EEG–fNIRS
Papers and Code
Cedalion Tutorial: A Python-based framework for comprehensive analysis of multimodal fNIRS & DOT from the lab to the everyday world
Jan 09, 2026Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and diffuse optical tomography (DOT) are rapidly evolving toward wearable, multimodal, and data-driven, AI-supported neuroimaging in the everyday world. However, current analytical tools are fragmented across platforms, limiting reproducibility, interoperability, and integration with modern machine learning (ML) workflows. Cedalion is a Python-based open-source framework designed to unify advanced model-based and data-driven analysis of multimodal fNIRS and DOT data within a reproducible, extensible, and community-driven environment. Cedalion integrates forward modelling, photogrammetric optode co-registration, signal processing, GLM Analysis, DOT image reconstruction, and ML-based data-driven methods within a single standardized architecture based on the Python ecosystem. It adheres to SNIRF and BIDS standards, supports cloud-executable Jupyter notebooks, and provides containerized workflows for scalable, fully reproducible analysis pipelines that can be provided alongside original research publications. Cedalion connects established optical-neuroimaging pipelines with ML frameworks such as scikit-learn and PyTorch, enabling seamless multimodal fusion with EEG, MEG, and physiological data. It implements validated algorithms for signal-quality assessment, motion correction, GLM modelling, and DOT reconstruction, complemented by modules for simulation, data augmentation, and multimodal physiology analysis. Automated documentation links each method to its source publication, and continuous-integration testing ensures robustness. This tutorial paper provides seven fully executable notebooks that demonstrate core features. Cedalion offers an open, transparent, and community extensible foundation that supports reproducible, scalable, cloud- and ML-ready fNIRS/DOT workflows for laboratory-based and real-world neuroimaging.
NeuroCLIP: A Multimodal Contrastive Learning Method for rTMS-treated Methamphetamine Addiction Analysis
Jul 27, 2025Methamphetamine dependence poses a significant global health challenge, yet its assessment and the evaluation of treatments like repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) frequently depend on subjective self-reports, which may introduce uncertainties. While objective neuroimaging modalities such as electroencephalography (EEG) and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) offer alternatives, their individual limitations and the reliance on conventional, often hand-crafted, feature extraction can compromise the reliability of derived biomarkers. To overcome these limitations, we propose NeuroCLIP, a novel deep learning framework integrating simultaneously recorded EEG and fNIRS data through a progressive learning strategy. This approach offers a robust and trustworthy biomarker for methamphetamine addiction. Validation experiments show that NeuroCLIP significantly improves discriminative capabilities among the methamphetamine-dependent individuals and healthy controls compared to models using either EEG or only fNIRS alone. Furthermore, the proposed framework facilitates objective, brain-based evaluation of rTMS treatment efficacy, demonstrating measurable shifts in neural patterns towards healthy control profiles after treatment. Critically, we establish the trustworthiness of the multimodal data-driven biomarker by showing its strong correlation with psychometrically validated craving scores. These findings suggest that biomarker derived from EEG-fNIRS data via NeuroCLIP offers enhanced robustness and reliability over single-modality approaches, providing a valuable tool for addiction neuroscience research and potentially improving clinical assessments.
NeuGPT: Unified multi-modal Neural GPT
Oct 28, 2024This paper introduces NeuGPT, a groundbreaking multi-modal language generation model designed to harmonize the fragmented landscape of neural recording research. Traditionally, studies in the field have been compartmentalized by signal type, with EEG, MEG, ECoG, SEEG, fMRI, and fNIRS data being analyzed in isolation. Recognizing the untapped potential for cross-pollination and the adaptability of neural signals across varying experimental conditions, we set out to develop a unified model capable of interfacing with multiple modalities. Drawing inspiration from the success of pre-trained large models in NLP, computer vision, and speech processing, NeuGPT is architected to process a diverse array of neural recordings and interact with speech and text data. Our model mainly focus on brain-to-text decoding, improving SOTA from 6.94 to 12.92 on BLEU-1 and 6.93 to 13.06 on ROUGE-1F. It can also simulate brain signals, thereby serving as a novel neural interface. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/NeuSpeech/NeuGPT}{NeuSpeech/NeuGPT (https://github.com/NeuSpeech/NeuGPT) .}
SCDM: Unified Representation Learning for EEG-to-fNIRS Cross-Modal Generation in MI-BCIs
Jul 01, 2024Hybrid motor imagery brain-computer interfaces (MI-BCIs), which integrate both electroencephalography (EEG) and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) signals, outperform those based solely on EEG. However, simultaneously recording EEG and fNIRS signals is highly challenging due to the difficulty of colocating both types of sensors on the same scalp surface. This physical constraint complicates the acquisition of high-quality hybrid signals, thereby limiting the widespread application of hybrid MI-BCIs. To facilitate the acquisition of hybrid EEG-fNIRS signals, this study proposes the spatio-temporal controlled diffusion model (SCDM) as a framework for cross-modal generation from EEG to fNIRS. The model utilizes two core modules, the spatial cross-modal generation (SCG) module and the multi-scale temporal representation (MTR) module, which adaptively learn the respective latent temporal and spatial representations of both signals in a unified representation space. The SCG module further maps EEG representations to fNIRS representations by leveraging their spatial relationships. Experimental results show high similarity between synthetic and real fNIRS signals. The joint classification performance of EEG and synthetic fNIRS signals is comparable to or even better than that of EEG with real fNIRS signals. Furthermore, the synthetic signals exhibit similar spatio-temporal features to real signals while preserving spatial relationships with EEG signals. Experimental results suggest that the SCDM may represent a promising paradigm for the acquisition of hybrid EEG-fNIRS signals in MI-BCI systems.
Multimodal Physiological Signals Representation Learning via Multiscale Contrasting for Depression Recognition
Jun 26, 2024



Depression recognition based on physiological signals such as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and electroencephalogram (EEG) has made considerable progress. However, most existing studies ignore the complementarity and semantic consistency of multimodal physiological signals under the same stimulation task in complex spatio-temporal patterns. In this paper, we introduce a multimodal physiological signals representation learning framework using Siamese architecture via multiscale contrasting for depression recognition (MRLMC). First, fNIRS and EEG are transformed into different but correlated data based on a time-domain data augmentation strategy. Then, we design a spatio-temporal contrasting module to learn the representation of fNIRS and EEG through weight-sharing multiscale spatio-temporal convolution. Furthermore, to enhance the learning of semantic representation associated with stimulation tasks, a semantic consistency contrast module is proposed, aiming to maximize the semantic similarity of fNIRS and EEG. Extensive experiments on publicly available and self-collected multimodal physiological signals datasets indicate that MRLMC outperforms the state-of-the-art models. Moreover, our proposed framework is capable of transferring to multimodal time series downstream tasks.
Synthesizing Affective Neurophysiological Signals Using Generative Models: A Review Paper
Jun 05, 2023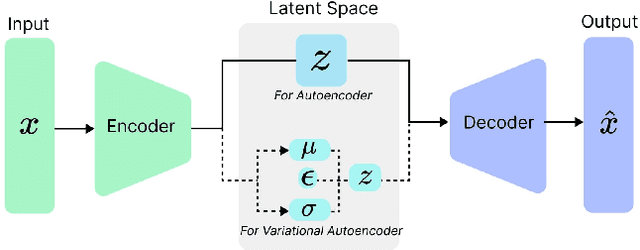

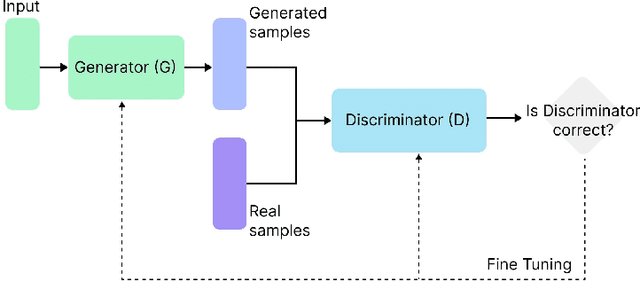
The integration of emotional intelligence in machines is an important step in advancing human-computer interaction. This demands the development of reliable end-to-end emotion recognition systems. However, the scarcity of public affective datasets presents a challenge. In this literature review, we emphasize the use of generative models to address this issue in neurophysiological signals, particularly Electroencephalogram (EEG) and Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS). We provide a comprehensive analysis of different generative models used in the field, examining their input formulation, deployment strategies, and methodologies for evaluating the quality of synthesized data. This review serves as a comprehensive overview, offering insights into the advantages, challenges, and promising future directions in the application of generative models in emotion recognition systems. Through this review, we aim to facilitate the progression of neurophysiological data augmentation, thereby supporting the development of more efficient and reliable emotion recognition systems.
Identification of Cognitive Workload during Surgical Tasks with Multimodal Deep Learning
Sep 12, 2022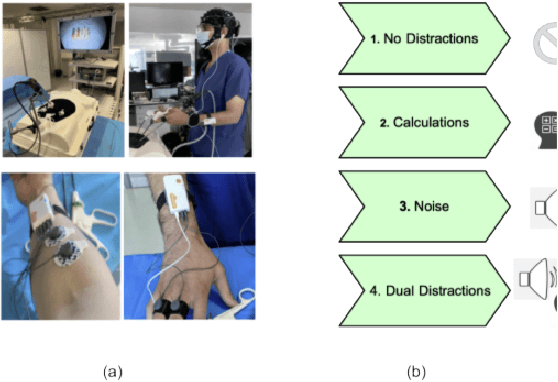
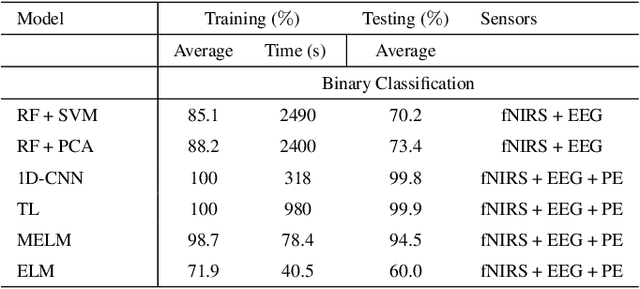
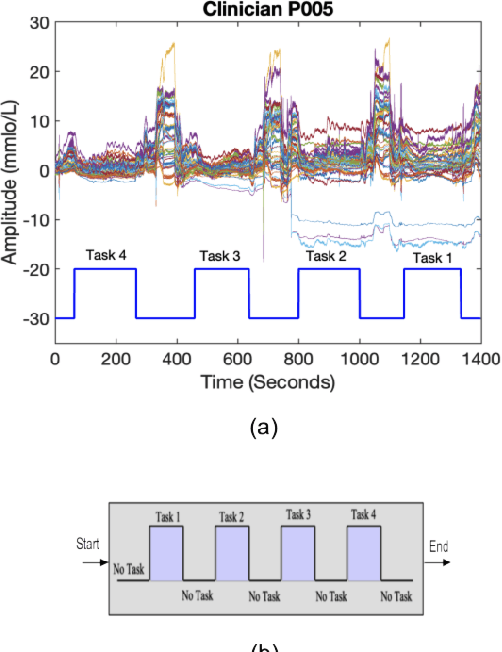
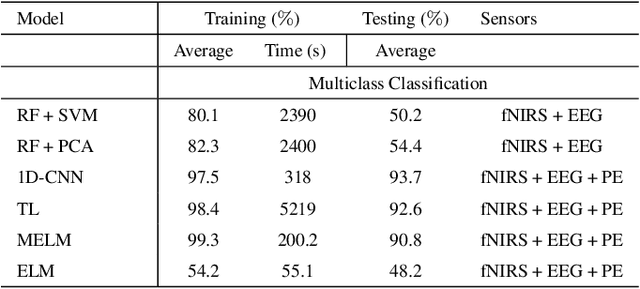
In operating Rooms (ORs), activities are usually different from other typical working environments. In particular, surgeons are frequently exposed to multiple psycho-organizational constraints that may cause negative repercussions on their health and performance. This is commonly attributed to an increase in the associated Cognitive Workload (CWL) that results from dealing with unexpected and repetitive tasks, as well as large amounts of information and potentially risky cognitive overload. In this paper, a cascade of two machine learning approaches is suggested for the multimodal recognition of CWL in a number of four different surgical tasks. First, a model based on the concept of transfer learning is used to identify if a surgeon is experiencing any CWL. Secondly, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) uses this information to identify different types of CWL associated to each surgical task. The suggested multimodal approach consider adjacent signals from electroencephalogram (EEG), functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and pupil eye diameter. The concatenation of signals allows complex correlations in terms of time (temporal) and channel location (spatial). Data collection is performed by a Multi-sensing AI Environment for Surgical Task $\&$ Role Optimisation platform (MAESTRO) developed at HARMS Lab. To compare the performance of the proposed methodology, a number of state-of-art machine learning techniques have been implemented. The tests show that the proposed model has a precision of 93%.
Motion Artifacts Correction from Single-Channel EEG and fNIRS Signals using Novel Wavelet Packet Decomposition in Combination with Canonical Correlation Analysis
Apr 09, 2022



The electroencephalogram (EEG) and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) signals, highly non-stationary in nature, greatly suffers from motion artifacts while recorded using wearable sensors. This paper proposes two robust methods: i) Wavelet packet decomposition (WPD), and ii) WPD in combination with canonical correlation analysis (WPD-CCA), for motion artifact correction from single-channel EEG and fNIRS signals. The efficacy of these proposed techniques is tested using a benchmark dataset and the performance of the proposed methods is measured using two well-established performance matrices: i) Difference in the signal to noise ratio ({\Delta}SNR) and ii) Percentage reduction in motion artifacts ({\eta}). The proposed WPD-based single-stage motion artifacts correction technique produces the highest average {\Delta}SNR (29.44 dB) when db2 wavelet packet is incorporated whereas the greatest average {\eta} (53.48%) is obtained using db1 wavelet packet for all the available 23 EEG recordings. Our proposed two-stage motion artifacts correction technique i.e. the WPD-CCA method utilizing db1 wavelet packet has shown the best denoising performance producing an average {\Delta}SNR and {\eta} values of 30.76 dB and 59.51%, respectively for all the EEG recordings. On the other hand, the two-stage motion artifacts removal technique i.e. WPD-CCA has produced the best average {\Delta}SNR (16.55 dB, utilizing db1 wavelet packet) and largest average {\eta} (41.40%, using fk8 wavelet packet). The highest average {\Delta}SNR and {\eta} using single-stage artifacts removal techniques (WPD) are found as 16.11 dB and 26.40%, respectively for all the fNIRS signals using fk4 wavelet packet. In both EEG and fNIRS modalities, the percentage reduction in motion artifacts increases by 11.28% and 56.82%, respectively when two-stage WPD-CCA techniques are employed.
Dyadic aggregated autoregressive (DASAR) model for time-frequency representation of biomedical signals
May 13, 2021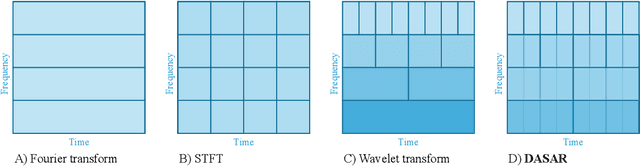
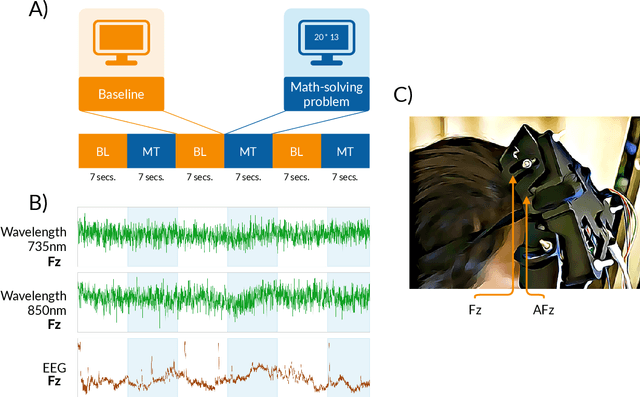
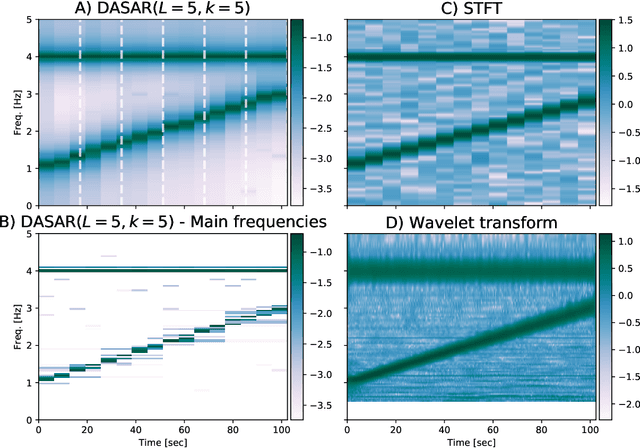
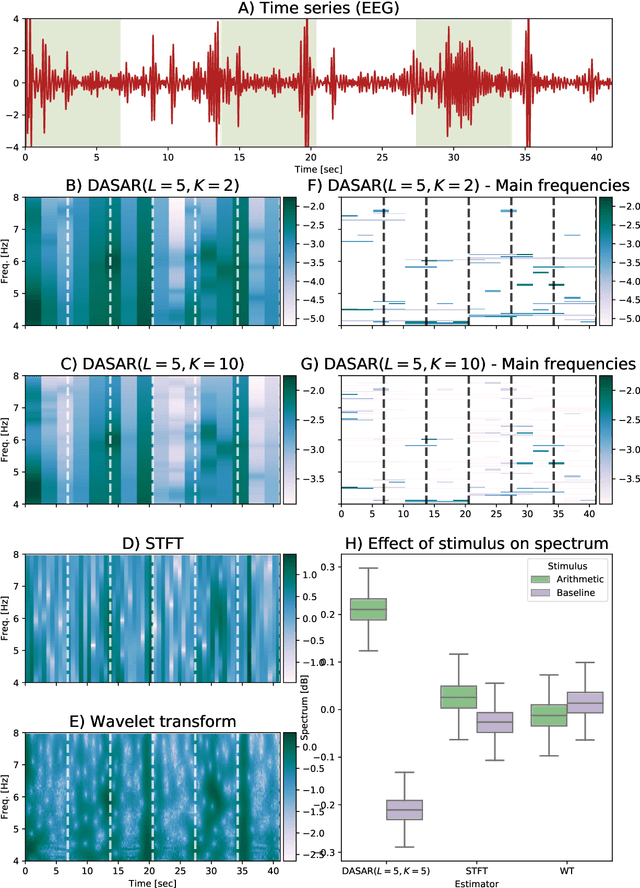
This paper introduces a new time-frequency representation method for biomedical signals: the dyadic aggregated autoregressive (DASAR) model. Signals, such as electroencephalograms (EEGs) and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), exhibit physiological information through time-evolving spectrum components at specific frequency intervals: 0-50 Hz (EEG) or 0-150 mHz (fNIRS). Spectrotemporal features in signals are conventionally estimated using short-time Fourier transform (STFT) and wavelet transform (WT). However, both methods may not offer the most robust or compact representation despite their widespread use in biomedical contexts. The presented method, DASAR, improves precise frequency identification and tracking of interpretable frequency components with a parsimonious set of parameters. DASAR achieves these characteristics by assuming that the biomedical time-varying spectrum comprises several independent stochastic oscillators with (piecewise) time-varying frequencies. Local stationarity can be assumed within dyadic subdivisions of the recordings, while the stochastic oscillators can be modeled with an aggregation of second-order autoregressive models (ASAR). DASAR can provide a more accurate representation of the (highly contrasted) EEG and fNIRS frequency ranges by increasing the estimation accuracy in user-defined spectrum region of interest (SROI). A mental arithmetic experiment on a hybrid EEG-fNIRS was conducted to assess the efficiency of the method. Our proposed technique, STFT, and WT were applied on both biomedical signals to discover potential oscillators that improve the discrimination between the task condition and its baseline. The results show that DASAR provided the highest spectrum differentiation and it was the only method that could identify Mayer waves as narrow-band artifacts at 97.4-97.5 mHz.
CNNATT: Deep EEG & fNIRS Real-Time Decoding of bimanual forces
Mar 23, 2021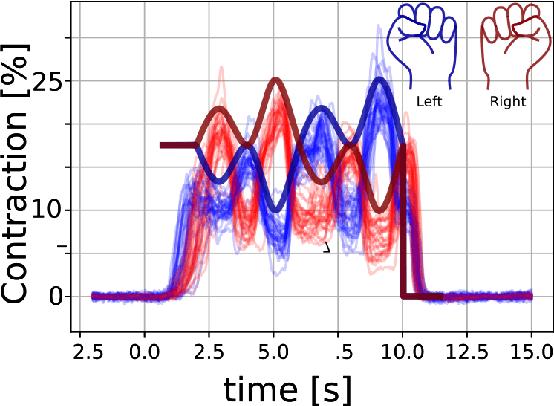
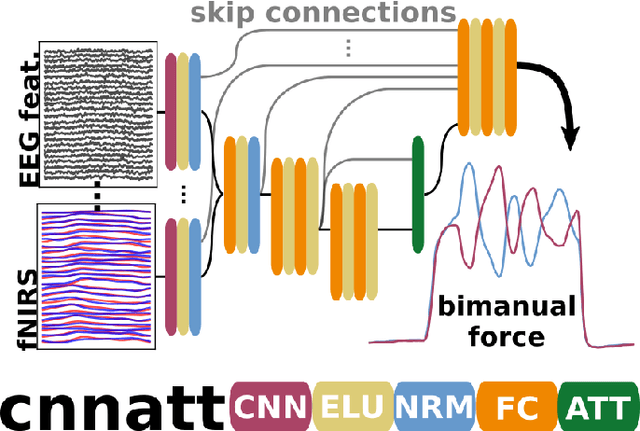
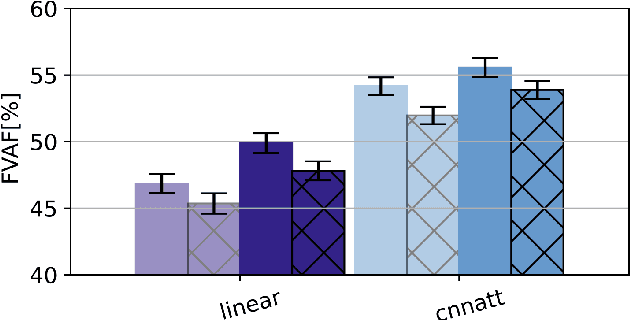
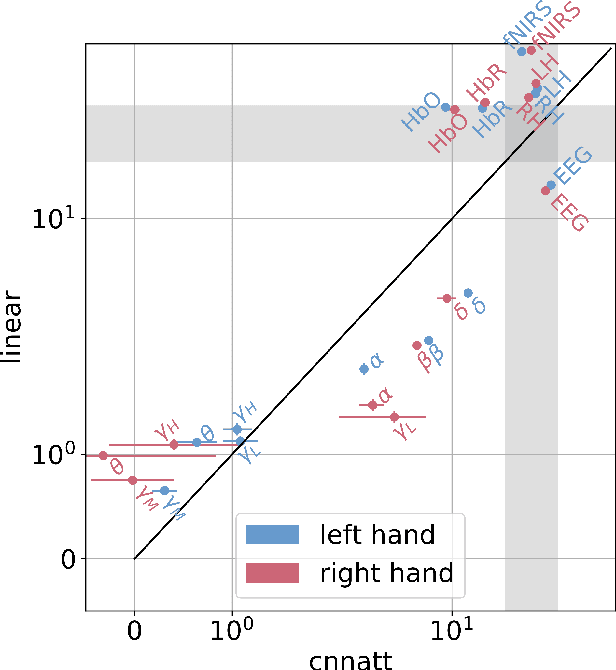
Non-invasive cortical neural interfaces have only achieved modest performance in cortical decoding of limb movements and their forces, compared to invasive brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). While non-invasive methodologies are safer, cheaper and vastly more accessible technologies, signals suffer from either poor resolution in the space domain (EEG) or the temporal domain (BOLD signal of functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy, fNIRS). The non-invasive BCI decoding of bimanual force generation and the continuous force signal has not been realised before and so we introduce an isometric grip force tracking task to evaluate the decoding. We find that combining EEG and fNIRS using deep neural networks works better than linear models to decode continuous grip force modulations produced by the left and the right hand. Our multi-modal deep learning decoder achieves 55.2 FVAF[%] in force reconstruction and improves the decoding performance by at least 15% over each individual modality. Our results show a way to achieve continuous hand force decoding using cortical signals obtained with non-invasive mobile brain imaging has immediate impact for rehabilitation, restoration and consumer applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge