Khandaker Reajul Islam
Self-CephaloNet: A Two-stage Novel Framework using Operational Neural Network for Cephalometric Analysis
Jan 19, 2025Abstract:Cephalometric analysis is essential for the diagnosis and treatment planning of orthodontics. In lateral cephalograms, however, the manual detection of anatomical landmarks is a time-consuming procedure. Deep learning solutions hold the potential to address the time constraints associated with certain tasks; however, concerns regarding their performance have been observed. To address this critical issue, we proposed an end-to-end cascaded deep learning framework (Self-CepahloNet) for the task, which demonstrated benchmark performance over the ISBI 2015 dataset in predicting 19 dental landmarks. Due to their adaptive nodal capabilities, Self-ONN (self-operational neural networks) demonstrate superior learning performance for complex feature spaces over conventional convolutional neural networks. To leverage this attribute, we introduced a novel self-bottleneck in the HRNetV2 (High Resolution Network) backbone, which has exhibited benchmark performance on the ISBI 2015 dataset for the dental landmark detection task. Our first-stage results surpassed previous studies, showcasing the efficacy of our singular end-to-end deep learning model, which achieved a remarkable 70.95% success rate in detecting cephalometric landmarks within a 2mm range for the Test1 and Test2 datasets. Moreover, the second stage significantly improved overall performance, yielding an impressive 82.25% average success rate for the datasets above within the same 2mm distance. Furthermore, external validation was conducted using the PKU cephalogram dataset. Our model demonstrated a commendable success rate of 75.95% within the 2mm range.
A Shallow U-Net Architecture for Reliably Predicting Blood Pressure from Photoplethysmogram and Electrocardiogram Signals
Nov 12, 2021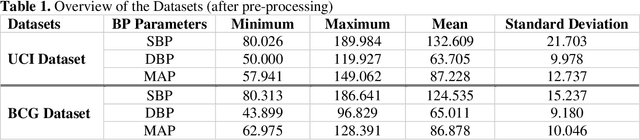
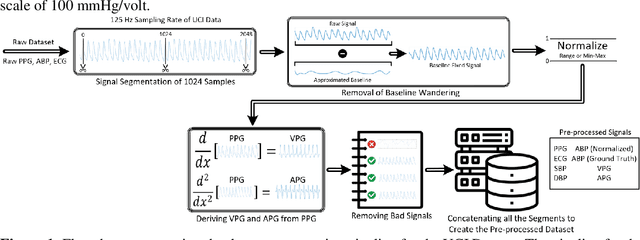
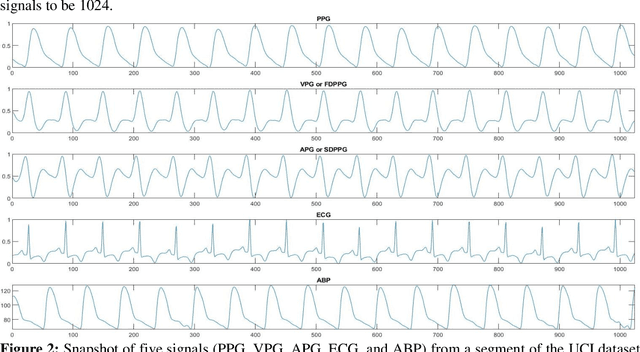
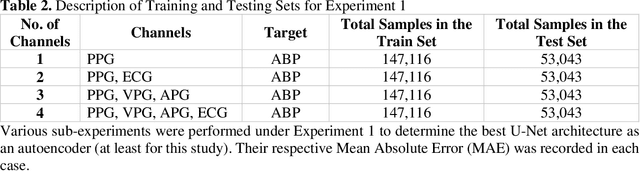
Abstract:Cardiovascular diseases are the most common causes of death around the world. To detect and treat heart-related diseases, continuous Blood Pressure (BP) monitoring along with many other parameters are required. Several invasive and non-invasive methods have been developed for this purpose. Most existing methods used in the hospitals for continuous monitoring of BP are invasive. On the contrary, cuff-based BP monitoring methods, which can predict Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) and Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP), cannot be used for continuous monitoring. Several studies attempted to predict BP from non-invasively collectible signals such as Photoplethysmogram (PPG) and Electrocardiogram (ECG), which can be used for continuous monitoring. In this study, we explored the applicability of autoencoders in predicting BP from PPG and ECG signals. The investigation was carried out on 12,000 instances of 942 patients of the MIMIC-II dataset and it was found that a very shallow, one-dimensional autoencoder can extract the relevant features to predict the SBP and DBP with the state-of-the-art performance on a very large dataset. Independent test set from a portion of the MIMIC-II dataset provides an MAE of 2.333 and 0.713 for SBP and DBP, respectively. On an external dataset of forty subjects, the model trained on the MIMIC-II dataset, provides an MAE of 2.728 and 1.166 for SBP and DBP, respectively. For both the cases, the results met British Hypertension Society (BHS) Grade A and surpassed the studies from the current literature.
COV-ECGNET: COVID-19 detection using ECG trace images with deep convolutional neural network
Jun 01, 2021



Abstract:The reliable and rapid identification of the COVID-19 has become crucial to prevent the rapid spread of the disease, ease lockdown restrictions and reduce pressure on public health infrastructures. Recently, several methods and techniques have been proposed to detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus using different images and data. However, this is the first study that will explore the possibility of using deep convolutional neural network (CNN) models to detect COVID-19 from electrocardiogram (ECG) trace images. In this work, COVID-19 and other cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) were detected using deep-learning techniques. A public dataset of ECG images consists of 1937 images from five distinct categories, such as Normal, COVID-19, myocardial infarction (MI), abnormal heartbeat (AHB), and recovered myocardial infarction (RMI) were used in this study. Six different deep CNN models (ResNet18, ResNet50, ResNet101, InceptionV3, DenseNet201, and MobileNetv2) were used to investigate three different classification schemes: two-class classification (Normal vs COVID-19); three-class classification (Normal, COVID-19, and Other CVDs), and finally, five-class classification (Normal, COVID-19, MI, AHB, and RMI). For two-class and three-class classification, Densenet201 outperforms other networks with an accuracy of 99.1%, and 97.36%, respectively; while for the five-class classification, InceptionV3 outperforms others with an accuracy of 97.83%. ScoreCAM visualization confirms that the networks are learning from the relevant area of the trace images. Since the proposed method uses ECG trace images which can be captured by smartphones and are readily available facilities in low-resources countries, this study will help in faster computer-aided diagnosis of COVID-19 and other cardiac abnormalities.
Can AI help in screening Viral and COVID-19 pneumonia?
Apr 28, 2020

Abstract:Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a pandemic disease, which has already infected around 3 million people and caused fatalities of above 200 thousand. The aim of this paper is to automatically detect COVID-19 pneumonia patients using digital x-ray images while maximizing the accuracy in detection using image pre-processing and deep-learning techniques. A public database was created by the authors using three public databases and by collecting images from recently published articles. The database contains a mixture of 190 COVID-19, 1345 viral pneumonia, and 1341 normal chest x-ray images. An image augmented training set was created with around 2600 images of each category for training and validating four different pre-trained deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). These networks were tested for the classification of two different schemes (normal and COVID-19 pneumonia; normal, viral and COVID-19 pneumonia). The classification accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and precision for both the schemes were 98.3%, 96.7%, 100%, 100% and 98.3%, 96.7%, 99%, 100%, respectively. The high accuracy of this computer-aided diagnostic tool can significantly improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosing cases with COVID-19. This would be highly useful in this pandemic where disease burden and need for preventive measures are at odds with available resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge