Nabil Ibtehaz
Fusion of regional and sparse attention in Vision Transformers
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Modern vision transformers leverage visually inspired local interaction between pixels through attention computed within window or grid regions, in contrast to the global attention employed in the original ViT. Regional attention restricts pixel interactions within specific regions, while sparse attention disperses them across sparse grids. These differing approaches pose a challenge between maintaining hierarchical relationships vs. capturing a global context. In this study, drawing inspiration from atrous convolution, we propose Atrous Attention, a blend of regional and sparse attention that dynamically integrates both local and global information while preserving hierarchical structures. Based on this, we introduce a versatile, hybrid vision transformer backbone called ACC-ViT, tailored for standard vision tasks. Our compact model achieves approximately 84% accuracy on ImageNet-1K with fewer than 28.5 million parameters, outperforming the state-of-the-art MaxViT by 0.42% while requiring 8.4% fewer parameters.
Modally Reduced Representation Learning of Multi-Lead ECG Signals through Simultaneous Alignment and Reconstruction
May 24, 2024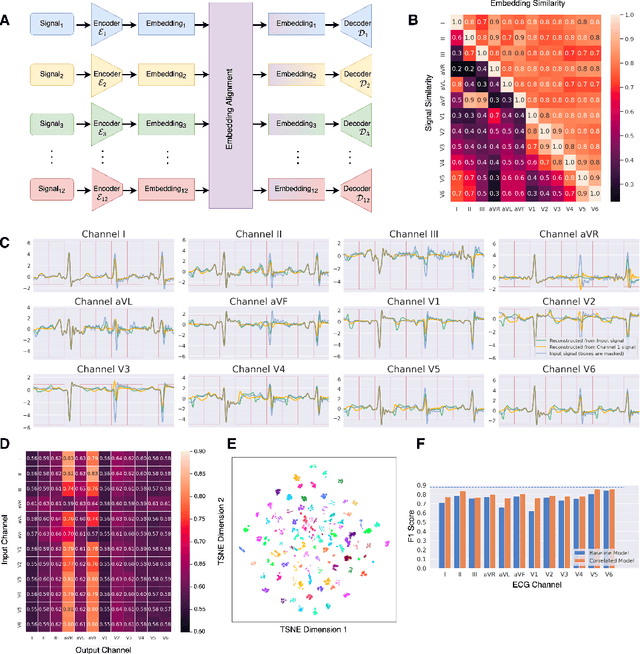
Abstract:Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals, profiling the electrical activities of the heart, are used for a plethora of diagnostic applications. However, ECG systems require multiple leads or channels of signals to capture the complete view of the cardiac system, which limits their application in smartwatches and wearables. In this work, we propose a modally reduced representation learning method for ECG signals that is capable of generating channel-agnostic, unified representations for ECG signals. Through joint optimization of reconstruction and alignment, we ensure that the embeddings of the different channels contain an amalgamation of the overall information across channels while also retaining their specific information. On an independent test dataset, we generated highly correlated channel embeddings from different ECG channels, leading to a moderate approximation of the 12-lead signals from a single-channel embedding. Our generated embeddings can work as competent features for ECG signals for downstream tasks.
* Accepted as a Workshop Paper at TS4H@ICLR2024
ACC-ViT : Atrous Convolution's Comeback in Vision Transformers
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Transformers have elevated to the state-of-the-art vision architectures through innovations in attention mechanism inspired from visual perception. At present two classes of attentions prevail in vision transformers, regional and sparse attention. The former bounds the pixel interactions within a region; the latter spreads them across sparse grids. The opposing natures of them have resulted in a dilemma between either preserving hierarchical relation or attaining a global context. In this work, taking inspiration from atrous convolution, we introduce Atrous Attention, a fusion of regional and sparse attention, which can adaptively consolidate both local and global information, while maintaining hierarchical relations. As a further tribute to atrous convolution, we redesign the ubiquitous inverted residual convolution blocks with atrous convolution. Finally, we propose a generalized, hybrid vision transformer backbone, named ACC-ViT, following conventional practices for standard vision tasks. Our tiny version model achieves $\sim 84 \%$ accuracy on ImageNet-1K, with less than $28.5$ million parameters, which is $0.42\%$ improvement over state-of-the-art MaxViT while having $8.4\%$ less parameters. In addition, we have investigated the efficacy of ACC-ViT backbone under different evaluation settings, such as finetuning, linear probing, and zero-shot learning on tasks involving medical image analysis, object detection, and language-image contrastive learning. ACC-ViT is therefore a strong vision backbone, which is also competitive in mobile-scale versions, ideal for niche applications with small datasets.
ACC-UNet: A Completely Convolutional UNet model for the 2020s
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:This decade is marked by the introduction of Vision Transformer, a radical paradigm shift in broad computer vision. A similar trend is followed in medical imaging, UNet, one of the most influential architectures, has been redesigned with transformers. Recently, the efficacy of convolutional models in vision is being reinvestigated by seminal works such as ConvNext, which elevates a ResNet to Swin Transformer level. Deriving inspiration from this, we aim to improve a purely convolutional UNet model so that it can be on par with the transformer-based models, e.g, Swin-Unet or UCTransNet. We examined several advantages of the transformer-based UNet models, primarily long-range dependencies and cross-level skip connections. We attempted to emulate them through convolution operations and thus propose, ACC-UNet, a completely convolutional UNet model that brings the best of both worlds, the inherent inductive biases of convnets with the design decisions of transformers. ACC-UNet was evaluated on 5 different medical image segmentation benchmarks and consistently outperformed convnets, transformers, and their hybrids. Notably, ACC-UNet outperforms state-of-the-art models Swin-Unet and UCTransNet by $2.64 \pm 2.54\%$ and $0.45 \pm 1.61\%$ in terms of dice score, respectively, while using a fraction of their parameters ($59.26\%$ and $24.24\%$). Our codes are available at https://github.com/kiharalab/ACC-UNet.
RamanNet: A generalized neural network architecture for Raman Spectrum Analysis
Jan 20, 2022



Abstract:Raman spectroscopy provides a vibrational profile of the molecules and thus can be used to uniquely identify different kind of materials. This sort of fingerprinting molecules has thus led to widespread application of Raman spectrum in various fields like medical dignostics, forensics, mineralogy, bacteriology and virology etc. Despite the recent rise in Raman spectra data volume, there has not been any significant effort in developing generalized machine learning methods for Raman spectra analysis. We examine, experiment and evaluate existing methods and conjecture that neither current sequential models nor traditional machine learning models are satisfactorily sufficient to analyze Raman spectra. Both has their perks and pitfalls, therefore we attempt to mix the best of both worlds and propose a novel network architecture RamanNet. RamanNet is immune to invariance property in CNN and at the same time better than traditional machine learning models for the inclusion of sparse connectivity. Our experiments on 4 public datasets demonstrate superior performance over the much complex state-of-the-art methods and thus RamanNet has the potential to become the defacto standard in Raman spectra data analysis
Lung-Originated Tumor Segmentation from Computed Tomography Scan (LOTUS) Benchmark
Jan 03, 2022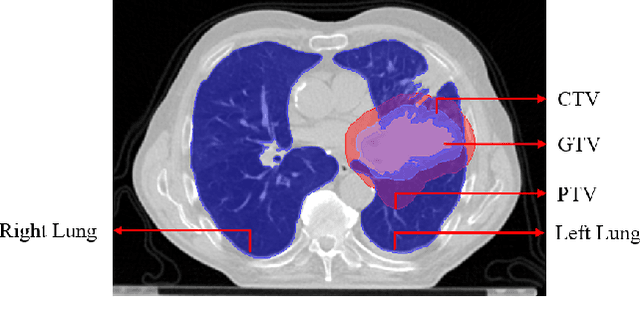
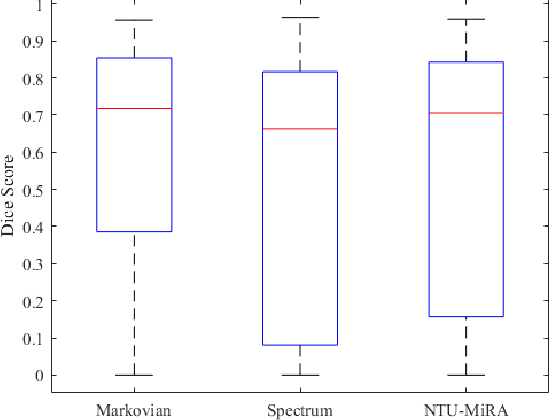
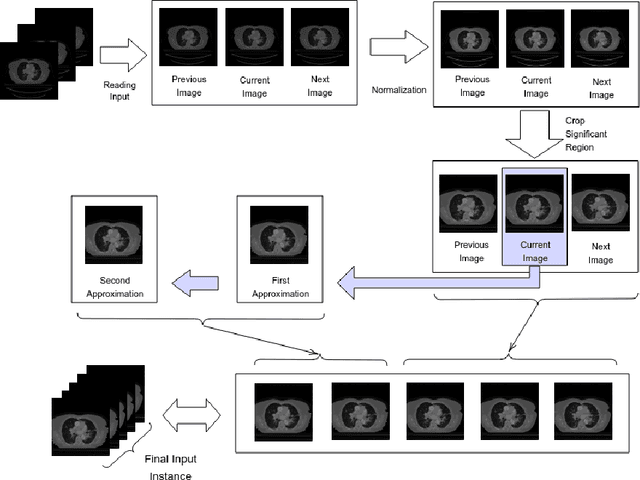
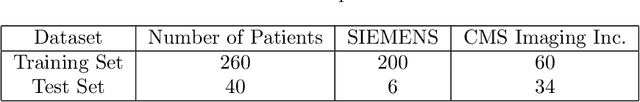
Abstract:Lung cancer is one of the deadliest cancers, and in part its effective diagnosis and treatment depend on the accurate delineation of the tumor. Human-centered segmentation, which is currently the most common approach, is subject to inter-observer variability, and is also time-consuming, considering the fact that only experts are capable of providing annotations. Automatic and semi-automatic tumor segmentation methods have recently shown promising results. However, as different researchers have validated their algorithms using various datasets and performance metrics, reliably evaluating these methods is still an open challenge. The goal of the Lung-Originated Tumor Segmentation from Computed Tomography Scan (LOTUS) Benchmark created through 2018 IEEE Video and Image Processing (VIP) Cup competition, is to provide a unique dataset and pre-defined metrics, so that different researchers can develop and evaluate their methods in a unified fashion. The 2018 VIP Cup started with a global engagement from 42 countries to access the competition data. At the registration stage, there were 129 members clustered into 28 teams from 10 countries, out of which 9 teams made it to the final stage and 6 teams successfully completed all the required tasks. In a nutshell, all the algorithms proposed during the competition, are based on deep learning models combined with a false positive reduction technique. Methods developed by the three finalists show promising results in tumor segmentation, however, more effort should be put into reducing the false positive rate. This competition manuscript presents an overview of the VIP-Cup challenge, along with the proposed algorithms and results.
Segmentation of Lung Tumor from CT Images using Deep Supervision
Nov 17, 2021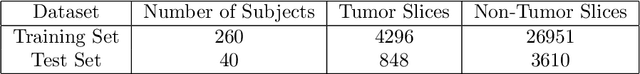
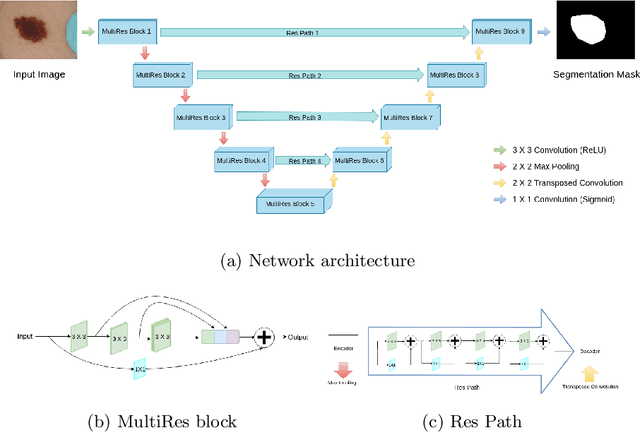
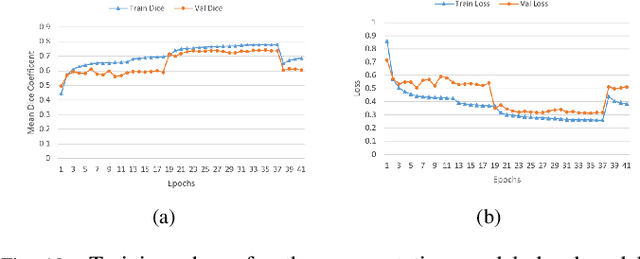
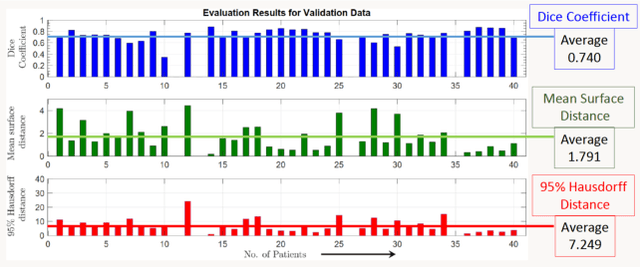
Abstract:Lung cancer is a leading cause of death in most countries of the world. Since prompt diagnosis of tumors can allow oncologists to discern their nature, type and the mode of treatment, tumor detection and segmentation from CT Scan images is a crucial field of study worldwide. This paper approaches lung tumor segmentation by applying two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform (DWT) on the LOTUS dataset for more meticulous texture analysis whilst integrating information from neighboring CT slices before feeding them to a Deeply Supervised MultiResUNet model. Variations in learning rates, decay and optimization algorithms while training the network have led to different dice co-efficients, the detailed statistics of which have been included in this paper. We also discuss the challenges in this dataset and how we opted to overcome them. In essence, this study aims to maximize the success rate of predicting tumor regions from two dimensional CT Scan slices by experimenting with a number of adequate networks, resulting in a dice co-efficient of 0.8472.
A Shallow U-Net Architecture for Reliably Predicting Blood Pressure from Photoplethysmogram and Electrocardiogram Signals
Nov 12, 2021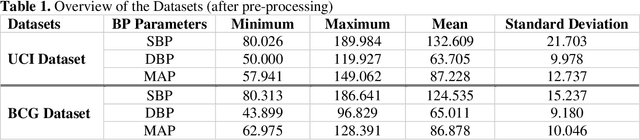
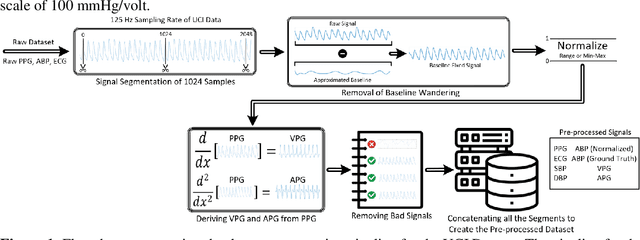
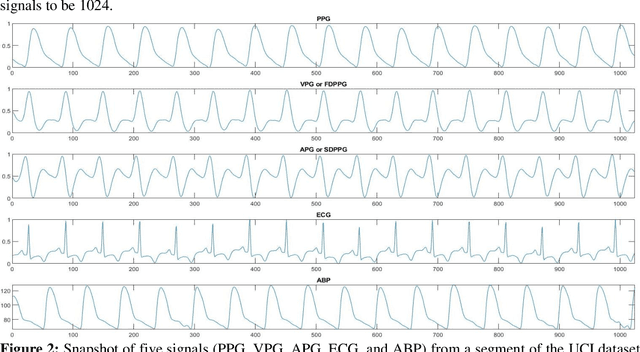
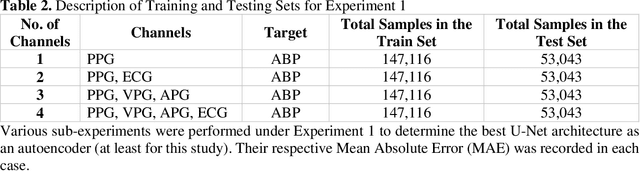
Abstract:Cardiovascular diseases are the most common causes of death around the world. To detect and treat heart-related diseases, continuous Blood Pressure (BP) monitoring along with many other parameters are required. Several invasive and non-invasive methods have been developed for this purpose. Most existing methods used in the hospitals for continuous monitoring of BP are invasive. On the contrary, cuff-based BP monitoring methods, which can predict Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) and Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP), cannot be used for continuous monitoring. Several studies attempted to predict BP from non-invasively collectible signals such as Photoplethysmogram (PPG) and Electrocardiogram (ECG), which can be used for continuous monitoring. In this study, we explored the applicability of autoencoders in predicting BP from PPG and ECG signals. The investigation was carried out on 12,000 instances of 942 patients of the MIMIC-II dataset and it was found that a very shallow, one-dimensional autoencoder can extract the relevant features to predict the SBP and DBP with the state-of-the-art performance on a very large dataset. Independent test set from a portion of the MIMIC-II dataset provides an MAE of 2.333 and 0.713 for SBP and DBP, respectively. On an external dataset of forty subjects, the model trained on the MIMIC-II dataset, provides an MAE of 2.728 and 1.166 for SBP and DBP, respectively. For both the cases, the results met British Hypertension Society (BHS) Grade A and surpassed the studies from the current literature.
QUCoughScope: An Artificially Intelligent Mobile Application to Detect Asymptomatic COVID-19 Patients using Cough and Breathing Sounds
Mar 20, 2021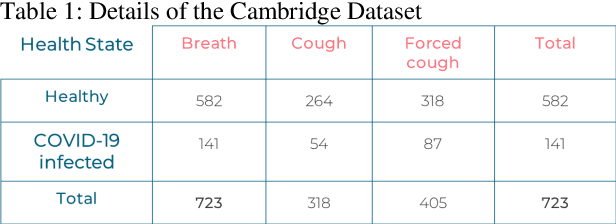
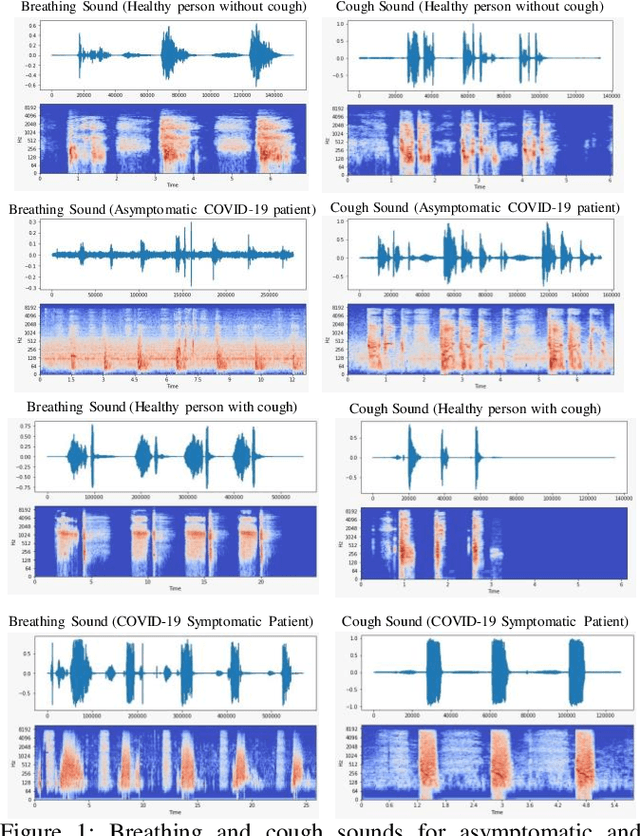

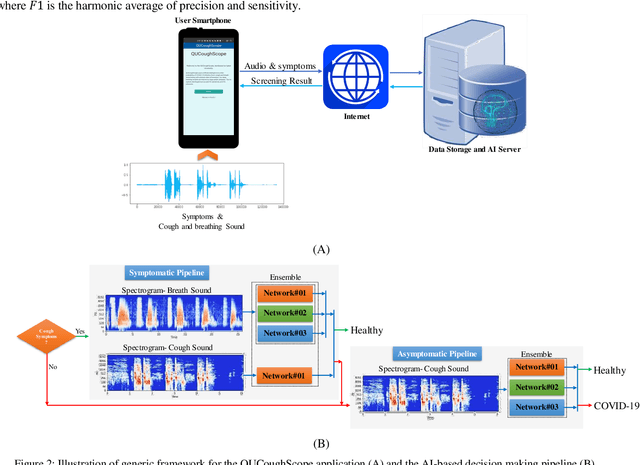
Abstract:In the break of COVID-19 pandemic, mass testing has become essential to reduce the spread of the virus. Several recent studies suggest that a significant number of COVID-19 patients display no physical symptoms whatsoever. Therefore, it is unlikely that these patients will undergo COVID-19 test, which increases their chances of unintentionally spreading the virus. Currently, the primary diagnostic tool to detect COVID-19 is RT-PCR test on collected respiratory specimens from the suspected case. This requires patients to travel to a laboratory facility to be tested, thereby potentially infecting others along the way.It is evident from recent researches that asymptomatic COVID-19 patients cough and breath in a different way than the healthy people. Several research groups have created mobile and web-platform for crowdsourcing the symptoms, cough and breathing sounds from healthy, COVID-19 and Non-COVID patients. Some of these data repositories were made public. We have received such a repository from Cambridge University team under data-sharing agreement, where we have cough and breathing sound samples for 582 and 141 healthy and COVID-19 patients, respectively. 87 COVID-19 patients were asymptomatic, while rest of them have cough. We have developed an Android application to automatically screen COVID-19 from the comfort of people homes. Test subjects can simply download a mobile application, enter their symptoms, record an audio clip of their cough and breath, and upload the data anonymously to our servers. Our backend server converts the audio clip to spectrogram and then apply our state-of-the-art machine learning model to classify between cough sounds produced by COVID-19 patients, as opposed to healthy subjects or those with other respiratory conditions. The system can detect asymptomatic COVID-19 patients with a sensitivity more than 91%.
COVID-19 Infection Localization and Severity Grading from Chest X-ray Images
Mar 14, 2021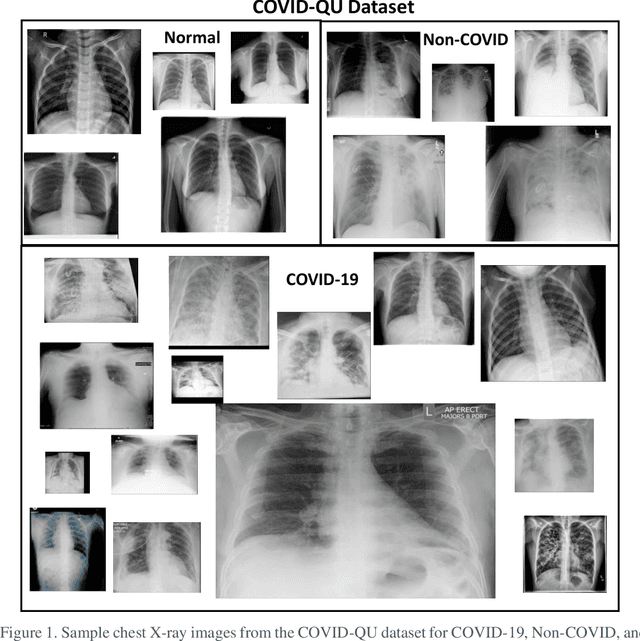
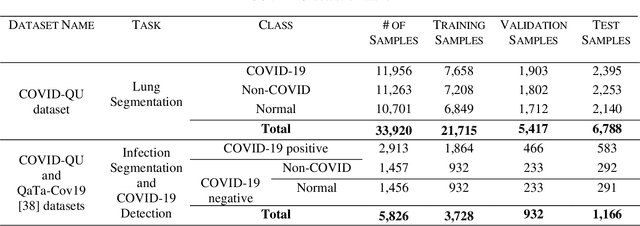
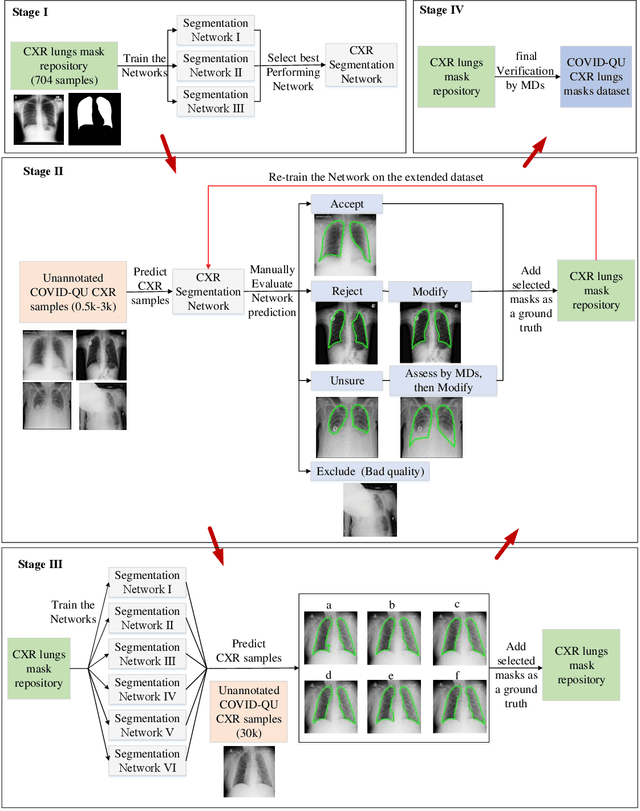
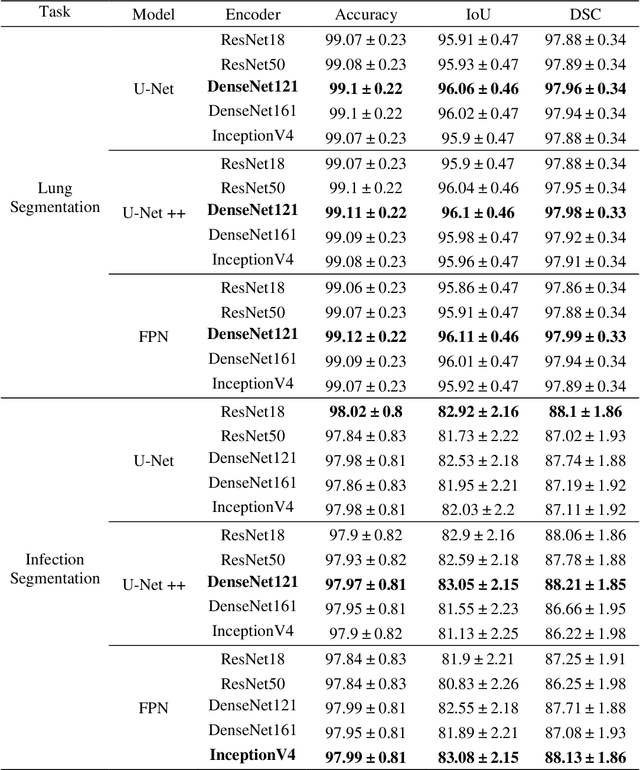
Abstract:Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been the main agenda of the whole world, since it came into sight in December 2019 as it has significantly affected the world economy and healthcare system. Given the effects of COVID-19 on pulmonary tissues, chest radiographic imaging has become a necessity for screening and monitoring the disease. Numerous studies have proposed Deep Learning approaches for the automatic diagnosis of COVID-19. Although these methods achieved astonishing performance in detection, they have used limited chest X-ray (CXR) repositories for evaluation, usually with a few hundred COVID-19 CXR images only. Thus, such data scarcity prevents reliable evaluation with the potential of overfitting. In addition, most studies showed no or limited capability in infection localization and severity grading of COVID-19 pneumonia. In this study, we address this urgent need by proposing a systematic and unified approach for lung segmentation and COVID-19 localization with infection quantification from CXR images. To accomplish this, we have constructed the largest benchmark dataset with 33,920 CXR images, including 11,956 COVID-19 samples, where the annotation of ground-truth lung segmentation masks is performed on CXRs by a novel human-machine collaborative approach. An extensive set of experiments was performed using the state-of-the-art segmentation networks, U-Net, U-Net++, and Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN). The developed network, after an extensive iterative process, reached a superior performance for lung region segmentation with Intersection over Union (IoU) of 96.11% and Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 97.99%. Furthermore, COVID-19 infections of various shapes and types were reliably localized with 83.05% IoU and 88.21% DSC. Finally, the proposed approach has achieved an outstanding COVID-19 detection performance with both sensitivity and specificity values above 99%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge