https://github.com/HUST-SLOW/MuSc-V2}{https://github.com/HUST-SLOW/MuSc-V2}.
Single-Step Reconstruction-Free Anomaly Detection and Segmentation via Diffusion Models
Aug 06, 2025Generative models have demonstrated significant success in anomaly detection and segmentation over the past decade. Recently, diffusion models have emerged as a powerful alternative, outperforming previous approaches such as GANs and VAEs. In typical diffusion-based anomaly detection, a model is trained on normal data, and during inference, anomalous images are perturbed to a predefined intermediate step in the forward diffusion process. The corresponding normal image is then reconstructed through iterative reverse sampling. However, reconstruction-based approaches present three major challenges: (1) the reconstruction process is computationally expensive due to multiple sampling steps, making real-time applications impractical; (2) for complex or subtle patterns, the reconstructed image may correspond to a different normal pattern rather than the original input; and (3) Choosing an appropriate intermediate noise level is challenging because it is application-dependent and often assumes prior knowledge of anomalies, an assumption that does not hold in unsupervised settings. We introduce Reconstruction-free Anomaly Detection with Attention-based diffusion models in Real-time (RADAR), which overcomes the limitations of reconstruction-based anomaly detection. Unlike current SOTA methods that reconstruct the input image, RADAR directly produces anomaly maps from the diffusion model, improving both detection accuracy and computational efficiency. We evaluate RADAR on real-world 3D-printed material and the MVTec-AD dataset. Our approach surpasses state-of-the-art diffusion-based and statistical machine learning models across all key metrics, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Specifically, RADAR improves F1 score by 7% on MVTec-AD and 13% on the 3D-printed material dataset compared to the next best model. Code available at: https://github.com/mehrdadmoradi124/RADAR
Mentor3AD: Feature Reconstruction-based 3D Anomaly Detection via Multi-modality Mentor Learning
May 27, 2025Multimodal feature reconstruction is a promising approach for 3D anomaly detection, leveraging the complementary information from dual modalities. We further advance this paradigm by utilizing multi-modal mentor learning, which fuses intermediate features to further distinguish normal from feature differences. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method called Mentor3AD, which utilizes multi-modal mentor learning. By leveraging the shared features of different modalities, Mentor3AD can extract more effective features and guide feature reconstruction, ultimately improving detection performance. Specifically, Mentor3AD includes a Mentor of Fusion Module (MFM) that merges features extracted from RGB and 3D modalities to create a mentor feature. Additionally, we have designed a Mentor of Guidance Module (MGM) to facilitate cross-modal reconstruction, supported by the mentor feature. Lastly, we introduce a Voting Module (VM) to more accurately generate the final anomaly score. Extensive comparative and ablation studies on MVTec 3D-AD and Eyecandies have verified the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Boosting Global-Local Feature Matching via Anomaly Synthesis for Multi-Class Point Cloud Anomaly Detection
May 12, 2025Point cloud anomaly detection is essential for various industrial applications. The huge computation and storage costs caused by the increasing product classes limit the application of single-class unsupervised methods, necessitating the development of multi-class unsupervised methods. However, the feature similarity between normal and anomalous points from different class data leads to the feature confusion problem, which greatly hinders the performance of multi-class methods. Therefore, we introduce a multi-class point cloud anomaly detection method, named GLFM, leveraging global-local feature matching to progressively separate data that are prone to confusion across multiple classes. Specifically, GLFM is structured into three stages: Stage-I proposes an anomaly synthesis pipeline that stretches point clouds to create abundant anomaly data that are utilized to adapt the point cloud feature extractor for better feature representation. Stage-II establishes the global and local memory banks according to the global and local feature distributions of all the training data, weakening the impact of feature confusion on the establishment of the memory bank. Stage-III implements anomaly detection of test data leveraging its feature distance from global and local memory banks. Extensive experiments on the MVTec 3D-AD, Real3D-AD and actual industry parts dataset showcase our proposed GLFM's superior point cloud anomaly detection performance. The code is available at https://github.com/hustCYQ/GLFM-Multi-class-3DAD.
G$^{2}$SF-MIAD: Geometry-Guided Score Fusion for Multimodal Industrial Anomaly Detection
Mar 13, 2025



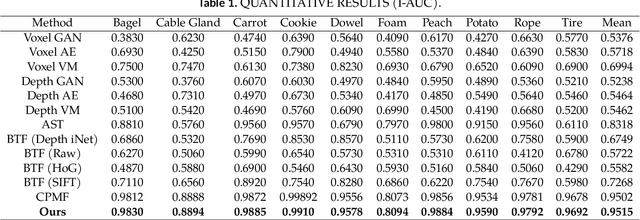
Industrial quality inspection plays a critical role in modern manufacturing by identifying defective products during production. While single-modality approaches using either 3D point clouds or 2D RGB images suffer from information incompleteness, multimodal anomaly detection offers promise through the complementary fusion of crossmodal data. However, existing methods face challenges in effectively integrating unimodal results and improving discriminative power. To address these limitations, we first reinterpret memory bank-based anomaly scores in single modalities as isotropic Euclidean distances in local feature spaces. Dynamically evolving from Eulidean metrics, we propose a novel \underline{G}eometry-\underline{G}uided \underline{S}core \underline{F}usion (G$^{2}$SF) framework that progressively learns an anisotropic local distance metric as a unified score for the fusion task. Through a geometric encoding operator, a novel Local Scale Prediction Network (LSPN) is proposed to predict direction-aware scaling factors that characterize first-order local feature distributions, thereby enhancing discrimination between normal and anomalous patterns. Additionally, we develop specialized loss functions and score aggregation strategy from geometric priors to ensure both metric generalization and efficacy. Comprehensive evaluations on the MVTec-3D AD dataset demonstrate the state-of-the-art detection performance of our method with low positive rate and better recall, which is essential in industrial application, and detailed ablation analysis validates each component's contribution.
Optimized CNNs for Rapid 3D Point Cloud Object Recognition
Dec 03, 2024

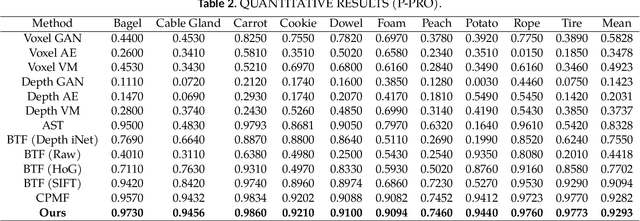
This study introduces a method for efficiently detecting objects within 3D point clouds using convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Our approach adopts a unique feature-centric voting mechanism to construct convolutional layers that capitalize on the typical sparsity observed in input data. We explore the trade-off between accuracy and speed across diverse network architectures and advocate for integrating an $\mathcal{L}_1$ penalty on filter activations to augment sparsity within intermediate layers. This research pioneers the proposal of sparse convolutional layers combined with $\mathcal{L}_1$ regularization to effectively handle large-scale 3D data processing. Our method's efficacy is demonstrated on the MVTec 3D-AD object detection benchmark. The Vote3Deep models, with just three layers, outperform the previous state-of-the-art in both laser-only approaches and combined laser-vision methods. Additionally, they maintain competitive processing speeds. This underscores our approach's capability to substantially enhance detection performance while ensuring computational efficiency suitable for real-time applications.
SeaS: Few-shot Industrial Anomaly Image Generation with Separation and Sharing Fine-tuning
Oct 19, 2024



Current segmentation methods require many training images and precise masks, while insufficient anomaly images hinder their application in industrial scenarios. To address such an issue, we explore producing diverse anomalies and accurate pixel-wise annotations. By observing the real production lines, we find that anomalies vary randomly in shape and appearance, whereas products hold globally consistent patterns with slight local variations. Such a characteristic inspires us to develop a Separation and Sharing Fine-tuning (SeaS) approach using only a few abnormal and some normal images. Firstly, we propose the Unbalanced Abnormal (UA) Text Prompt tailored to industrial anomaly generation, consisting of one product token and several anomaly tokens. Then, for anomaly images, we propose a Decoupled Anomaly Alignment (DA) loss to bind the attributes of the anomalies to different anomaly tokens. Re-blending such attributes may produce never-seen anomalies, achieving a high diversity of anomalies. For normal images, we propose a Normal-image Alignment (NA) loss to learn the products' key features that are used to synthesize products with both global consistency and local variations. The two training processes are separated but conducted on a shared U-Net. Finally, SeaS produces high-fidelity annotations for the generated anomalies by fusing discriminative features of U-Net and high-resolution VAE features. Extensive evaluations on the challenging MVTec AD and MVTec 3D AD dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. For anomaly image generation, we achieve 1.88 on IS and 0.34 on IC-LPIPS on MVTec AD dataset, 1.95 on IS and 0.30 on IC-LPIPS on MVTec 3D AD dataset. For downstream task, using our generated anomaly image-mask pairs, three common segmentation methods achieve an average 11.17% improvement on IoU on MVTec AD dataset, and a 15.49% enhancement in IoU on MVTec 3D AD dataset.
DAS3D: Dual-modality Anomaly Synthesis for 3D Anomaly Detection
Oct 13, 2024



Synthesizing anomaly samples has proven to be an effective strategy for self-supervised 2D industrial anomaly detection. However, this approach has been rarely explored in multi-modality anomaly detection, particularly involving 3D and RGB images. In this paper, we propose a novel dual-modality augmentation method for 3D anomaly synthesis, which is simple and capable of mimicking the characteristics of 3D defects. Incorporating with our anomaly synthesis method, we introduce a reconstruction-based discriminative anomaly detection network, in which a dual-modal discriminator is employed to fuse the original and reconstructed embedding of two modalities for anomaly detection. Additionally, we design an augmentation dropout mechanism to enhance the generalizability of the discriminator. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on detection precision and achieves competitive segmentation performance on both MVTec 3D-AD and Eyescandies datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge