Segmentation of Lung Tumor from CT Images using Deep Supervision
Paper and Code
Nov 17, 2021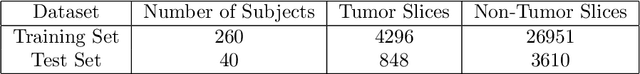
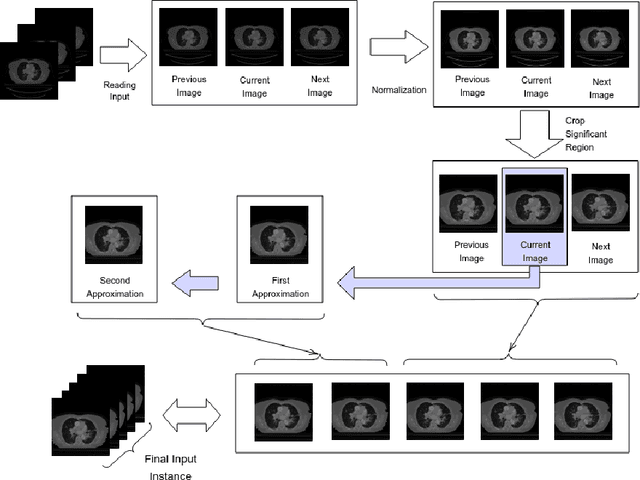
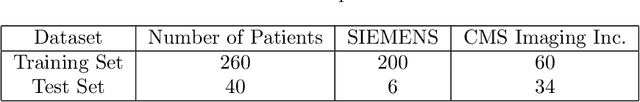
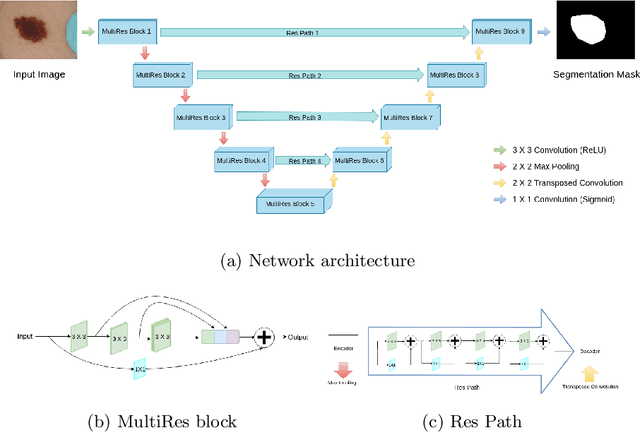
Lung cancer is a leading cause of death in most countries of the world. Since prompt diagnosis of tumors can allow oncologists to discern their nature, type and the mode of treatment, tumor detection and segmentation from CT Scan images is a crucial field of study worldwide. This paper approaches lung tumor segmentation by applying two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform (DWT) on the LOTUS dataset for more meticulous texture analysis whilst integrating information from neighboring CT slices before feeding them to a Deeply Supervised MultiResUNet model. Variations in learning rates, decay and optimization algorithms while training the network have led to different dice co-efficients, the detailed statistics of which have been included in this paper. We also discuss the challenges in this dataset and how we opted to overcome them. In essence, this study aims to maximize the success rate of predicting tumor regions from two dimensional CT Scan slices by experimenting with a number of adequate networks, resulting in a dice co-efficient of 0.8472.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge