Md Shafayet Hossain
Motion Artifacts Correction from Single-Channel EEG and fNIRS Signals using Novel Wavelet Packet Decomposition in Combination with Canonical Correlation Analysis
Apr 09, 2022



Abstract:The electroencephalogram (EEG) and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) signals, highly non-stationary in nature, greatly suffers from motion artifacts while recorded using wearable sensors. This paper proposes two robust methods: i) Wavelet packet decomposition (WPD), and ii) WPD in combination with canonical correlation analysis (WPD-CCA), for motion artifact correction from single-channel EEG and fNIRS signals. The efficacy of these proposed techniques is tested using a benchmark dataset and the performance of the proposed methods is measured using two well-established performance matrices: i) Difference in the signal to noise ratio ({\Delta}SNR) and ii) Percentage reduction in motion artifacts ({\eta}). The proposed WPD-based single-stage motion artifacts correction technique produces the highest average {\Delta}SNR (29.44 dB) when db2 wavelet packet is incorporated whereas the greatest average {\eta} (53.48%) is obtained using db1 wavelet packet for all the available 23 EEG recordings. Our proposed two-stage motion artifacts correction technique i.e. the WPD-CCA method utilizing db1 wavelet packet has shown the best denoising performance producing an average {\Delta}SNR and {\eta} values of 30.76 dB and 59.51%, respectively for all the EEG recordings. On the other hand, the two-stage motion artifacts removal technique i.e. WPD-CCA has produced the best average {\Delta}SNR (16.55 dB, utilizing db1 wavelet packet) and largest average {\eta} (41.40%, using fk8 wavelet packet). The highest average {\Delta}SNR and {\eta} using single-stage artifacts removal techniques (WPD) are found as 16.11 dB and 26.40%, respectively for all the fNIRS signals using fk4 wavelet packet. In both EEG and fNIRS modalities, the percentage reduction in motion artifacts increases by 11.28% and 56.82%, respectively when two-stage WPD-CCA techniques are employed.
A Shallow U-Net Architecture for Reliably Predicting Blood Pressure from Photoplethysmogram and Electrocardiogram Signals
Nov 12, 2021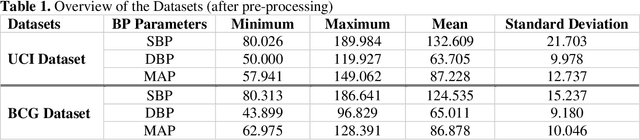
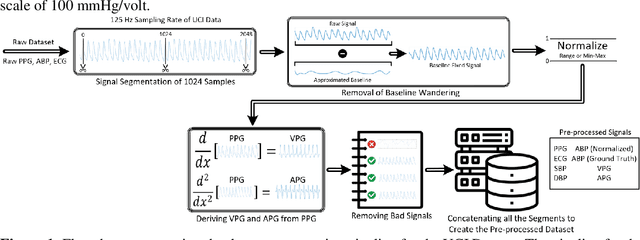
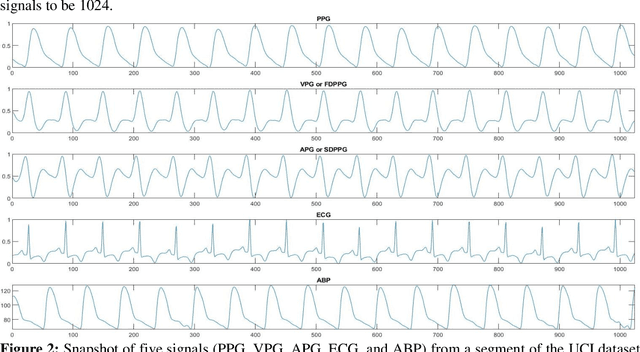
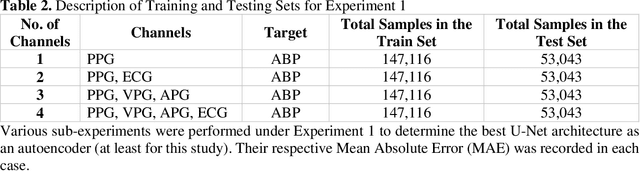
Abstract:Cardiovascular diseases are the most common causes of death around the world. To detect and treat heart-related diseases, continuous Blood Pressure (BP) monitoring along with many other parameters are required. Several invasive and non-invasive methods have been developed for this purpose. Most existing methods used in the hospitals for continuous monitoring of BP are invasive. On the contrary, cuff-based BP monitoring methods, which can predict Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) and Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP), cannot be used for continuous monitoring. Several studies attempted to predict BP from non-invasively collectible signals such as Photoplethysmogram (PPG) and Electrocardiogram (ECG), which can be used for continuous monitoring. In this study, we explored the applicability of autoencoders in predicting BP from PPG and ECG signals. The investigation was carried out on 12,000 instances of 942 patients of the MIMIC-II dataset and it was found that a very shallow, one-dimensional autoencoder can extract the relevant features to predict the SBP and DBP with the state-of-the-art performance on a very large dataset. Independent test set from a portion of the MIMIC-II dataset provides an MAE of 2.333 and 0.713 for SBP and DBP, respectively. On an external dataset of forty subjects, the model trained on the MIMIC-II dataset, provides an MAE of 2.728 and 1.166 for SBP and DBP, respectively. For both the cases, the results met British Hypertension Society (BHS) Grade A and surpassed the studies from the current literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge